Abstract
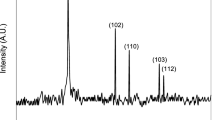
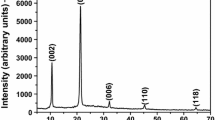
Indium selenide thin films were deposited onto glass substrates kept at 150 °C by thermal evaporation of α-In2Se3. Some of the films were annealed at 150 °C and 200 °C and they all were found to exhibit p-type conductivity without intentional doping. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) established that the films have an atomic content of In51Se49. X-ray diffraction (XRD) indicated that the as-grown films were amorphous in nature and became polycrystalline β-In2Se3 films after annealing. The analysis of conductivity temperature-dependence measurements in the range 320–100 K revealed that thermal excitation and thermionic emission of the carriers are the predominant conduction mechanisms above 200 K in the amorphous and polycrystalline samples, respectively. The carrier transport below 200 K is due to variable range hopping in all the samples. Hall measurements revealed that the mobility of the polycrystalline films is limited by the scattering of the charged carriers through the grain boundaries above 200 K. © 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Julien, M. Eddrief, K. KambasandM. Balkanski,Thin Solid Films 137(1986) 27.
A. Aruchamy, “Photoelectrochemistry and Photovoltaics of Layered Semiconductors”, (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, 1992).
J. C. Bernede, S. Marsillac, A. ConanandA. Godoy,J. Phys. Condens Matter 8(1996) 3439.
M. Parlak, Ç. ErÇelebi, I. GÜnal, Z. SalaevaandK. Allakhverdiev,Thin Solid Films 258(1995) 860.
M. ParlakandÇ. ErÇelebi, ibid.322(1998) 334.
M. ParlakandÇ. ErÇelebi,J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 10(1999) 313.
S. Marsillac, J. C. BernedeandA. Conan,J. Mater. Sci. 31(1996) 581.
B. Thomas,Appl. Phys. A 54(1992) 293.
D. V. K. SastryandP. J. Reddy,Thin Solid Films 105(1983) 139.
I. GunalandA. F. Qasrawi,J. Mater. Sci. 34(1999) 1.
N. F. MottandE. A. Davis, “Electronic Process in Non Crystalline Materials”, 2nd Edn. (Clarendon Oxford, 1979).
J. Y. Seto,J. Appl. Phys. 46(1975) 5247.
M. V. Garcia-Cuenca, J. L. MorenzaandJ. Esteve, ibid.56(1984) 1738.
R. M. Hill,Phil. Mag. 24(1971) 1307.
D. K. PaulandS. S. Mitra,Phys. Rev. Lett. 31(1973) 1000.
M. Persin, A. Persin, B. CelustkaandB. Etlinger,Thin Solid Films 11(1972) 153.
R. L. Petritz,Phys. Rev. 104(1956) 1508.
G. Micocci, A. Tepore, R. RellaandP. Siciliano,Phys. Status Solidi A 148(1995) 431.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qasrawi, A.F., Parlak, M., Erçelebi, Ç. et al. Characterization of p-In2Se3 thin films. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 12, 473–476 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012247618073
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012247618073