Abstract
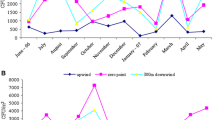
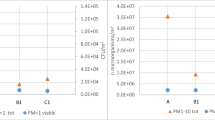
Composting is a biological process that has thepotential to emit large quantities ofbioaerosols and, therefore, could adverselyaffect public health. Numerous previousstudies have demonstrated bioaerosol levelselevated above background adjacent tocomposting waste materials, but effects onoffsite bioaerosol levels due tocomposting-facility bioaerosol emissions havenot been extensively investigated. Of the fewsuch studies published, most have not foundelevated compost-related bioaerosols downwindfrom the composting operation. We investigatedviable Aspergillus fumigatus andthermophilic actinomycete levels upwind anddownwind of a large yard-waste compostingfacility and sought to determine whether levelsin a residential neighborhood near the facilitywere elevated above background levels due tofacility bioaerosol emissions. Mean bioaerosollevels at the composting facility weresignificantly higher than the mean backgroundlevels, exceeding the background means byroughly 20-fold. When a neighborhood samplingsite about 500 m from the facility was in thedownwind direction mean levels weresignificantly higher than for other winddirections, and excursions well abovebackground levels were significantly morefrequent than at background sites. There was asignificant temporal correlation betweenbioaerosol levels at the composting facilityand the downwind sampling site. The resultsindicate that bioaerosol emissions from a largeyard-waste composting facility cansignificantly increase bioaerosol exposurelevels at least 500 m downwind from thefacility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnow P.M., Sadigh M., Costas C., Weil D. and Chudy R.: 1991, Endemic and epidemic aspergillosis associated with in-hospital replication of Aspergillus organisms. J Infect Dis 164, 998–1002.
Austwick P.K.C.: 1963, Ecology of Aspergillus fumigatus and the pathogenic phycomycetes. Rec Prog Micro 8, 644–651.
Browne M.L., Ju C.L., Recer G.M., Kallenbach L.R., Melius J.M. and Horn E.G.: in press, A prospective study of health symptoms and Aspergillus fumigatus spore concentrations near a grass and leaf composting facility. Compost Sci Util.
Buttner M.P., Willeke K. and Grinshpun S.A.: 1997, Sampling and analysis of airborne microorganisms. In: C.J. Hurst et al. (eds), Manual of Environmental Microbiology. ASM Press, Washington, D.C., pp. 629–640.
Clark C.S., Bjornson H.S., Schwartz-Fulton J., Holland J.W. and Gortside P.S.: 1984, Biological health risks associated with the composting of wastewater treatment plant sludge. J Water Poll Cont Fed 56, 1269–1276.
Clark C.S., Rylander R. and Larsson L.: 1983, Levels of gram negative bacteria, Aspergillus fumigatus, dust and endotoxin at compost plants. Appl Environ Micro 45, 1501–1505.
Danneberg G., Gruneklee E., Seitz M., Hartung J. and Driesel A.J.: 1997, Microbial and endotoxin immissions in the neighborhood of a composting plant. Ann Agric Environ Med 4, 169–173.
E&A Environmental Consultants, Inc.: 1993, Report to Earthgro, Lebanon, Connecticut.
Fischer J.L., Beffa T., Lyon P.-F. and Arango M.: 1998, Aspergillus fumigatus in windrow composting: Effect of turning frequency. Waste Manage Res 16, 320–329.
Flannigan B. and Miller J.D.: 1994, Health implications of fungi in indoor environments-an overview. In: R.A. Samson et al. (eds), Health Implications of Fungi in Indoor Environments. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 3–28.
Folmsbee M. and Strevett K.A.: 1999, Bioaerosol concentration at an outdoor composting center. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 49, 554–561.
Gerson S.L., Barker P., Jacobs M.R., Creger R. and Lazarus H.M.: 1994, Aspergillosis due to carpet contamination. Infect Contr Hosp Epidemiol 15, 221–223.
Heederik D. and Smid T.: 1994, Epidemiology: mortality and morbidity. In: R. Rylander and R.R. Jacobs (eds), Organic Dusts, Exposure, Effects, and Prevention. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp. 127–138.
Hyatt G.W. and Richard T.: 1992, Guest editorial. Biomass and Bioenergy 3, 121–125.
Johanning E., Olmsted E. and Yang C.: 1995, Medical issues related to municipal waste composting. Am Indus Hygiene Assn Proceed 1995 (Abstr.), 24.
Kramer M.N., Kruup V.P. and Fink J.N.: 1989, Allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis from a contaminated dump site. Am Rev Resp Dis 140, 1086–1088.
Kwong-Chung K.J.and Bennet J.E.: 1992, Medical Mycology. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia.
Loo V.G., Bertrand C., Dixon C., Vitye D., DeSalis B., McLean A.P.H., Brox A. and Robson H.G.: 1996, Control of construction-associated nosocomial aspergillosis in an antiquated hematology unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 17, 360–364.
Marsh P.B., Millner P.D., and Kla J.M.: 1979, A guide to the recent literature on aspergillosis as caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, a fungus frequently found in self-heating organic matter. Mycopathologica 69, 67–81.
