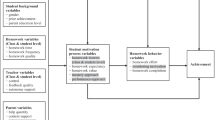
Abstract
The study examined the preferred and actual homework styles of 272 seventh graders (134 males and 138 females) who were characterized by (1) three levels of self‐perceived homework achievement, (2) three levels of academic achievement, and (3) three levels of homework achievement. Consistencies and differences in the distinguishing components were found within and between the different types of achievement. Although different patterns of distinguishing components emerged between preferred and actual homework styles, there were remarkable consistencies between them that distinguished the achievement levels. In general, high achievers were more self‐, parent‐, and teacher‐motivated and persistent, organized their homework in some order, preferred or did homework in a bright home environment and by themselves, and did better with specific instructions, when compared with low achievers. However, neither preferred nor actual perceptual preferences distinguished the levels of achievement. In both preferred and actual situations, students in the high homework achievement group were more parent-motivated than those in the low homework achievement group, demonstrating the importance of parental involvement in the home learning environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Biggs, J. (1989). Approaches to the enhancement of tertiary teaching. Higher Education Research and Development, 8, 7–25.
Boulmetis, J., & Sabula, A. M. (1996). Achievement gains via instruction that matches learning style perceptual preferences. Journal of Continuing Higher Education, 44(3), 15–24.
Bursuck, W. D. (Ed.). (1995). Homework: Issues and practices for students with learning disabilities. Austin, TX: Pro·Ed.
Callan, R. J. (1996). Learning styles in the high school: A novel approach. NASSP Bulletin, 80(557), 66–71.
Caudill, G. (1998). Matching teaching and learning styles. Technology Connection, 4(11), 24–25.
Cooper, H. (1994). The battle over homework: An administrator's guide to setting sound and effective policies. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
Cooper, H. (1998, April). Family, student, and assignment characteristics of positive homework experiences. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, San Diego, CA.
Dart, B., Burnett, P., Boulton-Lewis, G., Campbell, J., Smith, D., & McCrindle, A. (1999). Classroom learning environments and students' approaches to learning. Learning Environments Research, 2, 137–156.
Dunn, R., Griggs, S., Olson, J., Beasley, M., & Gorman, B. S. (1995). A meta-analytic validation of the Dunn and Dunn model of learning style preferences. Journal of Educational Research, 88, 353–362.
Entwistle, D. R., & Hayduk, L. A. (1988). Lasting effects of elementary school. Sociology of Education, 61, 147–159.
Epstein, J. L. (1998, April). Interactive homework: Effective strategies to connect home and school. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, San Diego, CA.
Fehrmann, P. G., Keith, T. Z., & Reimers, T. M. (1987). Home influence on school learning: Direct and indirect effects of parental involvement on high school grades. Journal of Educational Research, 80, 330–337.
Fraser, B. J. (1994). Research on classroom and school climate. In D. Gabel (Ed.), Handbook of research on science teaching and learning (pp. 493–541). New York: Macmillan.
Fraser, B. J. (1998). Science learning environments: Assessments, effects and determinants. In B. J. Fraser & K. G. Tobin (Eds.), International handbook of science education (pp. 527–564). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer.
Fraser, B. J., & Fisher, D. L. (1983). Use of actual and preferred classroom environment scales in person-environment fit research. Journal of Educational Psychology, 75, 303–313.
Gonzales, R. R., & Samuel, R. (1985). Relationship between acculturation, cognitive style, and intelligence: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 16, 190–205.
Hazler, R. J., & Hazler, K. Y. (1993). Children's quotes on learning and helpful adults. Journal of Humanistic Education and Development, 31, 189–192.
Hodgin, J., & Wooliscroft, C. (1997). Eric learns to read: Learning styles at work. Educational Leadership, 54, 43–45.
Hong, E., & Milgram, R. M. (1999). Preferred and actual homework style: A cross-cultural examination. Educational Research, 41, 251–265.
Hong, E., & Milgram, R. M. (2000). Homework: Motivation and learning preference. Westport, CT: Greenwood.
Hong, E., Milgram, R. M., & Perkins, P. G. (1995). Homework style and homework behavior of Korean and American children. Journal of Research and Development in Education, 28, 197–207.
Hong, E., & Suh, B. K. (1995). An analysis of change in Korean-American and Korean students' learning styles. Psychological Reports, 76, 691–699.
Keith, T. Z. (1987). Children and homework. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Children's needs: Psychological perspectives (275–282). Washington, DC: National Association of School Psychologists.
Keith, T. Z., & Benson, M. J. (1992). Effects of manipulable influences on high school grades across five ethnic groups. Journal of Educational Research, 86, 85–93.
Knorr, C. L. (1981). A synthesis of homework research and related literature. (ERIC Document Reproductive Service No. ED 199 933).
Lenehan, M. C., Dunn, R., Inghan, J., Signer, B., & Murray, J. B. (1994). Effects of learning-style intervention on college students' achievement, anxiety, anger and curiosity. Journal of College Student Development, 35, 461–466.
Maeroff, G. (1989). The school-smart parent. New York: Times Books.
Marino, J. F. (1993). Homework: A fresh approach to a perennial problem. Momentum, 24, 69–71.
Milgram, R. M., & Hong, E. (1996a). Homework Preference Questionnaire. Unpublished document, Tel-Aviv University, School of Education and University of Nevada, Las Vegas, College of Education.
Milgram, R. M., & Hong, E. (1996b). Homework Questionnaire. Unpublished document, Tel-Aviv University, School of Education and University of Nevada, Las Vegas, College of Education.
Ramsden, P. (1992). Learning to teach in higher education. London: Routledge.
Reid, J. M. (1987). The learning style preferences of ESL students. TESOL Quarterly, 21, 87–111.
Renzulli, J., & Reis, S. M. (1998). Talent development through curriculum differentiation. NASSP Bulletin, 82, 61–64.
Reynolds, A. J., & Walberg, H. J. (1991). A structural model of science achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83, 97–107.
Rosemond, J. K. (1990). Ending the homework hassle: Understanding, preventing, and solving school performance problems. New York: Andrews and McMeel.
Sinatra, C. (1990). Five diverse secondary schools where learning style instruction works. Reading, Writing, and Learning Disabilities, 6, 323–334.
Walberg, H. J., & Paschal, R. (1994). Homework. In T. Husen & T. N. Postlethwaite (Eds.), The international encyclopedia of education (2nd ed., pp. 2628–2631). Oxford, UK: Pergamon.
Wood, J. A. (1987). Helping students with homework. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, E. Homework style, homework environment, and academic achievement. Learning Environments Research 4, 7–23 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011458407666
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011458407666