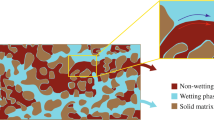
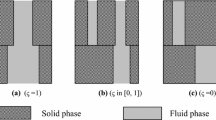
Abstract
In this paper, a set of equations governing the electromagnetic/acoustic coupling in partially saturated porous rocks in the low-frequency regime is derived. The equations are obtained by volume averaging of fundamental electromagnetic and mechanical equations valid at the pore-scale, following the same procedure as the one developed in the seminal paper of S. Pride for porous media where the fluid electrolyte fully saturates the pore space. In the present approach, it is assumed that the porous rock is partially saturated with a wetting-fluid electrolyte (water) and a non-wetting fluid (air). We also assume that an electromagnetic/mechanical coupling exists at the water–solid and water–air contact surfaces through adsorbed excess charges balanced by mobile ions in the water. The proposed approach is valid at the low-frequency regime, where capillary pressure perturbations can be safely neglected. The governing equations thus derived are similar to the ones obtained by Pride with the main difference that the various coefficients, including the electrokinetic coupling coefficient and electric conductivity appearing in the transport equations, are functions of the water saturation and depend on electrical and topological properties of both electric double layers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, B.: Analysis of the propagation of sound waves in partially saturated soils by means of a macroscopic linear poroelastic model. Transp. Porous. Med. 80(B06209), 173–192 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9360-y
Allègre, V., Lehmann, F., Ackerer, P., et al.: Modelling the streaming potential dependence on water content during drainage: 1. A 1D modelling of SP using finite element method. Geophys. J. Int. 189, 285–295 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05371.x
Allègre, V., Maineult, A., Lehmann, F., et al.: Self-potential response to drainage-imbibition cycles. Geophys. J. Int. 197(3), 1410–1424 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggu055
Allégre, V., Jouniaux, L., Lehmann, F., et al.: Influence of water pressure dynamics and fluid flow on the streaming-potential response for unsaturated conditions. Geophys. Prospect. 63, 694–712 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2478.12206
Bear, J.: Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Dover Civil and Mechanical Engineering Series, Dover, (1988). https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=picSrNsgY8oC
Berryman, J.G., Thigpen, L., Chin, R.C.Y.: Bulk elastic wave propagation in partially saturated porous solids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 84(1), 360–373 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.396938
Biot, M.A.: Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid: I. Low frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 28(2), 168–178 (1956)
Bordes, C., Garambois, S., Jouniaux, L., et al.: Seismoelectric measurements for the characterization of partially saturated porous media. In: AGU proceedings, American Geophysical Union, fall Meeting 2009, abstract #NS31B-1161 (2009)
Bordes, C., Sénéchal, P., Barrière, J., et al.: Impact of water saturation on seismoelectric transfer functions: a laboratory study of coseismic phenomenon. Geophys. J. Int. 200, 1317–1335 (2015)
Creux, P., Lachaise, J., Graciaa, A., et al.: Specific cation effects at the hydroxide-charged air/water interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 3753–3755 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp070060s
Culligan, K., Wildenschild, D., Christensen, B., et al.: Interfacial area measurements for unsaturated flow through a porous medium. Water Resour. Res. 40(W12), 413 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1029/2004WR003278
Demirel, Y.: Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics: Transport and Rate Processes in Physical, Chemical and Biological Systems, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2007)
Dupuis, J.C., Butler, K.E., Kepic, A.W.: Seismoelectric imaging of the vadose zone of a sand aquifer. Geophysics 72, A81–A85 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2773780
Fiorentino, E., Toussaint, R., Jouniaux, L.: Two-phase lattice Boltzmann modelling of streaming potentials: influence of the gas-water interface on the electrokinetic coupling. Geophys. J. Int. 208, 1139–1156 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggw417
Frenkel, J.: On the theory of seismic and electroseismic phenomena in a moist soil. J. Phys. 8(4), 230–241 (1944)
Grobbe, N., Revil, A., Zhu, Z., et al. (eds.): Seismoelectric Exploration: Theory, Experiments, and Applications, Geophysical Monograph Series. Wiley, New Jersey (2020)
Guichet, X., Jouniaux, L., Pozzi, J.P.: Streaming potential of a sand column in partial saturation conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 108(B3), 2141 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB001517
Haines, S.H., Pride, S.R.: Seismoelectric numerical modeling on a grid. Geophysics 71(6), 57–65 (2006)
Haines, S.S., Guitton, A., Biondi, B.: Seismoelectric data processing for surface surveys of shallow targets. Geophysics 72, G1–G8 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2424542
Jackson, M.D.: Multiphase electrokinetic coupling: insights into the impact of fluid and charge distribution at the pore scale from a bundle of capillary tubes model. J. Geophys. Res. 115(B07), 206 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB007092
Jardani, A., Revil, A.: Seismoelectric couplings in a poroelastic material containing two immiscible fluid phases. Geophys. J. Int. 202(2), 850–870 (2015)
Jougnot, D., Linde, N., Revil, A., et al.: Derivation of soil-specific streaming potential electrical parameters from hydrodynamic characteristics of partially saturated soils. Vadose Zone J. (2012). https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2011.0086
Jouniaux, L., Zyserman, F.: A review on electrokinetically induced seismo-electrics, electro-seismics, and seismo-magnetics for Earth sciences. Solid Earth 7, 249–284 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5194/se-7-249-2016
