Abstract
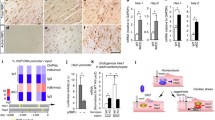
Tissue hypoxia has been identified as being a particularly important stimulus for triggering angiogenesis. Here we report early effects of hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) on the protein expression profiles and localization patterns of the VEGF and Angiopoietin-Tie systems in adult rat myocardium. Western blot as well as immunohistochemical analyses were performed on hearts obtained from rats exposed to various durations of in vivo systemic hypoxemic hypoxia followed by 24 h reoxygenation. The relative time course of protein expression in response to increasing durations of hypoxia, as indicated from our experiments, seems to suggest the involvement of the VEGF system and the Ang-Tie system in early angiogenesis. An apparent relationship between the expression profiles of Flk-1 and Ang-2 was observed. The most significant and interesting relationship which came to light was the surprisingly coincident yet opposite temporal trends between Ang-1 and Ang-2 protein levels. In the 1 h hypoxia group, there was significant induction of Ang-2 expression (31.3% compared to its baseline control) in contrast to relatively mild Ang-1 expression (23.8% compared to its baseline control). Thereafter Ang-1 displayed a progressive increase in expression, parallel to a progressive decrease in Ang-2 expression, becoming most pronounced in the 4 h hypoxia group (Ang-1, 50% and Ang-2, 12.6% compared to respective baseline control values). This suggests that despite their being antagonists at the receptor level, regulation of Ang-1 and Ang-2 protein levels in response to hypoxia runs much deeper and seems to indicate modulatory control at the transcriptional and/or translational level. Two additional groups of rats were sacrificed 7 days after 4 h hypoxia + 24 h reoxygenation, or after a 28 h period of time-matched normoxia. Left ventricular tissue sections were used to determine capillary density (CD) by using anti-CD31 immunohistochemistry and computer-assisted morphometry. CD was significantly increased in the 4 h hypoxia group compared to control (1814 ± 56 vs. 1642 ± 43 counts/mm2) confirming that modulation of angiogenic factors and their receptors by H/R is capable of stimulating capillary proliferation in the myocardium. Our study presents the first evidence for the Ang-Tie system's involvement in early stages of myocardial angiogenesis along with the VEGF-Flk-1-Flt-1 system. The stimulation of myocardial angiogenesis by H/R may constitute a potential basis for a possible more long-lived adaptive response to stress afforded by preconditioning stimuli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeVries C, Escobedo JA, Veno H, Houck K, Ferrara N, Williams LT: The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science 255: 989-991, 1992
Millauer B, Shawver LK, Plate KH, Risau W, Ullrich A: Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature 367: 576-579, 1994
Witzenbichler B, Maisonpierre PC, Jones P, Yancopoulos GD, Isner JM: Chemotactic properties of angiopoietin-1 and-2, ligands for the endothelial-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie-2. J Biol Chem 273: 18514-18521, 1998
Kuo N, Benhayon D, Przybylski RJ, Martin RJ, LaManna JC: Prolonged hypoxia increases vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA and protein in adult mouse brain. J Appl Physiol 86: 260-264, 1999
Ladoux A, Frelin C: Hypoxia is a strong inducer of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression in the heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 195: 1005-1010, 1993
Minchenko A, Bauer T, Salceda S, Caro J: Hypoxic stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vitro and in vivo. Lab Invest 71: 374-379, 1994
Tuder RM, Voelkel NF, Flook BE: Increased gene expression for VEGF and the VEGF receptors KDR/Flk and Flt in lungs exposed to acute or to chronic hypoxia. Modulation of gene expression by nitric oxide. J Clin Invest 95: 1798-1807, 1995
Banai S, Shweiki D, Pinson A, Chandra M, Lazarovici G, Keshet E: Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression induced by myocardial ischemia: Implications for coronary angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 28: 1176-1179, 1994
Hashimoto E, Ogita T, Nakaoka T, Matsuoka R, Takao A, Kira Y: Rapid induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by transient ischemia in the rat heart. Am J Physiol 267: H1948-H1954, 1994
Li J, Brown LF, Hibberd MG, Grossman JD, Morgan JP, Simons M: VEGF, flk-1, and flt-1 expression in a rat myocardial infarction model of angiogenesis. Am J Physiol 270: H1803-H1811, 1996
Folkman J, Merler E, Abernathy C, Williams GJ: Isolation of a tumor factor responsible or angiogenesis. Exp Med 133: 275-288, 1971
Gozal E, Simakajornboon N, Gozal D: NF-κB induction during in vivo hypoxia in dorsocaudal brain stem of rat: Effect of MK-801 and LNAME. J Appl Physiol 85: 372-376, 1998
Preedy VR, Sugden PH: The effects of fasting and hypoxia on rates of protein synthesis in vivo in subcellular fractions of rat heart and gastrocnemius muscle. Biochem J 257: 519-527, 1989
Shima DT, Adams AP, Ferrara N, Yeo KT, Yeo TK, Allende R, Folkman J, D'Amore PA: Hypoxic induction of endothelial cell growth factors in retinal cells: Identification and characterization of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as the mitogen. Mol Med 1: 182-193, 1995
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E: Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogensin. Nature 359: 843-845, 1992
Marti H, Risau W: Systemic hypoxia changes the organ-specific distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15809-15814, 1998
Sandner P, Gess B, Wolf K, Kurtz A: Divergent regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vitro and in vivo. Lab Invest 71: 374-379, 1994
Dumont DJ, Fong GH, Puri MC, Gradwohl G, Alitalo K, Breitman ML: Vascularization of the mouse embryo: A study of flk-1, tek, tie and vascular endothelial growth factor expression during development. Dev Dyn 203: 80-92, 1995
Sato TN, Tozawa Y, Deutsch U, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fujiwara Y, Gendron-Maguire M, Gridley T, Wolburg H, Risau W, Qin Y: Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases tie-1 and tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature 376: 70-74, 1995
Davis S: Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell 87: 1161-1169, 1996
Mandriota SJ, Pepper MS: Regulation of angiopoietin-2 mRNA levels in bovine microvascular endothelial cells by cytokines and hypoxia. Circ Res 83: 852-859, 1998
Oh H, Takagi H, Suzuma K, Otani A, Matsumura M, Honda YJ: Biol Chem 274: 15732-15739, 1999
Wang H, Keiser JA: Vascular endothelial growth factor upregulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinases in vascular smooth muscle cells. Role of Flt-1. Circ Res 83: 832-840, 1998
Yabkowitz R, Meyer S, Black T, Elliott G, Merewether LA, Yamane HK: Inflammatory cytokines and vascular endothelial growth factor stimulate the release of soluble tie receptor from human endothelial cells via metalloproteinase activation. Blood 93: 1969-1979, 1999
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD: Requisite role of Angiopoietin-1, a ligand of the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 87: 1171-1180, 1996
Papapetropoulos A, Garcia-Cardena G, Dengler TJ, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD, Sessa WC: Direct actions of angiopoietin-1 on human endothelium: Evidence for network stabilization, cell survival, and interaction with other angiogenic growth factors. Lab Invest 79: 213-223, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, P.S., Estrada-Hernandez, T., Sasaki, H. et al. Early effects of hypoxia/reoxygenation on VEGF, Ang-1, Ang-2 and their receptors in the rat myocardium: Implications for myocardial angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 213, 145–153 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007180518474
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007180518474