Abstract
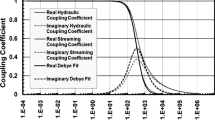
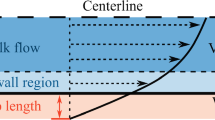
Effects of water saturation and wettability on the dielectric constant are investigated experimentally using four-electrode impedance measurements, and theoretically using models that account for the electrical double layer polarization. Complex impedance measurements, performed on Berea sandstone and on Ottawa-sand packs in the frequency range 10 Hz to 1 MHz, appear to indicate that the dielectric constant varies linearly with water saturations above 50%. The rate of change of dielectric constant with saturation is found to be a function of frequency. As the frequency increases this rate of change decreases. The decrease in the slope of the dielectric constant-water saturation profile with frequency is not intuitively obvious, but has been proven theoretically in this work. The dielectric constant of water-wet samples is found higher than that of the oil-wet samples at all water saturations. The difference is more pronounced at high water saturations near unity. The wettability changes have been simulated using a generalized Maxwell–Wagner model by varying the amount of ionic surface charge of rocks. In general oil-wetting agents react with the formation matrix by connecting their positively charged tails to the negatively charged silica surfaces, lowering the surface charge density. Simulations show that the effect of wettability changes on the dielectric constant is very significant. These conclusions are consistent with the experimental results presented in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bona, N., Rossi, E. and Capaccioli, S.: 1999, Wettability and dielectric constant, SCA paper 9925, presented at the Society of Core Analyst International Symposium, Golden, Colorado, 1-4 August.
Borner, F.D.: 1997, Combined complex conductivity and dielectric measurements on core samples, SCA paper 9736, presented at the Society of Core Analyst International Symposium, Alberta, Calgary, September 7-10.
Delacey, E.H.B. and White, L.R.: 1981, Dielectric response and conductivity of dilute suspensions of colloidal particles, J. Chem. Soc. 77, 2007-2039.
Garrouch, A.A. and Sharma, M.M.: 1994, The influence of clay content, stress, and wettability on the dielectric properties of Brine-saturated rocks, Geophysics 59, 909-917.
Garrouch, A.A. and Sharma, M.M.: 1998, Dielectric dispersion of partially saturated porous media in the frequency range 10Hz to 10MHz, The Log Analyst 39, 48-53.
Garrouch, A.A.: 1999, A systematic study revealing resistivity dispersion in porous media, The Log Analyst 40, 271-279.
Glover, P.W.J., Meredith, P.G., Sammonds, P.R. and Murrell, S.A.F.: 1994, Ionic surface electrical conductivity in sandstone, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 21635-21650.
Hasted, J. B.: 1973, Aqueous Dielectrics, Chapman and Hall.
Knight, R. and Abad, A.: 1995, Rock/water interaction in dielectric properties: Experiments with hydrophobic sandstones, Geophysics 60, 431-436.
Lima, O.A.L. and Sharma, M.M.: 1992, A generalized Maxwell-Wagner theory for membrane polarization in shaly sands, Geophysics 57, 431-440.
Lima, O.A.L. and Dalcin, C.L.R.: 1995, Application of a new shaly sand model for interpreting resistivity and dielectric log measurements, The Log Analyst 36, 29-41.
Lyklema, J.: 1991, Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science, Vol. I: Fundamentals, Academic Press.
Lyklema, J.: 1995, Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science, Volume II: Solid-liquid interfaces, Academic Press.
Nguyen, B., Bruining, J. and Slob, E.C.: 1999, Effects of wettability on dielectric properties of porous media, SPE paper 56507, presented in the 1999 SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, October 3-6.
Sharma, M.M., Garrouch, A.A. and Dunlap, H.F.: 1991, Effects of wettability, pore geometry, and stress on electrical conduction in fluid-saturated rocks, The Log Analyst, 32, 511-526.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrouch, A.A. A Novel Analysis of the Electrical Transport Mechanisms in Porous Media. Transport in Porous Media 44, 559–575 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010787907962
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010787907962