Abstract
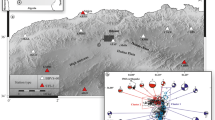
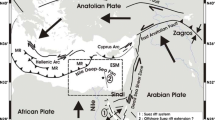
On 29–30 September 1996, an earthquake sequence occurred in the Füzesgyarmat region in eastern Hungary. The main shock had a magnitude of ML = 3.2 and was felt with a maximum intensity 4 MSK. It was preceded by a foreshock with a magnitude of ML = 2.8 and was followed, within six hours, by five aftershocks with magnitudes 2.1≤ML≤ 3.1. The dynamic source parameters of the Füzesgyarmat earthquake sequence have been derived from P-wave spectra of the Hungarian seismograph stations. The average of the obtained values at different stations shows that the main shock occurred on a fault length of 610 m, with relative displacement of 1.13 cm, stress drop of 7 bar and seismic moment of 3.96*1021 dyne.cm. The main shock was small to yield data for a full mechanism solution and no reliable single fault plane solution could be obtained due to the low signal to noise ratio at the recording stations. The parameters of the foreshock are fault length of 560m, seismic moment of 2.09*1021 dyne.cm, stress drop of 5.53 bar and relative displacement of 0.73 cm. The five aftershocks show source parameters similar to the foreshock stress drops (5.26≤ Δσ ≤ 5.76 bar), fault lengths (415 ≤L≤ 600 m), seismic moments (8.36*1020 ≤Mo ≤ 2.31*1021 dyne.cm) and relative displacements (0.52 ≤ ů ≤ 0.91 cm).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bada, G., Cloetingh, S., Gerner, P. and Horváth, F., 1998, Sources of recent tectonic stress in the Pannonian region: inferences from finite element modelling, Geophy. J. Int. 134, 87–101.
Badawy, A., 1995, Source parameters and tectonic implications of recent Sinai (Egypt) earthquakes, Acta Geod. Geoph. Hung. 30, 349–361.
Badawy, A. and Mónus, P., 1995, Dynamic source parameters of the 12thOctober 1992 earthquake, Cairo, Egypt, J. Geodynamics 20, 99–109.
Badawy, A., Horváth, F. and Tóth, L., 1998, Source parameters and tectonic interpretation of recent earthquakes (1995–1997) in the Pannonian basin, Tectonophysics (submitted).
Boatwright, J., 1980, A spectral theory of circular seismic sources: simple estimates of source dimension, dynamic stress drop and radiated seismic energy, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 70, 1–27.
Brune, J.B., 1970, Tectonic stress and spectra of seismic shear waves from earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 4997–5009.
Brune, J.B., 1971, Correction, J. Geophys. Res. 76, 5002.
Dövényi, P. and Horváth, F., 1988, A review of temperature, thermal conductivity and heat flow data from the Pannonian basin. In Royden, L. and Horváth, F. (eds), The Pannonian basin – A study in Basin Evolution, Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Mem. 45, 195–235.
Fletcher, J.B., 1980, Spectra from high-dynamic range digital recordings of Oroville, California, aftershocks and their source parameters, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 70, 735–755.
Gerner, P., Bada, G., Dövényi, P., Müller, B., Oncescu, M., Cloetingh, S. and Horváth, F., 1998, Recent tectonic stress and crustal deformation in and around Pannonain basin: data and models. In Durand, B., Jolivet, L., Horváth, F., and Séranne, M. (eds), The Mediterranean basins: Tertiary extension within the Alpine orogen. Integrated basins studies. 1 Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., London (in press).
Gibowicz, S.J., 1975, Variation of source properties: The Inangahua, New Zealand, aftershocks of 1968, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 65, 261–276.
Hanks, T. and Johnson, D.A., 1976, Geophysical assessment of peak accelerations, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 66, 959–968.
Hanks, T. and McGuire, R., 1981, The character of high-frequency strong ground motion, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 71, 2071–2095.
Horváth, F., 1995, Phases of compression during the evolution of the Pannonian basin and its bearing on hydrocarbon exploration, Mar. petrol. Geol. 12, 837–844.
Horváth, F. and Cloetingh, S., 1996, Stress-induced late stage subsidence anomalies in the Pannonian basin, Tectonophysics 266, 287–300.
Iio, Y., 1992, Seismic source spectrum of microearthquakes, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 82, 2391–2409.
Kanamori, H. and Anderson, D.L., 1975, Theoretical basis of some empirical relations in seismology, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 65, 1073–1095.
Kitaibel, P. and Tomtsányi, Á., 1814, Dissertatio de terrae motu in genere, ac in specie Mórensi anno 1810. die 14 januarii orto. Buda, Hungary.
Kulhánek, O., Van Eck, T., John, N., Meyer, K. and Wahlström, R., 1983, Spectra of the earthquake sequence February-March, 1981, in south-central Sweden, Tectonophysics 93, 337–350.
Lankreijer, A., 1998, Rheology and basement control on extensional basin evolution in central and eastern Europe: Variscan and Alpine-Carpathian-Pannonian tectonics. Ph.D. thesis Vrije University, Amsterdam.
Lankreijer, A., Mocanu, V. and Cloetingh, S., 1997, Lateral variations in lithosphere strength in the Romanian Carpathian: constraints on basin evolution, Tectonophysics 272, 269–290.
Marion, G.E., and Long, L.T., 1980, Microearthquake spectra in the southeastern United States, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 70, 1037–1054.
Quin, H., 1990, Dynamic stress drop and rupture of October 15, 1979 Imperial Valley, California, earthquake, Tectonphysics 175, 93–117.
Randall, M.J., 1973, The spectral theory of seismic sources, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 63, 1133–1144.
Scholz, C.H., 1990, The mechanics of earthquakes and faulting. Cambridge, 439 pp. Cambridge University press.
Thatcher, W. and Hanks, T.C., 1973, Source parameters of southern California earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res. 78, 8547–8576.
Tóth, L. and Mónus, P., 1997, The Microseismic Monitoring Network of the Paks NPP. In Seismic safety of the Paks Nuclear Power Plant, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, pp. 113–121.
Tóth, L., Mónus, P. and Zsiros, T., 1996, Hungarian earthquake bulletin, 1995. GeoRisk, Budapest, pp. 69.
Tóth, L., Mónus, P. and Zsiros, T., 1997, Hungarian earthquake bulletin, 1996. GeoRisk, Budapest, pp. 67.
Tóth, L., Mónus, P. and Zsiros, T., 1998, Hungarian earthquake bulletin, 1997. GeoRisk, Budapest, pp. 68.
Zsiros, T., Mónus, P. and Tóth, L., 1988, Hungarian Earthquake Cataloge (456–1986). Published by MTA GGKI, pp. 182.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badawy, A. P-wave spectra of the Füzesgyarmat, eastern Hungary earthquake sequence. Journal of Seismology 4, 49–58 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009878410608
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009878410608