Abstract
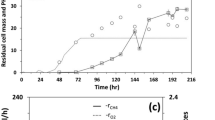
Influences of the control of glucose and oxygen concentrations on cell growth and poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) accumulation in Alcaligenes eutrophus were studied. Glucose affects both biosynthesis and glycolysis directly and the other pathways indirectly. PHB accumulation could also be stimulated under oxygen limitation conditions, but the final PHB content within the cells was less than in the case of nitrogen limitation. When the culture was shifted from the PHB accumulation state to balanced growth conditions, PHB degradation occurred in the cells. The cell growth was inhibited by high PHB content within the cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A.J. & Dawes, E.A. 1990 Occurrence, metabolism, meta-bolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiological Reviews 54, 450-472.
Blackklob, F. & Schlegel, H.G. 1968 Regulation of glucose-6-phospate dehydrogenase from Hydrogenomonas by ATP and reduced pyridine nucleotides. Archives of Microbiology 63, 177-196.
Doi, Y., Kunioka, M., Nakamura, Y. & Soga, K. 1987 Biosynthesis of copolyesters in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 from 13C-labelled acetate and propionate. Macromolecules 20, 2988-2991.
Doi, Y., Kawaguchi, Y. & Koyama, N. 1992 Synthesis and degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates in Alcaligenes cutrophus. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 103, 103-108.
Du, G.C., Chen, J. & Lun, S.Y. 1997 Study on fed-batch culture for the production of polyhydroxybutyrate with Alcaligenes eutrophus. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology 3, 371-374.
Du, G.C. 1997 Study on the biosynthesis of poly-α-hydroxyalkano-ates(PHAs) with Alcaligenes eutrophus. Ph.D. Dissertation. Wuxi University of Light Industry, Jiangsu, China.
Haywood, G.E., Anderson, A.J., Ewing, D.F. & Dawes, E.A. 1990 Accumulation of a polyhydroxyalkanoate containing primly 3-hydroxydecanoate from simple carbohydrate substrates by Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIMB 40135. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 56, 3354-3359.
Haywood, G.W., Anderson, A.J., Chu, J. & Dawes, E.A. 1988 Characterization of two 3-ketothiolases in the polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesizing organism Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiology Letters 52, 91-96.
Haywood, G.W., Anderson, A.J., Chu, J. & Dawes, E.A. 1988 The role of NADH-and NADPH-linked acetoacetyl-CoA reductases in the poly-3-hydroxyalkanoate synthesizing organism Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiology Letters 52, 259-264.
Heinzle, E. & Lafferty, R.M. 1980 A kinetic model for growth and synthesis of poly-3-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) from Alcaligenes eutrophus. European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 11, 8-16.
Ishihara, Y., Shimizu, H. & Shioya, S. 1996 Mole fraction control of poly(3-hydroxybutyric-co-3-hydroxyvaleric) acid in fed-batch culture of Alcaligenes eutrophus. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering 81, 422-428.
James, G.C. 1996 Metabolic modeling of growth and poly-±-hydroxy-butyrate(PHB) production in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Ph.D. Dissertation. California Institute of Technology, USA.
Mansfield, D.A., Anderson, A.J. & Naylor, L.A. 1995 Regulation of PHB metabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 41(Suppl. 1), 44-49.
Oeding, V. & Schlegel, H.G. 1973 ±-Ketothiolase from Hydrogenomonas eutrophus H16 and its significance in the regulation of poly-±-hydroxybutyric metabolism. Biochemical Journal 134, 239-248.
Peoples, O.P. & Sinskey, A.J. 1989 Poly-±-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) biosynthesis in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Identification and characterization of the PHB polymerase gene(phb C). Journal of Biological Chemistry 264, 15298-15303.
Peter, J.S. & Dawes, E.A. 1973 The regulation of poly-±-hydroxybutyrate metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochemical Journal 134, 225-238.
Riis, V. & Mai, W. 1988 Gas chromatographic determination of poly-±-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass after hydrochloric acid propanolysis. Journal of Chromatography 445, 285-289.
Schubert, P., Steinbuchel, A. & Schlegel, H.G. 1988 Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus genes for synthesis of poly-±-hydroxybutyric acid(PHB) and synthesis of PHB in E. coli. Journal of Bacteriology 170, 5837-5847.
Senior, P.J. & Dawes, E.A. 1971 Poly-±-hydroxybutyrate synthesis and the regulation of glucose metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochemical Journal 125, 55-66.
Shi, H.D. & Shiraishi, M.K. 1997 Metabolic flux analysis of poly(±-hydroxybutyric acid) in Alcaligenes eutrophus from various carbon sources. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering 84, 579-587.
Wilke, D. & Schlegel, H.G. 1975 Regulation of the pyruvate kinase from Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 in vitro and in vivo. Archives of Microbiology 105, 109-115.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, GC., Chen, J., Gao, HJ. et al. Effects of environmental conditions on cell growth and poly-β-hydroxybutyrate accumulation in Alcaligenes eutrophus. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 16, 9–13 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008922113483
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008922113483