Abstract
1. Changes in the phosphorylation state of AMPA-type glutamate receptors are thought to underlie activity-dependent synaptic modification. It has been established that the GluR1 subunit is phosphorylated on two distinct sites, Ser-831 and Ser-845, by CaMKII and by PKA, respectively, and that phosphorylation by either kinase correlates with an increase in the AMPA receptor-mediated current. GluR1 is concentrated in postsynaptic densities and it is expected that this particular receptor pool is involved in synaptic modification. The present study describes the regulation of the phosphorylation state of GluR1 in isolated postsynaptic densities.
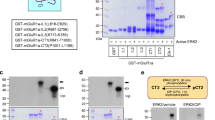
2. Addition of Ca2+/calmodulin to the postsynaptic density fraction promotes phosphorylation of GluR1, and under these conditions, dephosphorylation is prevented by the inclusion of phosphatase type 1 inhibitors, microcystin-LR and Inhibitor-1. CaMKII and phosphatase type 1 are also found to be enriched in the PSD fraction compared to the parent fractions.
3. On the other hand, the addition of cAMP, either by itself or with exogenous PKA, does not change the phosphorylation state of GluR1. Prior incubation of PSDs under dephosphorylating conditions results in only a small PKA-mediated phosphorylation of GluR1.
4. These results support the hypothesis that PSDs contain the molecular machinery to promote the phosphorylation as well as the dephosphorylation of GluR1 on Ser-831, while Ser-845, the site phosphorylated by PKA, appears to be mostly occluded. Thus, it is possible that a large pool of PSD-associated GluR1 is regulated through modification of the phosphorylation state of the Ser-831 site only.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Barria, A., Derkach, V., and Soderling, T. R. (1997a). Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the ?-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl1-4-isoxazolepropionate type glutamate receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272:32727-32730.
Barria, A., Muller, D., Derkach, V., Griffith, L. C., and Soderling, T. R. (1997b). Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation.Science 276:2042-2045.
Benke, T. A., Luthi, A., Issac, J. T. R., and Collingridge, G. L. (1998). Modulation of AMPA receptor unitary conductance by synaptic activity. Nature 393:793.
Blackstone, C., Murphy, T. H., Moss, S. J., Baraban, J. M., and Huganir, R. L. (1994). Cyclic AMP and synaptic activity-dependent phosphorylation of AMPA-preferring glutamate receptors. J. Neurosci. 14:7585-7593.
Derkach, V., Barria, A., and Soderling, T. R. (1999). Ca2+/calmodulin-kinase II enhances channel conductance of ?-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl1-4-isoxazole-propionate type glutamate receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:3269-3274.
Dosemeci, A., and Reese, T. S. (1993). Inhibition of endogenous phosphatase in a postsynaptic density fraction allows extensive phosphorylation of the major postsynaptic density protein. J. Neurochem. 61:550-555.
Hayashi, Y., Ishida, A., Katagiri, H., Mishina, M., Fujisawa, H., Manabe, T., and Takahashi, T. (1997). Calcium-and calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of AMPA type glutamate receptor subunits by endogenous protein kinases in the post-synaptic density. Mol. Brain Res. 46:338-342.
Hemmings, H. C., Girault, J.-A., Nairn, A. C., Bertuzzi, G., and Greengard, P. (1992). Distribution of protein phosphatase Inhibitor-1 in brain and peripheral tissue of various species: Comparison with DARPP-32. J. Neuochem. 59:1053-1061.
Hollmann, M., and Heinemann, S. (1994). Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17:31-108.
Kameyama, K., Lee, H-.K., Bear, M. F., and Huganir, R. F. (1998). Involvement of a postsynaptic protein kinase A substrate in the expression of homosynaptic long-term depression. Neuron 21:1163-1175.
Kirkwood, A., Dudek, S. M., Gold, J. T., Aizenman, C. D., and Bear, M. F. (1993). Common forms of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus and neocortex in vitro. Science 260:1518-1521.
