Abstract
SUMMARY
1. In vivo 1H and 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques were applied to reveal biochemical changes in the rat brain caused by prolonged ethanol consumption.
2. Three models of ethanol intoxication were used.
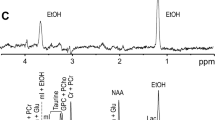
3. 1H MRS showed a significant decrease in the concentration of myo-inositol in the brain of rats fed with 20% ethanol for 8 weeks. This change is consistent with perturbances in astrocytes. On the other hand, N-acetyl aspartate and choline content did not differ from controls.
4. 31P MRS did not reveal any significant changes in the high-energy phosphates or intracellular free Mg2+ content in the brain of rats after 14 weeks of 20% ethanol drinking. The intracellular pH was diminished.
5. By means of a 31P saturation transfer technique, a significant decrease was observed for the pseudo first-order rate constant k for of the creatine kinase reaction in the brain of rats administered 30% ethanol for 3 weeks using a gastric tube.
6. The 1H MRS results may indicate that myo-inositol loss, reflecting a disorder in astrocytes, might be one of the first changes associated with alcoholism, which could be detected in the brain by means of in vivo 1H MRS.
7. The results from 31P MRS experiments suggest that alcoholism is associated with decreased brain energy metabolism.
8. 31P saturation transfer, which provides insight into the turnover of high-energy phosphates, could be a more suitable technique for studying the brain energetics in chronic pathological states than conventional 31P MRS.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bondy, S. C., and Guo, S. X. (1995). Regional selectivity in ethanol-induced prooxidant events within the brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 49:69-72.
Chutkow, J. G. (1990). Magnesium and the central (intra-dural) nervous system:Metabolism, neurophysiological functions, and clinical disorders. In Sigel, H., and Sigel, A. (eds.), Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Vol. 26: Compendium on Magnesium and Its Role in Biology, Nutrition and Physiology. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 441-461.
Clark, J. F., Harris, G. I., and Dillon, P. F. (1991). Multisite saturation transfer using DANTE and continuous wave. Magn. Reson. Med. 17:274-278.
Denays, R., Chao, S. L., Mathur-Devré, R., Jeghers, O., Fruhling, J., Noel, P., and Ham, H. R. (1993). Metabolic changes in the rat brain after acute and chronic ethanol intoxication: A 31PNMR spectroscopy study. Magn. Reson. Med. 29:719-723.
Fein, G., Meyerhoff, D. J., Di Sclafani, V., Ezekiel, F., Poole, N., Mackay, S., Dillon, W. P., Constans, J. M., and Weiner, M. V. (1994). 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging separates neuronal from glial changes in alcohol-related brain atrophy. In Alcohol and Glial Cells, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, pp. 227-241.
Frahm, J., Merboldt, K. D., and Hanicke, W. (1987). Localized proton spectroscopy using stimulated echoes. J. Magn. Reson. 72:502-508.
Geissler, A., Lock, G., Frund, R., Held, P., Hollerbach, S., Andus, T., Scholmerich, J., Feuerbach, S., and Holstege, A. (1997). Cerebral abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis detected by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging. Hepatology 25:48-54.
Govindaraju, V., Meyerhoff, D. J., Maudsley, A. A., Vermathen, M., and Weiner, M. W. (1997). Effects of brain membranes on 1H nuclear magnetic resonance signal intensity of ethanol in vitro. Alcohol Alcoholism 32:671-681.
Gvozdjáková, A., Kucharská, J., Braunová, Z., and Gvozdják, J. (1999). Chronic effect of ethanol decreases the level of coenzyme Q and vitamin E: An experimental study. Physiol. Res. 48:5P.
Harper, C., and Kril, J. (1989). Patterns of neuronal loss in the cerebral cortex in chronic alcoholic patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 92:81-89.
Häussinger, D., Laubenberger, J., vom Dahl, S., Ernst, T., Bayer, S., Langer, M., Gerok, W., and Hennig, J. (1994). Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies on human brain myo-inositol in hypoosmolarity and hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 107:1475-1480.
Jagannathan, N. R., Desai, N. G., and Raghunathan, P. (1996). Brain metabolite changes in alcoholism: An in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 14:553-557.
