Abstract
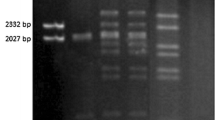
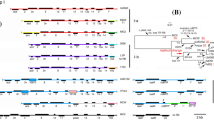
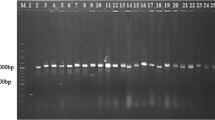
The fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora has been specifically and sensitively detected by PCR assays with primers derived from plasmid pEa29. The amplified fragment of approximately 1 kb can vary in length for individual strains, easily seen in a digest with restriction enzymes Sau3A or HpaII. DNA fragments from this variable region were cloned and DNA sequence analysis revealed short-sequence DNA repeat (SSR) motifs which were reiterated to various extents. The SSR units consisted of eight nucleotides (ATTACAGA), and terminated with ATTA which is part of an SSR. The shortest repetition consisted of four units and the longest one in Austrian E. amylovora strains was 15 units. The number of SSR units was remarkably stable during propagation of strains, but was occasionally changed when a strain was stressed by exposure to antibiotics, copper sulphate or storage at low temperature. Changes in the SSR number could be due to adjustment in bacterial fitness to environmental pressure. We designed oligonucleotide PCR primers from DNA sequences adjacent to the SSR region of pEA29 for rapid analysis of SSR length variations. With this PCR assay, more than 130 strains were classified into at least 11 types based on the number of repeats. E. amylovora strains isolated in Germany carried mostly six repeats in pEA29, which never changed under laboratory conditions. E. amylovora strains from Hungary and the Netherlands were quite divergent for the SSRs and further changes were sometimes observed after plating on agar medium. Homology search of nucleotide sequence data libraries revealed similarities of the SSR motif to partition functions of low copy number plasmids. Amino acid homology searches showed similarity of the deduced amino acid sequence in the ORF adjacent to the SSR motif to replication proteins of plasmids. The SSR may play a role in regulation of plasmid replication and partition as assumed for iterons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bereswill S, Pahl A, Bellemann P, Zeller W and Geider K (1992) Sensitive and species-specific detection of Erwinia amylovora by polymerase chain reaction analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 3522-3526
Bereswill S, Bugert P, Bruchmüller I and Geider K (1995) Identification of Erwinia amylovora by PCR with chromosomal DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 61: 2636-2642
Bereswill S, Jock S, Aldridge P, Janse JD and Geider K (1997) Molecular characterization of natural Erwinia amylovora strains deficient in levan synthesis. Phys Mol Plant Pathol 51: 215-225
Bereswill S, Jock S, Bellemann P and Geider K (1998) Identification of Erwinia amylovora by growth morphology on agar containing copper sulfate and by capsule staining with lectin. Plant Dis 82: 158-164
Bramhill D and Kornberg A (1988) Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell 52: 743-755
Brendler TG, Abeles AL, Reaves LD and Austin SJ (1997) The iteron bases and spacers of the P1 replication origin contain information that specifies the formation of a complex structure involved in initiation. Mol Microbiol 23: 559-567
Falkenstein H, Bellemann P, Walter S, Zeller W and Geider K (1988) Identification of Erwinia amylovora, the fireblight pathogen, by colony hybridization with DNA from plasmid pEA29. Appl Environ Microbiol 54: 2798-2802
Filutowicz M, Dellis S, Levchenko I, Urh M, Wu F and York D (1994) Regulation of replication of an iteron-containing DNA molecule. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Bio 48: 239-273
Fu J-F, Chang H-C, Chen Y-M, Chang Y-S and Liu S-T (1996) Characterization of the replicon of plasmid pSW500 of Erwinia stewartii. Mol Gen Genet 250: 699-704
Gallie DR and Kado CI (1987) Agrobacterium tumefaciens pTAR parA promoter region involved in autoregulation, incompatibility and plasmid partitioning. J Mol Biol 193: 465-478
Jorgensen R, Snyder C and Jones JDG (1987) T-DNA is organized predominantly in inverted repeat structures in plants transformed with Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 derivatives. Mol Gen Genet 207: 471-477
Lecomte P, Manceau C, Paulin J-P and Keck M (1997) Identification by PCR analysis on plasmid pEa29 of isolates of Erwinia amylovora responsible of an outbreak in Central Europe. Eur J Plant Pathol 103: 91-98
McManus PS and Jones AL (1995) Detection of Erwinia amylovora by nested PCR and PCR-dot-blot and reverse-blot hybridizations. Phytopathology 85: 618-623
Nevill-Manning CG, Wu TD and Brutlag DL (1998) Highly specific protein sequence motifs for genome analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 5865-5871
Strand S, Prolla TA, Liskay RM and Petes TD (1993) Destabilization of tracts of simple repetitive DNA in yeast by mutations affecting DNA mismatch repair. Nature 365: 274-276
Van Belkum A, Scherer S, van Alphen L and Verbrugh H (1998) Short-sequence DNA repeats in prokaryotic genomes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62: 275-293
Van der Zwet T (1996) Present worldwide distribution of fire blight. Acta Horticulture 411: 7-8
Van der Zwet T and Keil HL (1979) Fire blight: a bacterial disease of rosaceous plants. Agriculture handbook No. 510. U.S. Government printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Zhang Y and Geider K (1997) Differentiation of Erwinia amylovora strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 4421-4426
Zhang Y, Merighi M, Bazzi C and Geider K (1998) Genomic analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Erwinia amylovora strains from the Mediterranean region including Italy. J Plant Pathol 80: 225-232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, WS., Geider, K. Analysis of Variable Short-sequence DNA Repeats on the 29 kb Plasmid of Erwinia amylovora Strains. European Journal of Plant Pathology 105, 703–713 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008723717211
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008723717211