Abstract
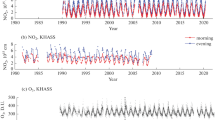
Measurements of the sum of peroxy radicals [HO2 + RO2],NOx (NO + NO2) and NOy (the sum of oxidisednitrogen species) made at Mace Head, on the Atlantic coast of Ireland in summer 1996 and spring 1997 are presented. Together with a suite of ancillary measurements, including the photolysis frequencies of O3 → O(1D)(j(O1D)) and NO2 (j(NO2)), the measured peroxy radicals are used to calculate meandailyozone tendency (defined as the difference of the in-situphotochemical ozone production and loss rates); these values are compared with values derived from the photochemical stationary state (PSS) expression. Although the correlation between the two sets of values is good, the PSS values are found to be significantly larger than those derived from the peroxy radical measurements, on average, in line with previous published work. Possible sources of error in these calculations are discussed in detail. The data are further divided up into five wind sectors, according to the instantaneous wind direction measured at the research station. Calculation of mean ozone tendencies by wind sector shows that ozone productivity was higher during spring (April–May) 1997 than during summer (July–August) 1996across all airmasses, suggesting that tropospheric photochemistry plays an important role in the widely-reported spring ozone maximum in the Northern Hemisphere. Ozone tendencies were close to zero for the relatively unpolluted south-west, west and north-west wind sectors in the summer campaign, whereas ozone productivity was greatest in the polluted south-east sector for both campaigns. Daytime weighted average ozone tendencies were +(0.3± 0.1) ppbv h−1 for summer 1996 and +(1.0± 0.5) ppbvh−1 for spring 1997. These figures reflect the higher mixing ratios of ozone precursors in spring overall, as well as the higher proportion of polluted air masses from the south-east arriving at the site during the spring campaign. The ozone compensation point, where photochemical ozone destruction and production processes are in balance, is calculated to be ca. 14 pptv NO for both campaigns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers, G. P., Granek, H., and Boers, R., 1997: Ozone in the marine boundary layer at Cape Grim: Model simulation, J. Atmos. Chem. 27, 179–195.
Bauguitte, S., 2000: A study of tropospheric reactive nitrogen oxides in the North Atlantic region, Ph.D. Thesis, The University of East Anglia, Norwich.
Baumann, K., Williams, E. J., Angevine, W. M., Roberts, J. M., Norton, R. B., Frost, G. J., Fehsenfeld, F. C., Springston, S. R., Bertman, S. B., and Hartsell, B., 2000: Ozone production and transport near Nashville, Tennessee: Results from the 1994 study at New Hendersonville, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 9137–9153.
Burkert, J., Andres-Hernandez, M. D., Stobener, D., Burrows, J. P., Weissenmayer, M., and Kraus, A., 2001: Peroxy radical and related trace gas measurements in the boundary layer above the Atlantic Ocean, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 5457–5477.
Cantrell, C. A., Stedman, D. H., and Wendel, G. J., 1984: Measurement of atmospheric peroxy radicals by chemical amplification, Anal. Chem. 56, 1496–1502.
Cantrell, C. A., Shetter, R. E., Calvert, J. G., Eisele, F. L., Williams, E., Baumann, K., Brune, W. H., Stevens P. S., and Mather, J. H., 1997: Peroxy radicals from photostationary-state deviations and steady-state calculations during the Tropospheric OH Photochemistry Experiment at Idaho Hill, Colorado, 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 6369–6378.
Cape, J. N., Methven, J., and Hudson, L. E., 2000: The use of trajectory cluster analysis to interpret trace gas measurements at Mace Head, Ireland, Atmos. Environ. 34, 3651–3663.
Cárdenas, L. M., Austin, J., Burgess, R. A., Clemitshaw, K. C., Dorling, S., Penkett, S. A., and Harrison, R. M., 1998: Relationships between CO, NOy, O3, NMHCs and PAN during winter, Atmos. Environ. 32, 3339–3351.
Carpenter, L. J., Monks, P. S., Bandy, B. J., Penkett, S. A., Galbally, I. E., and Meyer, C. P., 1997: A study of peroxy radicals and ozone photochemistry at coastal sites in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 25417–25427.
Carpenter, L. J., Clemitshaw, K. C., Burgess, R. A., Penkett, S. A., Cape, J. N., and McFayden, G. G., 1998: Investigation and evaluation of the NOx/O3 photochemical steady state, Atmos. Environ. 32, 3353–3365.
