Abstract
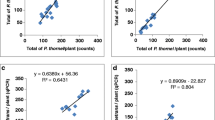
The gene CreAet for resistance to Heterodera avenae, transferred from Aegilops triuncialis to Triticum aestivum introgression line TR-353, was assessed for responses to Pratylenchus thornei under field conditions. After 2.5 months, P. thornei infestation on TR-353 was similar to those on its progenitors (T. aestivum H10-15, T. turgidum H1-1 and A. triuncialis A-1) and on the cultivar Capa. After 5 months, TR-353 hosted significantly more P. thornei per plant than A. triuncialis, T. aestivum H10-15 or cultivar Rinconada, being very close to the maximum value obtained from T. turgidum. The final infestation of line TR-353 by H. avenae was significantly lower than on the other plants, except for A. triuncialis. In addition, at 2.5 months, the abundance of P. thornei on TR-353 was intermediate between the introgression wheat line H93-8 (Cre2 gene) and the cultivar Loros (Cre1 gene), but the final number of P. thornei per plant on TR-353 was significantly greater than on Loros. Line TR-353 was not able to control P. thornei in the field, but it confirmed its resistance to H. avenae, which was significantly lower than those due to Cre1 and Cre2 genes. No competition was observed between P. thornei and H. avenae populations on line TR-353 or A. triuncialis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekal S, Jahier J and Rivoal R (1998) Host responses of different Triticeae to species of the cereal cyst nematode complex in relation to breeding resistant durum wheat. Fundamental and Applied Nematology 21: 359-370
Chevre AM, Jahier J and Trottet M (1989) Expression of disease resistance genes in amphyploids wheats - Triticum tauschii (Coss.) Schmal. Cereal Research Communications 17: 23-29
Cotton J (1970) Field experiments with spring barley resistant to cereal cyst nematode, 1965-1968. Annals of Applied Biology 65: 163-168
Delibes A, Romero D, Aguaded S, Duce A, Mena M, López-Braña I, Andrés MF, Martíxn-Sánchez JA and García-Olmedo F (1993) Resistance to the cereal cyst nematode (Heterodera avenaeWoll.) transferred from the wild grass Aegilops ventricosa to hexaploid wheat by a 'stepping-stone’ procedure. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 87: 402-408
Eastwood RF, Lagudah ES, Appels R, Hannah M and Kollmorgen JF (1991) Triticum tauschii: a novel source of resistance to cereal cyst nematode (Heterodera avenae). Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 42: 69-77
Eastwood RF, Lagudah ES, Halloran GM, Brown JS, Kollmorgen JF and Appels R (1993) Resistance to cereal cyst nematode in Triticum tauschii. In: Imrie BC and Hacker JB (eds) Proceedings of the 10th Australian Plant Breeding Conference, Vol2 (pp 7-8), Gold Coast, Australia
Farsi M, Vanstone VA, Fisher JM and Rathjen AJ (1995) Genetic variation in resistance to Pratylenchus neglectus in wheat and triticales. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 35: 597-602
Hanusova R, Hsam SLK, Bartos P and Zeller FJ (1996) Suppression of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm8 in Triticum aestivum L. (common wheat) cultivars carrying wheat-rye translocation T1BL-1RS. Heredity 77: 383-387
Jahier J, Tanguy M, Abelard P and Rivoal R (1996) Utilization of deletions to localize a gene for resistance to the cereal cyst nematode, Heterodera avenae, on an Aegilops ventricosa chromosome. Plant Breeding 115: 282-284
Kerber ER (1983) Suppression of rust resistance in amphiploids of Triticum. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Wheat Genetics Symposium (pp 813-817) Kyoto, Japan
Kerber ER and Dick PL (1979) Resistance of stem and leaf rust of wheat in Aegilops squarrosa and transfer of a gene for stem rust resistance to hexaploid wheat. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Wheat Genetics Symposium (pp 358-364) NewDelhi, India
Lasserre F, Rivoal R and Cook R (1994) Interactions between Heterodera avenae and Pratylenchus neglectus on wheat. Journal of Nematology 26: 336-344
McIntosh RA, Devos KM, Dubcovsky J and Rogers WJ (2001) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat: 2001 supplement. Annual Wheat Newsletters and Wheat Information Service (in press)
Nicol JM (2001) Important nematode pests of cereals. In: Curtis BC(ed) Wheat Production and Improvement. FAOPlant Production and Protection Series (in press)
Nicol JM, Davies KA, Hancock TW and Fisher JM (1999) Yield loss caused by Pratylenchus thornei on wheat in South Australia. Journal of Nematology 31: 367-376
