Abstract
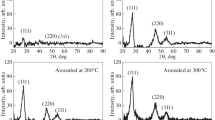
Nickel selenide thin films were synthesized on the amorphous templates utilizing a dip method. In the synthesis process, ascorbic acid acts as complexing agent. Hydrazine hydrate too plays a role of complexing agent and/or catalyst. Structural, optical, microscopic, electrical and thermoelectrical parameters were estimated. The X-ray diffraction spectrum of nickel selenide shows polycrystalline nature having hexagonal structure. The absorptivity of nickel selenide films is highly absorptive with a direct type of transition. The optical gap of NiSe was found to be 2.18 eV. The Urbach energy was found to be 0.275 eV. The ratio of Ni: Se in the thin film was 1:1. Micrograph of nickel selenide thin film showing irregular shaped fine grains distributed to the whole surface. The electrical conductance of nickel selenide suggests that the activation energy was found to be 0.024 and 0.331 eV for lower and higher temperature areas, respectively. At 300 K, the carrier concentration is estimated to be 2.58 × 1019 and 3.55 × 1019 at 525 K.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Anand, R. Rajan, M. Said, L. Tee, Adv. Energy Convers. Mater. 1, 55 (2020)
T. Anand, S. Shariza, Electrochim. Acta. 81(81), 64 (2012)
G. Chandra, D. Singh, D. Shrivastava, S. Sahu, J. Phys. D 17, 2125 (1984)
S. Kale, C. Lokhande, Mater. Chem. Phys. 62, 103 (2000)
P. Kalita, B. Sarma, H. Das, Bull. Mater. Sci. 23, 313 (2000)
T. Anand, M. Zaidan, S. Shariza, Proc. Eng. 53, 555 (2013)
A. Hamad, Z. Elmandouch, H. Elmeleegi, Acta Physica Polonia A 127, 901 (2015)
P. Nwofe, R. Chikwenze, P. Agbo, H. Igwe, Asian. J. Sci. Res. 10, 43 (2017)
W. Zhang, Z. Hui, Y. Cheng, L. Zhang, Y. Xie, Y. Qian, J. Cry. Growth 209, 213 (2000)
M. Xue, Z. Fu, Electrochem. Comm. 8, 1855 (2006)
Y. Liu, Q. Xu, R. Wang, Y. Zhang, L. Zhu, Z. Wang, W. Zheng, J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 797 (2020)
K. Anuar, W. Tan, A. Abdullah, H. Jelas, N. Saravanan, S. Ho, M. Yazid, Oriental J. Chem. 25, 813 (2009)
K. Anuar, M. Rosli, S. Ho, Int. J. Chem. Res. 3, 21 (2011)
P. Agbo, P. Nwofe, R. Chikwenze, O. Ozibo, IOSR J. Appl. Phys. 7, 99 (2015)
K. Sharma, D. Sharma, V. Kumar, Optik 182, 519 (2019)
P. Hankare, A. Manikshete, D. Sathe, P. Chate, Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21, 698 (2010)
G. Hodes, Chemical solution deposition of semiconductor films (Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 2003)
C. Lokhande, P. Patil, H. Tributsch, A. Ennaoui, Sol. Ener. Mater. Sol. Cells 55, 379 (1998)
P. Hankare, P. Chate, S. Delekar, M. Asabe, I. Mulla, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 67, 2310 (2006)
P. Hankare, B. Jadhav, K. Garadkar, P. Chate, I. Mulla, S. Delekar, J. Alloys Compd 490, 228 (2010)
N. Umeyama, M. Tokumoto, S. Yagi, M. Tomura, K. Tokiwa, T. Fujii, R. Toda, N. Miyakawa, S. Ikeda, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 053001 (2012)
A. Kassim, M. Rosli, H. Min, Inter. J. Chem. Res. 3, 21 (2011)
S. Ikhmayies, R. Ahmad-Bitar, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2, 221 (2013)
K. Aly, A. Elnaeim, M. Uosif, O. Abdel-Rahim. Physica B 406, 4227 (2011)
D. Sonavane, S. Jare, R. Survawanshi, R. Kathare, R. Bulakhe. Int. Res. J Sci Eng A2, 61 (2018)
Funding
The authors would like to thank to the University of Mumbai, Mumbai, for financial support for this project (Research Project No. 62 of 2012-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chate, P.A., Sathe, D.J. & Hake, S.L. Nickel selenide thin films: opto-electric and thermoelectric properties. Appl. Phys. A 128, 904 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06064-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06064-0