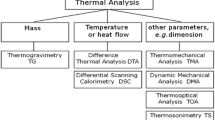
Abstract
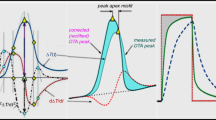
The supposition of even temperature distribution in the sample mass (‘ingradient’ approach) led to mathematical expressions describing the basic quantitative elements of thermal curves: the transformation duration, the peak height, the initial and final section peak areas and the total area. The simplest expression is that for the total peak area: S=(R2Hd/2k1)1nR1/R, where R, H, d, k1and R1are the radius, the specific thermal effect of sample transformation, the gravimetric density and the outer layer encircling the sample, respectively. For the other quantitative elements, the dependences are far more complicated, depending on the duration and variants of the transformation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diligensky, N.V., Egunov, V.P. & Efimov, A.P. Quantitative Thermal Analysis VII. Basic elements of thermal curves in the context of ingradient theory. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 54, 957–962 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010181012506
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010181012506