Abstract
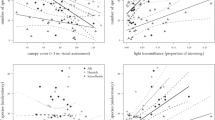
Both vertical and horizontal heterogeneity in red light levels and in the red/far red ratio were measured in a mountain grassland and correlated with the vegetation structure. Vertical change in the red/far red ratio was measured in three communities; canopy structure and density was investigated by the point-quadrat method and biomass harvesting. Quantities of both grasses and dicots were significantly correlated with R/FR ratio and red light intensity at ground level. In dicots, percentage cover determines their effect on light levels; in contrast, no single parameter suffices to capture the effect of grasses: grass biomass, number of hits (cover) and the mean height (distance from the soil surface) of grass hits are of importance. This indicates strikingly different geometry and optical properties of both plant groups.
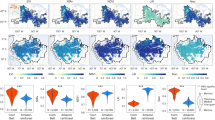
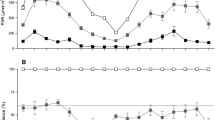
The fine-scale horizontal heterogeneity was assessed by means of a grid of 3.3×3.3 cm cells (plots of 8× cells) in the species-poor community. Both red light and R/FR ratio were determined at soil level in all the grid cells; fine-scale vegetation recording was done by counting all rooted stems (leaves for large rosette plants) in these cells. Spatial autocorrelation (Moran's I) of fine-scale heterogeneity in light levels, biomass per cell and individual species occurrences revealed many significant autocorrelations. Light levels (particularly red light) show autocorrelations at the distance of 1–2 cells (3.3–6.7 cm); biomass shows little autocorrelation. A multivariate analysis (redundancy analysis) showed that cellwise densities of two species had significant and systematic correlations with the light levels (both red light and R/FR ratio): a grass species with wide, mainly horizontal leaves, Anthoxanthum alpinum, was negatively correlated with light levels; Nardus stricta, with upright and narrow leaves and stems was positively correlated with light levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, A. D. Q. & Gitay, H. 1990. Resource pattern and community pattern in a dune slack. Pp. 191-200. In: Krahulec F., Agnew A. D. Q, Agnew S. & Willems J. H. (eds), Spatial processes in plant communities, SPB, The Hague.
Baldocchi, D. & Collineau, S. 1994. The physical nature of solar radiation in heterogeneous canopies: spatial and temporal aspects. Pp. 21-72. In: Caldwell M. M. & Pearcy R. W. (eds), Exploitation of environmental heterogeneity by plants. Academic, San Diego.
Ballaré, C. L., Sánchez, R. A., Scopel, A. L. & Chersa, C. M. 1988. Morphological responses of Datura ferox seedlings to presence of neighbours. Their relationships with canopy microclimate. Oecologia 76: 228-293.
Ballaré, C. L., Scopel, A. L. & Jordan, E. T. & Vierstra, R. D. 1994. Signaling among neighboring plants and the development of size inequalities in plant populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 10094-10098.
Casal, J. J. & Smith, H. 1989. The function, action and adaptive significance of phytochrome in light-grown plants. Plant, Cell Environment 12: 855-862.
Casal, J. J., Deregibus, V. A. & Sánchez, R. A. 1985. Variation in tiller dynamics and morphology in Lolium multiflorum Lam. Vegetative and reproductive plants as affected by differences in red/far-red irradiation. Ann. Bot. 56: 553-559.
Corré, W. J. 1983. Growth and morphogenesis of sun and shade plants II. The influence of light quality. Acta Bot. Neerl. 32: 185-202.
Deregibus, V. A., Sánchez, R. A., Casal, J. J. & Trlica, M. J. 1985. Tillering response to enrichment of red light beneath the canopy of humid natural grassland. J. Appl. Ecol. 22: 199-206.
Dixon W. J. 1992. BMDP statistical software manual. University of California Press, Berkeley.
Herben T., During H. J., Krahulec F. 1995. Spatiotemporal dynamics in mountain grasslands: species autocorrelations in space and time. Folia Geobot. Phytotax. 30: 185-196.
Herben T., Krahulec, F., Hadincová, V. & Pecháčková S. 1997. Fine-scale species interactions of clonal plants in a mountain grassland: a removal experiment. Oikos 78: 299-310.
Huber H. & Wiggerman L. 1997. Shade avoidance in the clonal herb Trifolium fragiferum: a field study with experimentally manipulated vegetation height. Plant Ecol. 130: 53-62.
Jackson, R. B. & Caldwell, M. M. 1992. Shading and the capture of localized soil nutrients: nutrient content, carbohydrates, and root uptake kinetics of a perennial tussock grass. Oecologia 91: 457-462.
Krahulec, F. 1990. Nardo-Agrostion communities in the Krkonoše andWest Carpathians Mts. Folia Geobot. Phytotax. 25: 337-347.
Leeflang L., During H. J. & Werger M. J. A. 1998 The role of petioles in light acquisition by Hydrocotyle vulgaris L. in a vertical light gradient. Oecologia 117: 235-238.
Mahdi, A. & Law, R. 1987. On the spatial organisation of plant species in a limestone grassland community. J. Ecol. 75: 459-476.