Nicol JM and Ortiz-Monasterio I (2001) Effect of the root lesion nematode, on wheat yields and plant susceptibility in Mexico. International Journal of Nematology (in press)
Nombela G and Bello A (1983) Modificaciones al método de extracción de nematodos fitoparásitos por centrifugación en azúcar. Boletín del Servicio de Defensa contra Plagas e Inspección Fitopatológica 9: 183-189
Nombela G, Navas A and Bello A(1994) Structure of the nematofauna in Spanish Mediterranean continental soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils 18: 183-192
Nombela G and Romero D (1999) Host response to Pratylenchus thornei of a wheat line carrying the Cre2 gene for resistance to Heterodera avenae. Nematology 1: 381-388
O'Brien PC, Fisher JM and Rathjen AJ (1980) Inheritance of resistance in two wheat cultivars to an Australian population of Heterodera avenae. Nematologica 26: 69-74
Ogbonnaya S, Seah I, Delibes A, Jahier J, Lopez-Bra00F1;a I, Eastwood RF and Lagudah ES (2001) Molecular-genetic characterisation of a new nematode resistance gene in wheat. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 102: 623-629
Orion D, Amir J and Krikun J (1984) Field observations on Pratylenchus thornei and its effects on wheat under arid conditions. Revue de Nématologie 7: 341-345
Rathjen AJ, Eastwood RF, Lewis JG and Dube AJ (1998) Breeding wheat for resistance to Heterodera avenae in Southeastern Australia. In: Braun HJ et al. (eds) Wheat: Prospects for Global Improvement (pp 113-120) Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands
Rivoal R, Laserre F and Cook R (1995) Consequences of long-term cropping with resistant cultivars on the population dynamics of the endoparasitic nematodes Heterodera avenae and Pratylenchus neglectus in a cereal production ecosystem. Nematologica 41: 516-529
Rivoal R, Valette S, Bel Hadj Fradi M, Mokabli A, Gauthier JP, Jahier J and Nicol J (2000) Identification and variability for virulence to Triticeae of CCN populations from mediterranean regions. Nematology 2: 785
Romero MD, Montes MJ, Sin E, López-Braña I, Duce A, Martín-Sánchez JA, Andrés MF and Delibes A (1998) A cereal cyst nematode (Heterodera avenae Woll.) resistance gene transferred from Aegilops triuncialis to hexaploid wheat. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 96: 1135-1140
StatSoft (1994) Statistica version 4.5 for the Windows operating system, reference for statistical procedures. StatSoft, Tulsa, OK.
Tobar A, Valor H and Talavera M (1995a) Effect of different cultivars, mainly of wheat, on the population densities of Pratylenchus thornei and Merlinius brevidens in dry soils in Spain. Nematologica 41: 642-644
Tobar A, Valor H and Talavera M (1995b) Kinetics of recovery from anhydrobiosis in Pratylenchus thornei, Merlinius brevidens and Heterodera avenae from dry field soils and dry roots of the host plant. Fundamental and Applied Nematology 18: 21-24
Thompson JP, Brennan PS, Clewett TG, Sheedy JG and Seymour NP (1999) Progress in breeding wheat for tolerance and resistance to root-lesion nematode (Pratylenchus thornei). Australasian Plant Pathology 28: 45-52
Thompson JP and Clewett TG (1986) Research on root-lesion nematode. In: Queensland Wheat Research Institute Biennial Report, 1982-1984 (pp 32-35) Toowoomba, Queensland, Australia
Thompson JP and Haak MI (1997) Resistance to root-lesion nematode (Pratylenchus thornei) in Aegilops tauschii Coss., the D-genome. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 48: 553-559
Townshend JL (1989) Population densities of four species of root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus) in the oat cultivars, Saia & OAC Woodstock. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 69:903-905
Vanstone VA, Rathjen AJ, Ware AH and Wheeler RD (1998) Relationship between root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus neglectus and P. thornei) and performance of wheat varieties. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 38: 181-188
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nombela, G., Dolores Romero, M. Field Response to Pratylenchus Thornei of a Wheat Line with the CreAet Gene for Resistance to Heterodera Avenae. European Journal of Plant Pathology 107, 749–755 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011923400460
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011923400460