Millner P.D.: 1982, Thermophilic and thermotolerant actinomycetes in sewage-sludge compost. Devel Indus Micro 23, 61–78.
Millner P.D., Bassett D.A. and Marsh P.B.: 1980, Dispersal of Aspergillus fumigatus from sewage sludge compost piles subjected to mechanical agitation in open air. Appl Environ Micro 39, 1000–1009.
Millner P.D., Marsh P.B., Snowden R.B. and Pair J.F.: 1977, Occurrence of Aspergillus fumigatus during composting of sewage sludge. Appl Environ Micro 34, 765–772.
Millner P.D., Olenchock S.A., Epstein E., Rylander R., Haines J., Walker J., Ooi B.L., Horn E. and Maritato M.: 1994, Bioaerosols associated with composting facilities. Comp Sci Utiliz 2, 6–57.
Mullins J.: 1974, The ecology of Aspergillus fumigatus (Fres). PhD thesis, University of Wales.
Mullins J., Harvey R. and Seaton A.: 1976, Sources and incidence of airborne Aspergillus fumigatus (Fres). Clin Aller 6, 209–217.
Mullins J., Hutcheson P.S. and Slavin R.G.: 1984, Aspergillus fumigatus spore concentration in outside air: Cardiff and St. Louis compared. Clin Aller 14, 351–354.
Neter J., Wasserman W., Kutner M.H.: 1990, Applied Linear Statistical Models: Regression, Analysis of Variance and Experimental Designs. Irwin, Homewood, IL.
New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH): 1994, A Prospective Study of Health Symptoms and Bioaerosol Levels Near a Yard Waste Composting Facility. Center for Environmental Health, Albany, NY.
Nielsen B.H., Wurtz H., Breum N.O. and Poulsen O.M.: 1997, Microorganisms and endotoxin in experimentally generated bioaerosols from composting household waste. Ann Agric Environ Med 4, 159–168.
Noble W.C. and Clayton Y.M.: 1963, Fungi in the air of hospital wards. J Gen Micro 32, 397–402.
Ogden E.C., Raynor G.S., Hayes J.V., Lewis D.M. and Haines J.H.: 1974, Manual for Sampling Airborne Pollen. Hafner Press, New York.
Opal S.M., Asp A.A., Cannady P.B. Jr., Morse P.L., Burton L.J. and Hammer P.G. II.: 1986, Efficacy of infection control measures during a nosocomial outbreak of disseminated aspergillosis associated with hospital construction. J Infect Dis 153, 634–637.
Passman F.J.: 1983, Recovery of Aspergillus fumigatus aerospora from municipal sewage composting operations in the state of Maine. Mycopathologia 83, 41–51.
Rhame F.S.: 1991, Prevention of nosocomial aspergillosis. J Hosp Infect 18(Suppl. A), 466–472.
Richard T.L.: 1992, Municipal solid waste composting: Physical and biological processing. Biomass and Bioenergy 3, 163–180.
Rylander R.: 1994, The clinical panorama. In: R. Rylander and R.R. Jacobs (eds), Organic Dusts, Exposure, Effects, and Prevention. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp. 117–123.
Rylander R.: 1999, Effects after mold exposure — which are the causative agents? In: E. Johanning (ed.), Bioaerosols, Fungi and Mycotoxins: Health Effects, Assessment, Prevention and Control. Eastern New York Occupational and Environmental Health Center, Albany, NY, pp. 28–32.
Steel R.G.D. and Torrie J.H.: 1980, Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York.
Syzdek L.D. and Haines J.H.: 1995, Monitoring Aspergillus fumigatus aerosols from a composting facility. Aerobiologia 11, 87–93.
Tolvanen O.K., Hanninen K.I., Veijanen A. and Villberg K.: 1998, Occupation hygiene in biowaste composting. Waste Manage Res 16, 525–540.
US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): 1971, National primary and secondary ambient air quality standards. Fed Reg 36, 22384.
van der Werf P.: 1996, Bioaerosols at a Canadian composting facility. Biocycle (September), 78–83.
Vincken W. and Roels P.: 1984, Hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to Aspergillus fumigatus in compost. Thorax 39, 74–75.
Walsh T.J. and Dixon D.M.: 1989, Nosocomial aspergillosis: Environmental microbiology, hospital epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. Eur J Epidemiol 5, 131–142.
Weber S., Kullman G., Petsonk E., Jones W.G., Olenchock S., Sorenson W., Parker J., Marcelo-Baciu R., Frazer D. and Castranova V.: 1993, Organic dust exposures from compost handling: Case presentation and respiratory exposure assessment. Am J Indus Med 24, 365–374.
Wouters I., Douwes J., Doekes G. and Heederik D.: 1997, Airway inflammation: an occupational health risk in waste composting workers. Eur Resp J (supp. Abstr.) 10, 315s.
Zwerling E.M. and Strom P.F.: 1991, Levels of Aspergillus fumigatus at yard waste composting facilities in New Jersey, Theobold Smith Society (Abstr.). Annual meeting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Recer, G.M., Browne, M.L., Horn, E.G. et al. Ambient air levels of Aspergillus fumigatus and thermophilic actinomycetes in a residential neighborhood near a yard-waste composting facility. Aerobiologia 17, 99–108 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010816114787
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010816114787