Kornau, H.-C., Schenker, L. T., Kennedy, M. B., and Seeburg, P. H. (1995). Domain interactions between NMDA receptor subunits and the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95. Science 269:1737-1740.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680-685.
Lee, H-.K., Kameyama, K., Huganir, R. F., and Bear, M. F. (1998). NMDA induces long-term synaptic depression and dephosphorylation of the GluR1 subunit of AMPA receptors in hippocampus. Neuron 21:1151-1162.
Lledo, P.-M., Hjelmstad, G. O., Mukherji, S., Soderling, T. R., Malenka, R. C., and Nicoll, R. A. (1995). Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II and long-term potentiation enhance synaptic transmission by the same mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:11175-11179.
Lowenstein, P. R., Shering, A. F., MacDougall, L. K., and Cohen, P. (1995). Immunolocalization of protein phosphatase Inhibitor-1 in the cerebral cortex of the rat, cat, and ferret. Brain Res. 679:80-92.
MacKintosh, C., Beattie, K. A., Klumpp, S., Cohen, P., and Codd, G. A. (1990). Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of proteins phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 264:187-192.
Malenka, R., Kauer, J., Perkel, D., Mauk, M., Kelly, P., Nicoll, R., and Waxham, M. (1989). An essential role for postsynaptic calmodulin and protein kinase activity in long-term potentiation. Nature 340:554-557.
Mammem, A. L., Kameyama, K., Roche, K. W., and Huganir, R. L. (1997). Phosphorylation of the ?-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor GluR1 subunit by calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 272:32528-32533.
McGlade-McCulloh, E., Yamamoto, H., Tan, S.-E., Brickery, D. A., and Soderling, T. R. (1993). Phosphorylation and regulation of glutamate receptors by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Nature 362:640-642.
Mulkey, R. M., Herron, C. E., and Malenka, R. C. (1993). An essential role for protein phosphatases in hippocampal long-term depression. Science 261:1051-1055.
Mulkey, R. M., Endo, S., Shenolikar, S., and Malenka, R. C. (1994). Involvement of a calcineurin/ Inhibitor-1 phosphatase cascade in hippocampal long-term depression. Nature 369:486-488.
Peterson, G. L. (1977). A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal. Biochem. 83:346-356.
Roche, K. W., O'Brien, R. J., Mammen, A. L., Bernhardt, J., and Huganir, R. L. (1996). Characterization of multiple phosphorylation sites on the AMPA receptor GluR1 Subunit. Neuron 16:1179-1188.
Shenolikar, S., and Nairn, A. C. (1991). Protein phosphatases: Recent progress. Adv. Sec. Mess. Phosphoprot. Res. 23:1-121.
Strack, S., Barban, M. A., Wadzinski, B. E., and Colbran, R. J. (1997). Differential inactivation of postsynaptic density-associated and soluble Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by protein phosphatases 1 and 2A. J. Neurochem. 68:2119-2128.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., and Gordon, J. (1979). Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:4350-4354.
Wenthold, R. J., Yokotani, N., Doi, and Wada, K. (1992). Immunochemical characterization of the non-NMDA glutamate receptor using subunit-specific antibodies: Evidence for a hetero-oligomeric structure in rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 267:501-507.
Westbrook, G. L. (1994). Glutamate receptor update. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 4:337-346.
Yan, Z., Wilson, L. H., Feng, J., Tomizawa, K., Allen, P. B., Fienberg, A. A., Nairn, A. C., and Greengard, P. (1999). Protein phosphatase 1modulation of neostriatalAMPAchannels: Regulation by DARPP-32 and spinophilin. Nature Neurosci. 2:13-17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinade, L., Dosemeci, A. Regulation of the Phosphorylation State of the AMPA Receptor GluR1 Subunit in the Postsynaptic Density. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20, 451–463 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007019030595
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007019030595