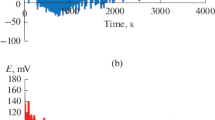
Abstract
Demanding for a reduction in materials degradation is a serious problem all over the world. Mössbauer spectroscopy (MS) is, among others, a very valuable tool to follow many degradation processes. Evidently, Fe is the most important Mössbauer element considering the overall presence of iron in everyday life.
MS may contribute to our knowledge about nearly all fields of materials degradation, chemical, mechanical, thermal, irradiative, etc. Following some general lines, corrosion is considered in particular. MS is applicable to investigate the bulk of materials as well as their surface layers with an information depth of ca. 250 nm. In general, it has to be applied as a surface sensitive method in combination with other relevant methods in order to get a detailed insight into ongoing processes. Some examples have been selected to elucidate the application of MS in this field.
Another class of examples concerns attempts to prevent corrosion, i.e., the application of coatings and transforming chemicals. A very effective and most natural way to reduce corrosion is the passivation of materials. The effect of passive layers and their destruction by environmental influences are discussed using results of MS and related methods. It is outlined that passivity is not restricted to chemically treated metals but can be considered as a general concept for preventing different kinds of materials from degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Meisel, J. de Phys. 41–C1 (1980) 63–70.
W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, in: Int. Conf. Appl. Mössbauer Effect, Jaipur 1981, Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Academy, pp. 284–286.
H. Mehner, H. Berndt and W. Meisel, J. de Phys. 41–C1 (1980) 395–396.
J.F. Marco, J. Davalos, J.R. Gancedo and M. Gracia, Hyperfine Interactions 46 (1989) 453–459.
J.F. Marco, J. Davalos, M. Gracia and J.R. Gancedo, Hyperfine Interactions 57 (1990) 1991–1996.
J. Davalos, M. Gracia, J.F. Marco and J.R. Gancedo, Hyperfine Interactions 69 (1991) 871–874.
J.F. Marco, J. Davalos, M. Gracia and J.R. Gancedo, Hyperfine Interactions 83 (1994) 111–123.
D. Hanzel, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, Hyperfine Interactions 57 (1990) 2206.
W. Meisel, Appl. Phys. A 59 (1994) 381–384.
P. Gütlich, W. Meisel and E. Mohs, Werkstoffe u. Korros. 33 (1982) 35–39.
W. Meisel, P. Griesbach, H.J. Grabke and P. Gütlich, Hyperfine Interactions 57 (1990) 2001–2008.
P. Griesbach, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, Hyperfine Interactions 69 (1991) 811–814.
W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, Werkstoffe and Korrosion 32 (1981) 296–301.
W. Meisel, U. Stumm, C. Thilmann, R. Gancedo and P. Gütlich, Hyperfine Interactions 41 (1988) 669–672.
U. Stumm, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, Hyperfine Interactions 57 (1990) 2115–2118.
W. Meisel, U. Stumm and P. Gütlich, Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 333 (1989) 555–560.
W. Meisel, Hyperfine Interactions 45 (1989) 73–90.
M. Lakatos-Varsanyi, Cs. Vertes, A. Vertes, L. Kiss, W. Meisel, P. Griesbach and P. Gü tlich, J. Electrochem. Soc. 139 (1992) 1301–1305.
J.F. Marco, J.R. Gancedo, W. Meisel, P. Griesbach and P. Gütlich, Corrosion 47 (1991) 498–500.
J.-M.R. Genin, A.A. Olowe, N.D. Benbouzid-Rollet, D. Prieur, M. Confente and B. Resiak, Hyperfine Interactions 69 (1991) 875–878.
Cs. Vertes, M. Lakatos-Varsanyi, W. Meisel, A. Vertes and P. Gütlich, Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 76 (1993) 20–21.
Cs. Vertes, M. Lakatos-Varsanyi, A. Vertes, W. Meisel and A. Horvath, Acta Chim. Hungar. Models 132 (1995) 597–606.
J.S. Brooks, G.L. Williams, D.W. Allen and E. de Grave, Phys. Chem. Glasses 33 (1992) 167–170.
J.A. Johnson, C.E. Johnson, K.F.E. Williams, D. Holland and M.M. Karim, Hyperfine Interactions 95 (1995) 41.
K.F.E. Williams, C.E. Johnson, D. Holland and M.M. Karim, J. Phys. Cond. Mat. 7 (1995) 9485.
D. Hanzel, P. Griesbach, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, Hyperfine Interactions 57 (1992) 1441.
W. Meisel, Hyperfine Interactions 92 (1994) 1213–1220.
W. Meisel, D. Sprenger and P. Gütlich, Surface Interface Anal. 22 (1994) 267–270.
G. Principi, A. Maddalena, A. Gupta, F. Geotti-Bianchini, S. Hreglich and M. Verita, Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 76 (1993) 215–217.
D. Sprenger, H. Bach, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 126 (1990) 111–129.
D. Sprenger, H. Bach, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, Surface Interface Anal. 20 (1993) 796–802.
C. Schultz-Münzenberg, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meisel, W. Degradation of materials and passivity. Hyperfine Interactions 111, 59–70 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012676911360
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012676911360