Carpenter, L. J., Green, T. J., Mills, G. P., Baugitte, S., Penkett, S. A., Zanis, P., Schuepbach, E., Schmidbauer, N., Monks, P. S., and Zellweger, C., 2000: Oxidized nitrogen and ozone production efficiencies in the springtime free troposphere over the Alps, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 14547–14559.
Carslaw, N., Creasey, D. J., Heard, D. E., Lewis, A. C., McQuaid, J. B., Pilling, M. J., Monks, P. S., Bandy, B. J., and Penkett, S. A., 1999: Modelling OH, HO2 and RO2 radicals in the marine boundary layer; (1) Model construction and comparison with field measurements, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 30241–30255.
Carslaw, N., Creasey, D. J., Jacobs, P. J., Lee, J. D., Lewis, A. C., McQuaid, J. B., Pilling, M. J., Bauguitte, S., Penkett, S. A., Monks, P. S., and Salisbury, G., 2002: The Eastern Atlantic Spring Experiment 1997 (EASE97): 2. Comparison of model concentrations of OH, HO2 and RO2 with measurements, J. Geophys. Res., submitted.
Clemitshaw, K. C., Carpenter, L. J., Penkett, S. A., and Jenkin, M. E., 1997: A calibrated peroxy radical chemical amplifier for ground-based tropospheric measurements, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 25405–25416.
Cox, R. A., 1999: Ozone and peroxy radical budgets in the marine boundary layer: Modeling the effect of NOx, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 8047–8056.
Cvitaš, T. and Kley, D., 1994: Mace Head, in The TOR Network: A Description of TOR Measurement Stations, EUROTRAC Special Publications, ISS, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, pp. 48–51.
DeMore, W. B., Sander, S. P., Golden, D. M., Hampson, R. F., Kurylo, M. J., Howard, C. J., Ravishankara, A. R., Kolb, C. E., and Molina, M. J., 1997: Chemical Kinetics and Photochemical Data for Use in Stratospheric Modelling, Evaluation Number 12, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, U.S.A.
Derwent, R. G., Simmonds, P. G., and Collins, W. J., 1994: Ozone and carbon monoxide measurements at a remote maritime location, Mace Head, Ireland, from 1990 to 1992, Atmos. Environ. 28, 2623–2637.
Derwent, R. G., Simmonds, P. G., Seuring, S., and Dimmer, C., 1998: Observation and interpretation of the seasonal cycles in the surface concentrations of ozone and carbon monoxide at Mace Head, Ireland from 1990 to 1994, Atmos. Environ. 32, 145–157.
Grenfell, J. L., Harrison, R. M., Allen, A. G., Shi, J. P., Penkett, S. A., O'Dowd, C. D., Smith, M. H., Hill, M. K., Robertson, L., Hewitt, C. N., Davison, B., Lewis, A. C., Creasey, D. J., Heard, D. E., Hebestreit, K., Alicke, B., and James, J., 1999: An analysis of rapid increases in condensation nuclei mixing ratios at a remote coastal site in western Ireland, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 13,771–13,780.
Harrison, R. M., Grenfell, J. L., Yamulki, S., Clemitshaw, K. C., Penkett, S. A., Cape, J. N., and McFadyen, G. G., 1999: Budget of NOy species measured at a coastal site, Atmos. Environ. 33, 4255–4272.
Honrath, R. E. and Jaffe, D. A., 1992: The seasonal cycle of nitrogen oxides in the Arctic troposphere at Barrow, Alaska, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 20615–20630.
Hov, Ø. and Stordal, F., 1992: Measurements of ozone and precursors at Ny-Alesund on Svalbard and Birkenes on the south coast of Norway, ozone profiles at Bjornoya and the interpretation of measured concentrations, in EUROTRAC TOR Annual Report, Vol. 9, ISS, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, pp. 175–183.
Junkermann, W., Platt, U., and Volz-Thomas, A., 1989: A photoelectric detector for the measurement of photolysis frequencies of ozone and other atmospheric molecules, J. Atmos. Chem. 8, 203–227.
Kleinman, L., Lee, Y-N., Springston, S. R., Lee, J. H., Nunnermacker, L., Weinstein-Lloyd. J., Zhou, X., and Newman, L., 1995: Peroxy radical concentration and ozone formation rate at a rural site in the southeastern United States, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 7263–7273.
