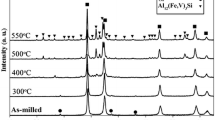
Abstract
Microstructural evolution in gas-atomized Al–14 wt%Ni–14wt% Mm alloy powders was studied during mechanical milling. It was noted that the as-solidified particle size of 200 μm increases up to 72 h of milling and, subsequently, there was continuous refinement to 20 μm on milling to 200 h. Two microstructurally different zones—Zone A, which is featureless, and Zone B, which has the structure of the as-solidified powder—were noted. The thickness of the Zone A increased with increasing milling time at the expense of Zone B. Zone A was found to be much harder than Zone B and, consequently, crack formation, eventually leading to microstructural refinement, was observed to start in the relatively weaker Zone B.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. Suryanarayana, Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 1–184 (2001).
B. S. Murty and S. Ranganathan, Intern. Mater. Rev. 43, 101–141 (1998).
C. Suryanarayana, Bibliography on Mechanical Alloying and Milling (Cambridge International Science, Cambridge, UK, 1995).
C. Suryanarayana, Met. Mater. 2, 195–209 (1996).
H. H. Liebermann, ed., Rapidly Solidified Alloys: Processes, Structures, Properties, Applications (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1993).
T. R. Anantharaman and C. Suryanarayana, Rapidly Solidi-fied Alloys: A Technological Overview (Trans Tech Publications, Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 1987).
L. Lu and M. O. Lai, Mechanical Alloying (Kluwer Acad., Boston, MA, 1998).
S. Ezz, A. Lawley, and M. J. Koczak, in Aluminum Alloys: Their Physical and Mechanical Properties, E. A. Starke, Jr. and T. H. Sanders, Jr., eds. (EMAS, Warley, West Highlands, UK, 1986), vol. II, pp. 1013–1028.
C. Suryanarayana, R. Sundaresan, and F. H. Froes, in Advances in Powder Metallurgy—1989, T. G. Gasbarre and W. F. Jandeska, Jr., compilers (Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1989), vol. 3, pp. 175–188.
K. F. Kobayashi, N. Tachibana, and P. H. Shingu, J. Mater. Sci. 25, 801–804 (1990).
M. L. Ovecoglu, C. Suryanarayana, and W. D. Nix, Metall. Mater. Trans. 27A, 1033–1041 (1996).
Y. H. Kim, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto, Mater. Trans, JIM 31, 747–749 (1990).
Y. H. Kim, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto, Mater. Trans. JIM 32, 331–338 (1991).
A. Inoue, K. Ohtera, A. P. Tsai, and T. Masumoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 27, L280–L282 (1988).
K. Higashi, T. Mukai, S. Tanimura, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto, Scripta Metall. Mater. 26, 191–196 (1992).
K. Higashi, T. Mukai, A. Uoya, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto, Mater. Trans. JIM 36, 1467–1475 (1995).
A. Inoue, K. Ohtera, A. P. Tsai, and T. Masumoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 27, L479–L482 (1988).
H. Chen, Y. He, G. J. Shiflet, and S. J. Poon, Scripta Metall. Mater. 25, 1421–1424 (1991).
K. Ohtera, T. Terabayashi, H. Nagahama, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto, Mater. Trans. JIM 33, 775–781 (1992).
K. Ohtera, K. Kita, H. Nagahama, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto, Mater. Sci. Eng. A179/180, 592–595 (1994).
G. M. Yoon, Y. H. Kim, B. H. Jung, and I. B. Kim, J. Korean Inst. Metal. Mater 34, 696–702 (1996).
S. J. Hong, T. S. Kim, H. S. Kim, W. T. Kim, and B. S. Chun, Mater. Sci. Eng. A271, 469–476 (1999).
S. J. Hong, C. Suryanarayana, and B. S. Chun, Scripta Mater., in press.
C. Suryanarayana and M. G. Norton, X-Ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach (Plenum, New York, 1998).
G. H. Chen, C. Suryanarayana, and F. H. Froes, Metall. Mater. Trans. 26A, 1379–1387 (1995).
J. S. Benjamin, Sci. Amer. 234, 40–48 (1976).
C. Suryanarayana, in ASM Handbook, Powder Metal Technologies and Applications, (ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1998), vol. 7, pp. 80–90.
P-Y. Lee, J-L. Yang, and H-M. Lin, J. Mater. Sci. 33, 235–239 (1998).
H. Jones, Mater. Sci. Eng. 5, 1–18 (1969).
H. Biloni and B. Chalmers, Trans. TMS-AIME 233, 373–378 (1965).
C. Suryanarayana, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 25, 36–42 (1972).
P. Ramachandrarao and T. R. Anantharaman, Trans. TMS-AIME 245, 890–892 (1969).
G. V. S. Sastry and C. Suryanarayana, Mater. Sci. Eng. 47, 193–208 (1981).
C. C. Koch, Nanostructured Mater. 2, 109–129 (1993).
C. C. Koch, Nanostructured Mater. 9, 13–22 (1997).
C. Suryanarayana and F. H. Froes, in Heat Resistant Materials, K. Natesan and D. J. Tillack, eds. (ASM International, Material Park, OH, 1991), pp.25–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S.J., Kim, T.S., Suryanarayana, C. et al. Microstructural Evolution during Mechanical Milling of Rapidly Solidified Al–14Ni–14Mm1 Alloy Powders. Journal of Materials Synthesis and Processing 9, 39–47 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011386615305
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011386615305