Abstract
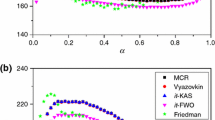
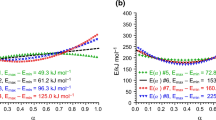
An analysis is presented of the consequences of the use of a one term equation containing apparent activation parameters, instead of the true rate equation to describe two successive decomposition reactions undergone by a solid compound. It is demonstrated that the apparent activation energy, obtained by means of isoconversional differential and integral methods, varies with the conversion degree for a relatively narrow temperature range and with temperature at a given value of the conversion degree. The activation energy values obtained with the isoconversional differential method are higher than the corresponding values obtained with the isoconversional integral method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Budrugeac, D. Homentcovschi and E. Segal, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 63 (2001) 459.
V. Marcu and E. Segal, Thermochim. Acta, 35 (1980) 43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Budrugeac, P., Homentcovschi, D. & Segal, E. Critical Analysis of the Isoconversional Methods for Evaluating the Activation Energy. II. The activation energy obtained from isothermal data corresponding to two successive reactions. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 63, 465–469 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010100712853
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010100712853