Liu, S. C., Trainer, M., Fehsenfeld, F. C., Parrish, D. D., Williams, E. J., Fahey, D.W., Hübler, G., and Murphy, P. C., 1987: Ozone production in the rural troposphere and the implications for regional and global ozone distributions, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 4191–4207.
Mihele, C. M. and Hastie, D. R., 1998: The sensitivity of the radical amplifier to ambient water vapour, Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 1911–1913.
Mihele, C.M., Mozurkewich, M., and Hastie, D. R., 1999: Radical loss in a chain reaction of CO and NO in the presence of water: Implications for the radical amplifier and atmospheric chemistry, Int. J. Chem. Kin. 31, 145–152.
Monks, P. S., Carpenter, L. J., Penkett, S. A., Ayers, G. P., Gillett, R. W., Galbally, I. E., and Meyer, C. P., 1998: Fundamental ozone photochemistry in the remote marine boundary layer: The SOAPEX experiment, measurement and theory, Atmos. Environ. 32, 3647–3664.
Monks, P. S., 2000: A review of the observations and origins of the spring ozone maximum, Atmos. Environ. 34, 3545–3561.
Monks, P. S., Salisbury, G., Holland, G., Penkett, S. A., and Ayers, G. P., 2000: A seasonal comparison of ozone photochemistry in the remote marine boundary layer, Atmos. Environ. 34, 2547–2561.
Novelli, P. C., Masarie, K. A., Tans, P. P., and Lang, P. M., 1994: Recent changes in atmospheric carbon monoxide, Science 263, 1587–1590.
Penkett, S. A. and Brice, K. A., 1986: The Spring maximum in photo-oxidants in the Northern Hemisphere troposphere, Nature 319, 655–657.
Penkett, S. A., Blake, N. J., Lightman, P., Marsh, A. R. W., Anwyl, P., and Butcher, G., 1993: The seasonal variation of non-methane hydrocarbons in the free troposphere over the North Atlantic Ocean: Possible evidence for extensive reaction of hydrocarbons with the nitrate radical, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 2865–2885.
Penkett, S. A., Monks, P. S., Carpenter, L. J., Clemitshaw, K. C., Ayers, G. P., Gillett, R. W., Galbally, I. E., and Meyer, C. P., 1997: Relationships between ozone photolysis rates and radical concentrations in clean marine air over the Southern ocean, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 12805–12817.
Salisbury, G., Rickard, A. R., Monks, P. S., Allan, B. J., Bauguitte, S., Penkett, S. A., Carslaw, N., Lewis, A. C., Creasey, D. J., Heard, D. E., Jacobs, P. J., and Lee, J. D., 2001, Production of peroxy radicals at night via reactions of ozone and the nitrate radical in the marine boundary layer, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 12669–12688.
Simmonds, P. G., Seuring, S., Nickless, G., and Derwent, R. G., 1997: Segregation and interpretation of ozone and carbon monoxide measurements by air mass origin at the TOR station Mace Head, Ireland, from 1987 to 1995, J. Atmos. Chem. 28, 45–59.
Solomon, P., Cowling, E., Hidy, G., and Furiness, C., 2000: Comparison of scientific findings from major ozone field studies in North America and Europe, Atmos. Environ. 34, 1885–1920.
Volz-Thomas, A., Mihelcic, D., Pätz, H.-W., Schultz, M., Gomišcek, B., Lindskog, A., Mowrer, J., Oyola, P., Hanson, K., Schmitt, R., Nielson, T., Eggelov, A., Stordal F., and Vosbeck, M., 1997: Photochemical ozone production rates at different TOR sites, in Ø. Hov (ed.), Transport and Chemical Transformation of Pollutants in the Troposphere, Vol. 6: Tropospheric Ozone Research, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Zanis, P., Monks, P. S., Schuepbach, E., Carpenter, L. J., Green, T. J., Mills, G. P., Bauguitte S., and Penkett, S. A., 2000: In-situ ozone production under free tropospheric conditions during FREETEX 98 in the Swiss Alps, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 24223–24234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salisbury, G., Monks, P.S., Bauguitte, S. et al. A Seasonal Comparison of the Ozone Photochemistry in Clean and Polluted Air Masses at Mace Head, Ireland. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry 41, 163–187 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014202229304
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014202229304