Jouniaux, L., Allègre, V., Toussaint, R., et al.: Saturation dependence of the streaming potential coefficient, American Geophysical Union (AGU), chap 5, pp 73–100 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119127383.ch5
Li, S., Pengra, D., Wong, P.: Onsager’s reciprocal relation and the hydraulic permeability of porous media. Phys. Rev. E 51(6), 5748–5751 (1995)
Linde, N., Jougnot, D., Revil, A., et al.: Streaming current generation in two-phase flow conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, LO3306 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL028878
Monachesi, L., Rubino, G., Rosas-Carbajal, M., et al.: An analytical study of seismoelectric signals produced by 1D mesoscopic heterogeneites. Geophys. J. Int. 201, 329–342 (2015)
Monachesi, L., Zyserman, F., Jouniaux, L.: An analytical solution to assess the SH seismoelectric response of the vadose zone. Geophys. J. Int. 213, 1999–2019 (2018)
Munch, F., Zyserman, F.: Detection of Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids Contamination by SH-TE Seismoelectrics: a Computational Feasibility Study. J. Appl. Geophys. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2016.03.026
Neev, J., Yeatts, F.R.: Electrokinetic effects in fluid-saturated poroelastic media. Phys. Rev. B 40(13), 9135–9141 (1989)
Pengra, D.B., Li, S.X., Wong, P.Z.: Determination of rock properties by low frequency ac electrokinetics. J. Geophys. Res. 104(B12), 29.485-29.508 (1999)
Perrier, F., Morat, P.: Characterization of electrical daily variations induced by capillary flow in the non-saturated zone. Pure Appl. Geophys. 157, 785–810 (2000)
Pride, S.: Governing equations for the coupled electromagnetics and acoustics of porous media. Phys. Rev. B 50, 15,678-15,695 (1994)
Pride, S.R., Gangi, A.F., Morgan, F.D.: Deriving the equations of motions for porous isotropic media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 92(6), 3278–3290 (1992)
Rapetti, F., Rousseaux, G.: On quasi-static models hidden in Maxwell’s equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 79, 92–106 (2014)
Revil, A., Cerepi, A.: Streaming potentials in two-phase flow conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31(L11), 605 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL020140
Revil, A., Linde, N., Cerepi, A., et al.: Electrokinetic coupling in unsaturated porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 313, 315–327 (2007)
Revil, A., Jardani, A., Sava, P., et al.: The Seismoelectric Method: Theory and Application. Wiley Blackwell, New Jersey (2015)
Rosas-Carbajal, M., Jougnot, D., Rubino, J., et al.: Seismoelectric Signals Producedc by Mesoscopic Heterogeneities. In: Grobbe, N., Revil, A., Zhu, Z., et al. (eds.) Seismoelectric Exploration: Theory, Experiments, and Applications, chap 9, pp. 249–287. Wiley, New Jersey (2020)
Santos, J., Corberó, J., Douglas, J.: Static and dynamic behavior of a porous solid saturated by a two-phase fluid. JASA (1990). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.399439
Santos, J., Douglas, J., Corbero, J., et al.: A model for wave propagation in a porous medium saturated by a two-phase fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87(4), 1467–1488 (1990)
Slattery, J.C.: Flow of viscoelastic fluids through porous media. AIChE J. 13(6), 1066–1071 (1967)
Thompson, A.H., Gist, G.A.: Geophysical applications of electrokinetic conversion. Lead. Edge 12, 1169–1173 (1993)
Vinogradov, J., Jackson, M.: Multiphase streaming potential in sandstones saturated with gas/brine and oil/brine during drainage and imbibition. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38(L01), 301 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL045726
Warden, S., Garambois, S., Jouniaux, L., et al.: Seismoelectric wave propagation numerical modeling in partially saturated materials. Geophys. J. Int. 194, 1498–1513 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt198
Yang, J., Sato, T.: Analytical study of saturation effects on seismic vertical amplification of soil layer. Geotechnique 51(2), 161–165 (2001)
Zyserman, F., Gauzellino, P., Santos, J.: Finite element modeling of SHTE and PSVTM electroseismics. J. Appl. Geophys. 72, 79–91 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2010.07.004
Zyserman, F., Jouniaux, L., Warden, S., et al.: Borehole seismoelectric logging using a shear-wave source: Possible application to CO\(_2\) disposal? Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 33, 82–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2014.12.009
Zyserman, F., Monachesi, L., Jouniaux, L.: Dependence of shear wave seismoelectrics on soil textures: a numerical study in the vadose zone. Geophys. J. Int. 208(2), 918–935 (2017)
Zyserman, F.I., Monachesi, L.B., Thompson, A.H., et al.: Numerical modelling of passive electroseismic surveying. Geophys. J. Int. 230(3), 1467–1488 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggac127
Acknowledgements
L.M. and F.Z. acknowledge support from FONCYT through grant PICT 2019-03220. F.Z. acknowledges support from CONICET through grant PIP 112-201501-00192. L.J., L.M. and F.Z. acknowledge support from CNRS/INSU through the PICS SEISMOFLUID.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no competing interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A Mechanical Constitutive Relations in the Case of Stagnant Non-Wetting Fluid
Appendix A Mechanical Constitutive Relations in the Case of Stagnant Non-Wetting Fluid
If the non-wetting fluid is assumed to be stagnant (\(p_{nw}=0\), \(\varvec{w_{nw}}=0\) and \(p_{w}=-p_{c}\)) then the volume average of the stress–strain relations are taken without the consideration of Eq. (60). Following Pride et al. (1992), taking into account that the wetting-fluid occupies a volume \(s_{w}\phi\) we obtain
where
In these expressions,
From Eq. (A2), if the solid displacement is negligible, then taking the first time derivative we have \(\dot{p}_{c}= \tilde{M} \nabla \cdot \varvec{\dot{w}_{w}}\).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Monachesi, L.B., Zyserman, F.I., Jouniaux, L. et al. Electromagnetic/Acoustic Coupling in Partially Saturated Porous Rocks: An Extension of Pride’s Theory. Transp Porous Med 149, 785–815 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-023-01983-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-023-01983-9