Abstract
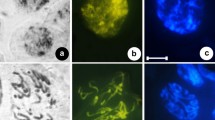
The Sicilian wild tetraploid oat Avena insularis is a close relative of A. magna and A. murphyi and is more plausible than either of these two species as the immediate tetraploid ancestor of A. sterilis and the other hexaploid oats. This report presents the C-banding karyotype of A. insularis. As in A. magna and A. murphyi, the chromosomal complement can be divided into two groups, one predominantly heterochromatic and the other predominantly euchromatic. The heterochromatic chromosome group of A. insularis consists of three pairs of metacentric and four pairs of submetacentric chromosomes. The euchromatic chromosome group consists of one pair of metacentric, five pairs of submetacentric, and one pair of subtelocentric chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum, B.R., 1977. Oats: Wild and Cultivated. A Monograph of the Genus Avena (Poaceae). Canada Dept. Agric. Supply and Service, Ottawa, Canada.
Fominaya, A., C. Vega & E. Ferrer, 1988. C-banding and nucleolar activity of tetraploid Avena species. Genome 30: 633–638.
Jellen, E.N. & B.S. Gill, 1995. C-banding variation in the Moroccan oat species Avena agadiriana (2n=4x=28). Theor. Appl. Genet. 92: 726–732.
Jellen, E.N., R.L. Phillips & H.W. Rines, 1993. C-banded karyotypes and polymorphisms in hexaploid oat accessions (Avena spp.) using Wright's stain. Genome 36: 1129–1137.
Jellen, E.N., B.S. Gill & T.S. Cox, 1994. Genomic in situ hybridization detects C-genome chromatin and intergenomic translocations in polyploid oat species (Genus Avena). Genome 37: 613–618.
Jellen, E.N., H.W. Rines, S.L. Fox, D.W. Davis, R.L. Phillips & B.S. Gill, 1997. Characterization of 'Sun II' oat monosomics through C-banding and identification of eight new 'Sun II' monosomics. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95: 1190–1195.
Ladizinsky, G., 1993. The taxonomic status of Avena magna: reappraisal. Lagascalia 17: 81–85.
Ladizinsky, G., 1998. A new species of Avena from Sicily, possibly the tetraploid progenitor of hexaploid oats. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 45: 263–269.
Ladizinsky, G., 1999. Cytogenetic relationships between Avena insularis (2n=28) and both A. strigosa (2n=14) and A. murphyi (2n=28). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 46: 501–504.
Leggett, J.M., H.M. Thomas, M.R. Meredith, M.W. Humphreys, W.G. Morgan, H. Thomas & I.P. King, 1994. Intergenomic translocations and the genomic composition of Avena maroccana Gdgr. revealed by FISH. Chromosome Res. 2: 163–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jellen, E., Ladizinsky, G. Giemsa C-banding in Avena insularis Ladizinsky. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 47, 227–230 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008769105071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008769105071