Jelicks, L. A., and Gupta, R. K. (1992). 31P-NMR of high energy phosphates in perfused rat heart during metabolic acidosis. Am. J. Physiol. 263(Heart Circ. Physiol. 32):H903-H909.
Krik, K., and Strange, K. (1998). Functional properties and physiological roles of organic solute channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 60:719-739.
Kril, J. J., Halliday, G. M., Svoboda, M. D., and Cartwright, H. (1997). The cerebral cortex is damaged in chronic alcoholics. Neuroscience 79:983-998.
Langleben, D., Bloomer, C., Fein, G., and Meyerhoff, D. J. (1998). Evidence of neuronal damage in the midbrain of chronic heavy drinkers. In Proc. ISMQM, p. 1716.
Lin, T.-I., and Morales, M. F. (1977). Application of one-step procedure for measuring inorganic phosphate in the presence of proteins: The actomyosin ATPase system. Analyt. Biochem. 77:10-16.
Martin, P. R., Gibbs, S. J., Nimmerrichter, A. A., Riddle, W. R., Welch, L. W., and Willcott, M. R. (1995). Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in recently abstinent alcoholics. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 19:1078-1082.
Mendelson, J. H., Ogata, M., and Mello, N. K. (1969). Effects of alcohol ingestion and withdrawal on magnesium status of alcoholics: Clinical and experimental findings. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 162:918-933.
Mierisová, Š., van den Boogaart, A., Tkáč, I., Van Hecke, P., Vanhamme, L., and Liptaj, T. (1998). A new approach for quantification of in vivo 1H MR spectra of brain using AMARES. NMR Biomed. 11:32-39.
Mlynárik, V., Kašparová, S., Liptaj, T., Dobrota, D., Horecký, J., and Belan, V. (1998). Creatine kinase reaction rates in rat brain during chronic ischemia. MAGMA 7:162-165.
Morris, G. A., and Freeman, R. (1978). Selective excitation in Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Magn. Reson. 29:433-462.
Mullins, P. G., and Vink, R. (1995). Chronic alcohol exposure decreases brain intracellular free magnesium concentration in rats. Neuroreport 6:1633-1636.
Pijnappel, W. W. F., van den Boogaart, A., de Beer, R., and van Ormondt, D. (1992). SVD-based quantification of magnetic resonance signals. J. Magn. Reson. 97:122-134.
Ross, B. D., Danielsen, E. R., and Bluml, S. (1996). Proton magnetic resonance spectoscopy: The new gold standard for diagnosis of clinical and subclinical hepatic encephalopathy? Digestive Diseases 14(Suppl 1):30-39.
Sauter, A., and Rudin, M. (1993). Determination of creatine kinase kinetic parameters in rat brain by NMR magnetisation transfer. Correlation with brain function. J. Biol. Chem. 268:13166-13171.
van den Boogaart, A., ALA-Korpela, M., Jokissari, J., and Griffiths, J. R. (1994). Time and frequency domain analysis of NMR data compared: An application to 1D 1H spectra of lipoproteins. Magn. Reson. Med. 31:347-358.
van der Veen, J. W. C., de Beer, R., Luyten, P. R., and van Ormondt, D. (1988). Accurate quantification of in vivo 31P NMR signals using the variable projection method and prior knowledge. Magn. Reson. Med. 6:92-98.
Vanhamme, L., van den Boogaart, A., and Van Huffel, S. (1997). Improved method for accurate and efficient quantification of MRS data with the use of prior knowledge. J. Magn. Reson. 129:35-43.
Wallimann, T., Doler, M., Schlattner, U., Eder, M., Hornemann, T., Kraft T., and Stolz, M. (1998). Creatine kinase: An enzyme with central role in cellular energy metabolism. MAGMA 6:116-119.
Zimatkin, S. M., and Karpuk, I. G. (1994). Regional and cellular distribution of mitochondrial high-affinity aldehyde dehydrogenase in the rat brain (an immunocytochemical study). Morfologiia 106:83-91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braunová, Z., Kašparová, S., Mlynárik, V. et al. Metabolic Changes in Rat Brain After Prolonged Ethanol Consumption Measured by 1H and 31P MRS Experiments. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20, 703–715 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007002925592
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007002925592