Mitchley, J. & Willems, J. H. 1995. Vertical canopy structure of Dutch chalk grasslands in relation to their management. Vegetatio 117: 17-27.
Molofsky, J. 1994. Population dynamics and pattern formation in theoretical populations. Ecology 75: 30-39.
Morgan, D. C. & Smith, H. 1979. A systematic relationship between phytochrome-controlled development and species habitat, for plants grown in simulated natural radiation. Planta 145: 253-258.
Murphy, J. S. & Briske, D. D. 1994. Density dependent regulation of ramet recruitment by the red:far red ratio of solar radiation: a field evaluation with the bunchgrass Schizachyrium scoparium. Oecologia 97: 462-469.
Palmer, M. W. & van der Maarel, E. 1995. Variance in species richness, species association and niche limitation. Oikos 73: 203-213.
Pearcy, R.W., Chazdon, R. L., Gross, L. J. &Mott, K. A. 1994. Photosynthetic utilization of sunflecks: a temporally patchy resource on a time scale of seconds to minutes. Pp. 175-208. In: Caldwell M. M. & Pearcy R. W. (eds),Exploitation of environmental heterogeneity by plants. Academic, San Diego.
Pecháčková, S. & Krahulec, F. 1995. Efficient nitrogen economy: key to the success of Polygonum bistorta in an abandoned mountain meadow. Folia Geobot. Phytotax. 30: 211-222.
Potvin, C. & Roff, D. A. 1993. Distribution free and robust statistical methods: viable alternatives to parametric statistics? Ecology 74: 1617-1628.
Ryel, J., Beyslag, W. & Caldwell, M. M. 1994. Light field heterogeneity among tussock grasses: theoretical considerations of light harvesting and seedling establishment in tussocks and uniform tiller distributions. Oecologia 98: 241-246.
Schmitt J. &Wulff R. D. 1993. Light spectral quality, phytochrome, and plant competition. Trends Ecol. Evol. 8: 47-51.
Silvertown, J. W., Prince, S. D. & Smith, B. A. 1989. A field portable instrument for mapping the microenvironment within grass canopies. Funct. Ecol. 2: 263-268.
Skálová H., Pecháčková S., Suzuki J., Herben T., Hara T., Hadincová V. & Krahulec F. 1997.Within population genetic differentiation in traits affecting clonal growth: Festuca rubra in a mountain grassland. J. Evol. Biol. 10: 383-406.
Skálová H. & Vosátka M. 1998. Growth response of three Festuca rubra clones to light quality and arbuscular mycorrhiza. Folia Geobot. 33: 159-170.
Smith, H. 1982. Light quality, photoperception, and plant strategy. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 33: 481-518.
Smith, H., Casal, J. J. & Jackson, G. M. 1990. Reflection signals and the perception by phytochrome of the proximity of neighbouring vegetation. Plant Cell Env. 13: 73-78.
Stark, J. M. 1994. Causes of soil nutrient heterogeneity at different scales. Pp. 255-284. In: Caldwell M. M. & Pearcy R. W. (eds), Exploitation of environmental heterogeneity by plants. Academic, San Diego.
Stone, L. & Ezrati, S. 1996. Chaos, cycles and spatiotemporal dynamics in plant ecology. J. Ecol. 84: 279-291.
Svensson, B. M., Floderus, B. & Callaghan, T. V. 1994. Lycopodium annotinum and light quality: growth responses under canopies of two Vaccinium species. Folia Geobot. Phytotax., 29: 159-166.
Tang, Y. &Washitani, I. 1995. Characteristics of small-scale heterogeneity in light availability within a Miscanthus sinensis canopy. Ecol. Res. 10: 189-197.
Tang, Y., Washitani, I. & Iwaki, H. 1992. Effects of microsite light availability on the survival and growth of oak seedlings within a grassland. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 105: 281-288.
ter Braak C. J. F. & Šmilauer P. 1998. CANOCO reference manual and User's guide to Canoco for Windows. Centre of Biometry Wageningen.
Thompson, L. & Harper, J. L. 1988. The effects of grasses in quality of transmitted radiation and its influence on growth of white clover Trifolium repens. Oecologia 75: 343-347.
Tutin, T. G. et al. 1964-1980. Flora Europaea. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Upton, G. J. G. & Fingleton, B. 1985. Spatial data analysis by example. Vol. I. Point pattern and quantitative data. Wiley & Sons, Chichester.
van der Hoeven, E. C., de Kroon, H. & During, H. J. 1990. Fine scale spatial distribution of leaves and shoots of two chalk grassland perennials. Vegetatio 86: 151-160.
van der Maarel, E. 1996. Pattern and process in the plant community: Fifty years after A.S. Watt. J. Veget. Sci. 7: 19-28.
Warren Wilson, J. 1963. Estimation of the foliage denseness and foliage angle by inclined point quadrats. Austr. J. Bot. 11: 95-105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skálová, H., Krahulec, F., During, H.J. et al. Grassland canopy composition and spatial heterogeneity in the light quality. Plant Ecology 143, 129–139 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009899803229
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009899803229