Abstract
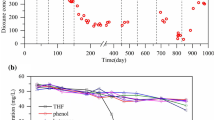
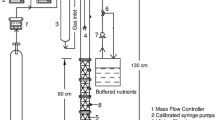
Upon inoculation with Hyphomicrobium MS3, theelimination capacity of a lab-scale biofilter for theodorant dimethyl sulfide (Me2S) can be stronglyincreased from less than 10 to more than 35 and 1000 gm-3d-1 using wood bark and compost as acarrier material, respectively. However, uponsupplementation of isobutyraldehyde (IBA) as a secondgaseous substrate, sequential degradation profiles of IBAand Me2S in physically separated sections wereobserved in the Hyphomicrobium MS3-inoculatedwood bark and compost biofilters. Contrary to this, thebiofiltration efficiency for Me2S remainedunaffected upon the supplementation of toluene as asecond gaseous substrate. Batch experiments with theliquid Hyphomicrobium MS3 culture confirmed thecompetitive effect of IBA on the Me2S degradingactivity: in the presence of both compounds, Hyphomicrobium MS3 preferred degradation of thecarbonyl compound. In technical terms, this means thatthe complete purification of a waste gas stream containingboth IBA and Me2S should be performed usingsufficiently high or bistage HyphomicrobiumMS3-inoculated biofilters. Design criteria have to beconceived in this respect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bally M, Wilberg E, K¨uhni M & Egli T (1994) Growth and regulation of enzyme synthesis in the nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA)-degrading bacterium Chelatobacter heintziiATCC 29600. Microbiology 140: 1927–1936
Bendinger B (1992) Microbiology of biofilters for the treatment of animal-rendering plant emissions: occurrence, identification and properties of isolated Coryneformbacteria. PhD Thesis, Universit ¨at Osnabruck, Germany
Bremner JM & Bundy LG (1974) Inhibition of nitrification in soils by volatile sulfur compounds. Soil Biol. Biochem. 6: 161–165
Cho K-S, Hirai M & Shoda M (1991) Degradation characteristics of hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol, dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide by Thiobacillus thioparusDW44 isolated from peat biofilter. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 71: 384–389
Chiou CT & Kile DE (1994) Effects of polar and nonpolar groups on the solubility of organic compounds in soil organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 28: 1139–1144
DeshussesMA, Hamer G & Dunn IJ (1995) Behavior of biofilters for waste air biotreatment. 2. Experimental evaluation of a dynamic model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29: 1059–1068
De Zwart JMM & Kuenen JG (1992) C1-cycle of sulfur compounds. Biodegradation 3: 37–59
Goldstein RM, Mallory LM & Alexander M (1985) Reasons for possible failure of inoculation to enhance biodegradation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 50: 977–983
Juliette LY, Hyman MR & Arp DJ (1993) Inhibition of ammonia oxidation in Nitrosomonas europaeaby sulfur compounds: thioethers are oxidized to sulfoxides by ammonia monooxygenase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 3718–3727
Robertson LA, VanNiel EWJ, TorremansRAM & Kuenen JG (1988) Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in aerobic chemostat cultures of Thiosphaera pantotropha. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 2812–2818
Smet E, Chasaya G, Van Langenhove H & Verstraete W (1996a) The effect of inoculation and the type of carrier material used on the biofiltration of methyl sulphides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45: 293–298
Smet E, Van Langenhove H & Verstraete W (1996b) Long term stability of a biofilter treating dimethyl sulphide. Appl.Microbiol. Biotechnol. 46: 191–196
Van Groenestijn JW & Hesselink PGM (1993) Biotechniques for air pollution control. Biodegradation 4: 283–301
Van Langenhove H, Bendinger B, Oberth¨ur R & Schamp N (1991) Organic sulfur compounds: persistent odourants in the biological treatment of complex waste gases. In: Dragt AJ & Van Ham J (Eds)Biotechniques for Air Pollution Abatement and OdourControl Policies, Proceedings of an International Symposium, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 27-29 October 1991 (pp 177–1982).
Elsevier, Amsterdam Van Langenhove H, LootensA & Schamp N(1989) Inhibitory effects of SO2 on biofiltration of aldehydes.Water, Air and Soil Pollution 47: 81–86
Weber F (1995) Toluene: biological waste-gas treatment, toxicity and microbial adaptation. PhD Thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, The Netherlands
Weckhuysen B, VriensL & Verachtert H (1993) The effect of nutrient supplementation on the biofiltration of butanal in contaminated air. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39: 395–399
Zhang L, Hirai M & Shoda M (1991) Removal characteristics of dimethyl sulfide, methanethiol and hydrogen sulfide by Hyphomicrobiumsp. I55 isolated from peat biofilter. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 72: 392–396
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smet, E., Van Langenhove, H. & Verstraete, W. Isobutyraldehyde as a competitor of the dimethyl sulfide degrading activity in biofilters. Biodegradation 8, 53–59 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008201412862
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008201412862