Abstract
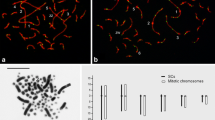
Giemsa-stained spread preparations and microspread preparations of Lemniscomys barbarus spermatocytes were made to investigate the meiotic behaviour of the peculiar sex chromosomes of this species. A typical sex vesicle is absent, as the X and Y chromosomes appear unfolded at zygotene and pachytene. In most cells, the sex chromosomes are associated at distal segments at metaphase I, probably as a consequence of a distal chiasma. The pairing segment is located in the heterochromatic regions of both sex chromosomes, which include silent ribosomal cistrons interspersed throughout the heterochromatin. This may suggest a possible involvement of ribosomal genes in both pairing and recombination processes. X–Y pairing proceeds beyond the pseudoautosomal region, thus involving heterologous segments of the differential regions, a fact that is clearly evident at the Y centromeric region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley T (1984) A re-examination of the case for homology between the X and Y chromosomes of mouse and man. Hum Genet 67: 372-377.
Ashley T (1985) Is crossover between the X and Y a regular feature of meiosis in mouse and man? Genetica 66: 161-167.
Ashley T, Moses MJ (1980) End association and segregation of the achiasmatic X and Y chromosomes of the sand rat Psammomys obesus. Chromosoma 78: 203-210.
Ashley T, Moses MJ, Solari AJ (1981) Fine structure and behaviour of a pericentric inversion in the sand rat, Psammomys obesus. J Cell Sci 50: 105-119.
Ashley T, Jaarola M, Fredga K (1989) Absence of synapsis during pachynema of the normal sized sex chromosomes of Microtus arvalis. Hereditas 111: 295-304.
Burgos M, Jiménez R, Olmos DM, Díaz de la Guardia R (1988) Heterogeneous heterochromatin and size variation in the sex chromosomes of Microtus cabrerae. Cytogenet Cell Genet 47: 75-79.
Burgoyne PS (1982) Genetic homology and crossing over in the X and Y chromosomes of mammals. Hum Genet 61: 85-90.
Carnero A, Jiménez R, Burgos M, Sánchez A, Díaz de la Guardia R (1991) Achiasmatic sex chromosomes in Pitymys duodecimcostatus: mechanisms of association and segregation. Cytogenet Cell Genet 56: 78-81.
Davisson MT, Poorman PA, Roderick TH, Moses MJ (1981) A pericentric inversion in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 30: 70-76.
de La Chapelle A, Tippett PA, Wetterstrand G, Page D (1984) Genetic evidence of X-Y interchange in a human XX male. Nature 307: 170-171.
Evans EP, Burtenshaw MD, Cattanach BM (1982) Meiotic crossing over between the X and Y chromosomes of male mice carrying the sex-reversing (Sxr) factor. Nature 300: 443-445.
Ford CE, Evans EP (1968) Meiotic preparations from mammalian testes. In: Benirschke K, ed. Comparative Mammalian Cytogenetics. Berlin: Springer Verlag, pp 461-464.
Fredga K, Santesson KB (1964) Male meiosis in Syrian, Chinese and European hamsters. Hereditas 52: 36-48.
Hayata I (1973) Chromosomal polymorphism caused by supernumerary chromosomes in the field mouse, Apodemus giliacus. Chromosoma 42: 403-414.
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36: 1014-1015.
Ishak B, Jaafar H, Maetz JL, Rumpler Y (1991) Absence of transcriptional activity of the B-chromosomes of Apodemus peninsulae during pachytene. Chromosoma 100: 278-281.
Jiménez R, Burgos M, Díaz de la Guardia R (1984) Meiotic behaviour of sex chromosomes and polymeiosis in three species of insectivores. Genetica 65: 187-192.
Jiménez R, Burgos M, Sánchez A, Díaz de la Guardia R (1990a) Synaptonemal complex analysis of spermatocytes of Talpa occidentalis (Insectivora, Mammalia): autosomal synapsis and substaging of zygonema and pachynema. Cytogenet Cell Genet 53: 97-102.
Jiménez R, Burgos M, Sánchez A, Díaz de la Guardia R (1990b) Synaptonemal complex analysis in Talpa occidentalis spermatocytes (Insectivora, Mammalia). II. Evolution of the X-chromosome self-pairing process. Cytogenet Cell Genet 54: 35-37.
