Abstract
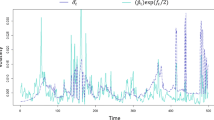
We analyze the Nikkei daily stock index and verify how wavelets can help in identifying, estimating and predicting its volatility features. While we study the conditional mean and variance dynamics, by utilizing statistical parametric inference techniques, we also decompose the observed signal with a data de-noising procedure. We thus investigate how wavelets discriminate among information at different resolution levels and we attempt to understand whether the de-noised data lead to a better identification of the underlying volatility process. We find that the wavelet data pre-processing strategy, by reducing the measurement error of the observed data, is useful for improving the volatility prediction power.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Andersen and T. Bollerslev, “Answering the critics: yes, ARCH models do provide good volatility forecasts, ” NBER Working Paper, 6023, 1997.
T. Andersen and T. Bollerslev, “Deutsche Mark-Dollar Volatility: Intraday Activity Patterns, Macroeconomic Announcements and Longer Run Dependencies, ” The Journal of Finance vol. 53 pp. 219–265, 1998.
T. Bollerslev, “Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity, ” Journal of Econometrics vol. 31 pp. 307–327, 1986.
T. Bollerslev, R. F. Engle, and D. B. Nelson, “ARCH models” in Handbook of Econometrics, vol.4 (R. F. Engle and D. McFadden eds) Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, 1994.
A. Bruce and H. V. Gao, S+Wavelets, StatSci Div., MathSoft Inc., Seattle, 1994.
R. Coifman and V. Wickerhauser, “Entropy based algorithms for best basis selection, ” IEEE Transactions on Information Theory vol. 38 pp. 713–718, 1992.
I. Daubechies, Ten Lectures on Wavelets, SIAM: Philadelphia, 1992.
D. Donoho and I. Johnstone, “Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage, ” Journal American Statistical Association vol. 90 pp. 1200–1224, 1993.
F.C. Drost and T.E. Nijman, “Temporal Aggregation of GARCH Processes, ” Econometrica vol. 61 pp. 909–927, 1993.
R.F. Engle, “Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity with estimates of the variance of the UK inflation, ” Econometrica vol. 50 pp. 987–1008, 1982.
R. Gallant and G. Tauchen, “A nonparametric approach to nonlinear time series analysis: estimation and simulation, ” in New directions in time series analysis, IMA Volumes in Mathematics and its Applications, Springer-Verlag, 1992.
J. S. Marron, S. Adak, I. M. Johnstone, M. H. Neumann and P. Patil, “Exact Risk Analysis of Wavelet Regression, ” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics vol. 7 pp. 278–309, 1998.
D. Martin, H. V. Gao, and Z. Ding, S+GARCH, Data Analysis Prod. Div., MathSoft Inc., Seattle, 1996.
I. Meyer, Wavelets: Algorithms and Applications, SIAM, Philadelphia, 1993.
A. Weigend, B. Huberman and D. Rumelhart, “Predicting sunspots and exchange rates with connectionist networks, ” in Nonlinear Modeling and Forecasting, SFI Studies in the Science of Complexity, Proc. vol. 12 (Casdagli M. and Eubank S., eds.) Addison-Wesley, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capobianco, E. Statistical Analysis of Financial Volatility by Wavelet Shrinkage. Methodology and Computing in Applied Probability 1, 423–443 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010010825105
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010010825105