Jiménez R, Carnero A, Burgo M, Sánchez A, Díaz de la Guardia R (1991) Achiasmatic giant sex chromosomes in the vole Microtus cabrerae (Rodentia, Microtidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 57: 56-58.
Kolomiets OL, Borbiev TE, Safronova LD, Borisov YM, Bogdanov YF (1988) Synaptonemal complex analysis of B-chromosome behavior in meiotic prophase I in the East-Asiatic mouse Apodemus peninsulae (Muridae, Rodentia). Cytogenet Cell Genet 48: 183-187.
McKee BD, Habera L, Vrana JA (1992) Evidence that intergenic spacer repeats of Drosophila melanogaster rRNA genes function as X-Y pairing sites in male meiosis, and a general model for achiasmatic pairing. Genetics 132: 529-544.
Moses MJ, Poorman PA (1981) Synaptosomal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements. II. Synaptic adjustment in a tandem duplication. Chromosoma 81: 519-535.
Moses MJ, Poorman PA, Roderick TH, Davisson MT (1982) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangement: IV. Synapsis and synaptic adjustment in two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma 84: 457-474.
Nanda I, Raman R (1981) Cytological similarity between the heterochromatin of the large X and Y chromosomes of the soft-furred field rat, Millardia meltada (family:Muridae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 30: 77-82.
Natarajan AT, Gropp A (1971) The meiotic behavior of autosomal heterochromatic segments in hedgehogs. Chromosoma 35: 143-152.
Nicklas RB (1961) Recurrent pole-to-pole movements of the sex chromosomes during prometaphase I in Melanopus differentialis spermatocytes. Chromosoma 12: 97-115.
Nicklas RB (1968) Chromosome segregation: an explanation of kinetochore reorientation. Genetics 60: 207-208.
Pogasianz HE (1970) Meiosis in the djungarian hamster. I. General pattern of male meiosis. Chromosoma 31: 392-404.
Polani PE (1982) Pairing of X and Y chromosomes, non-inactivation of X-linked genes and the maleness factor. Hum Genet 60: 207-211.
Pretel A, Díaz de la Guardia R (1978) Chromosomal polymorphism caused by a supernumerary chromosome in Rattus rattus ssp. frugivorus (Rafinesque, 1814) (Rodentia, Muridae). Experientia 34: 325-327.
Ratomponirina C, Viegas-Pequignot E, Petter F, Dutrillaux B, Rumpler Y (1989) Synaptonemal complex study in some species of Gerbillidae without heterochromatin interposition. Cytogenet Cell Genet 52: 23-7.
Ren X, Eisenhour L, Hong C, Lee Y, Mckee BD (1997) Roles of rDNA spacer and transcription unit-sequences in X-Y meiotic chromosome pairing in Drosophila melanogaster males. Chromosoma 106: 29-36.
Sharp P (1982) Sex chromosomes pairing during male meiosis in marsupials. Chromosoma 86: 27-47.
Solari AJ, Ashley T (1977) Ultrastructure and behavior of the achiasmatic, telosynaptic XY pair of the sand rat (Psammomys obesus). Chromosoma 62: 319-336.
Stitou S, Burgos M, Zurita F, Jiménez R, Sánchez A, Díz de la Guardia R (1997) Recent evolution of NOR-bearing and sex chromosomes of the North African rodent Lemniscomys barbarus. Chromosome Res 5: 481-485.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75: 304-306.
Wahrman J, Richler C, Neufeld E, Friedmann A (1983) The origin of multiple sex chromosomes in the gerbil Gerbillus gerbillus (Rodentia: Gerbillinae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 35: 161-80.
Wolf KW, Winking H, Fredga K (1987) Relationship between nucleoli and sex chromosomes during meiosis of the male wood lemming Myopus schisticolor: a fine structure study. Biol Cell 60: 15-24.
Wolf KW, Baumgart K, Winking H (1988) Meiotic association and segregation of the achiasmatic giant sex chromosomes in the male field vole (Microtus agrestis). Chromosoma 97: 124-133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stitou, S., Jiménez, R., Díaz de la Guardia, R. et al. Sex-chromosome pairing through heterochromatin in the African rodent Lemniscomys barbarus (Rodentia, Muridae). A synaptonemal complex study. Chromosome Res 8, 277–283 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009233825758
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009233825758