Abstract
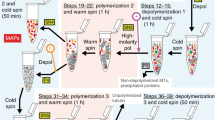
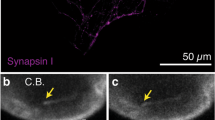
Brain microtubule dynamics were studied by video-enhanced differential interference contrast microscopy in a cytosolic extract from fetal rat brain, prepared under conditions designed to produce minimal alterations in microtubule stability. With urchin sperm axoneme fragments as nucleation seeds, the extract was shown to support cellular-like microtubule dynamics. Microtubules elongated from one end of the axonemes, and did not spontaneously self-assemble in the absence of axonemes. The following microtubule kinetic parameters were measured in the extract: velocity of elongation (8.1 mm/min), velocity of rapid shortening (5.8 mm/min), catastrophe frequency (0.17 min-1), and rescue frequency (1 min-1). These parameters were in close agreement with reported values for growth cones of living neurons. Microtubule properties in the fetal brain extract were shown to be affected by agents with known effects on the cytoskeleton. pp60c-src, a tyrosine kinase important in cell adhesion molecule-dependent axon growth, caused small increases in the frequency of microtubule catastrophe (0.31 min-1) and rescue (2 min-1) without changing the velocities of elongation or rapid-shortening. Although pp60c-src phosphorylated purified porcine brain tubulin in vitro, it did not elicit significant changes in its polymerization properties, suggesting that other cytoskeletal proteins in the brain extract are involved in modulating microtubule dynamics. The cytosolic extract of fetal rat brain provides a useful system for studying regulation of microtubule assembly in neuronal growth cones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atashi, J. R., Klinz, S. G., Ingraham, C. A., Matten, W. T., Schachner, M. & Maness, P. F. (1992) Neural cell adhesion molecules modulate tyrosine phosphorylation of tubulin nerve growth cone membranes. Neuron 8,831–42.
Aubry, M. A. & Maness, P. F. (1988) Developmental regulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in rat brain. Journal of Neuroscience Research 21,473–9.
Bamburg, J. E., Bray, D. & Chapman, K. (1986) Assembly of microtubules at the tip of growing axons. Nature 321,788–90.
Bare, D. J., Wilkie, M. B., Lauder, J. M. & Maness, P. F. (1993) p59fyn in rat brain is localized in developing axonal tracts and subpopulations of adult neurons and glia. Oncogene 8,1429–36.
Beggs, H. E., Soriano, P. & Maness, P. F. (1994) Inhibition of NCAM-dependent neurite outgrowth in fynminus neurons. Journal of Cell Biology 127,825–33.
Belmont, L. D., Hyman, A. A. Sawin, K. E. & Mitchison, T. J. (1990) Real-time visualization of cell cycle-dependent changes in microtubule dynamics in cytoplasmic extracts. Cell 62,579–89.
Cox, M. E. & Maness, P. F. (1991) Neurite extension and protein tyrosine phosphorylation elicited by inducible expression of the v-src oncogene in a PC12 cell line. Experimental Cell Research 195,423–41.
Cox, M. E. & Maness, P. F. (1993) Tyrosine phosphorylation of a-tubulin is an early response to NGF and pp60c-src in PC12 Cells. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 4,63–72.
Fults, D. W., Lauder, J. & Maness, P. F. (1985) pp60c-src is localized in processes of developing cerebellar neurons. Molecular Cell Biology 5,27–32.
Gard, D. L. & Kirschner, M. W. (1987) Microtubule assembly in cytoplasmic extracts of Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Journal of Cell Biology 105,2191–201.
Gliksman, N. R., Parsons, S. F. & Salmon, E. D. (1992) Okadaic acid induces interphase to mitoticlike microtubule dynamic instability by inactivating rescue. Journal of Cell Biology 119,1271–6.
Himes, R. H., Newhouse, C. S., Haskins, K. M. & Burton, P. R. (1979) Effects of sulfonate anions on the self-assembly of brain tubulin. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 87,1031–8.
Ignelzi, M. A., Miller, D. R., Soriano, P. & Maness, P. F. (1994) Impaired neurite outgrowth of srcminus cerebellar neurons on the cell adhesion molecule L1. Neuron 12,873–84.
Klinz, S. G., Schachner, M. & Maness, P. F. (1995) L1 and N-CAM antibodies trigger protein phosphatase activity in growth cone-enriched membranes. Journal of Neurochemistry 65,84–95.
Lebeau, J. M., Wiestler, O. D. & Walter, G. (1987) An altered form of pp60c-src is expressed primarily in the central nervous system. Molecular Cell Biology 7,4115–17.
Maness, P. F., Aubry, M., Frame, L. & Pfenninger, K. H. (1988) The c-src gene product in developing brain in enriched in nerve growth cone membrane. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 85,5001–5.
Matten, W. T., Aubry, M., West, J. & Maness, P. F. (1990) Tubulin is phosphorylated at tyrosine by pp60c-src in nerve growth cone membranes. Journal of Cell Biology 111,1959–70.
Mitchison, T. & Kirschner, M. (1988) Cytoskeletal dynamics and nerve growth. Neuron 1,761–72.
Morgan, D. O., Kaplan, J. M., Bishop, J. M. & Varmus, H. E. (1991) Production of pp60c-src by baculovirus expression and immunoaffinity purification. Methods in Enzymology 200,645–60.
O′ Brien, E. T., Salmon, E. D., Walker, R. A. & Erickson, H. P. (1990) Effects of magnesium on the dynamic instability of individual microtubules. Biochemistry 29,6648–56.
Schulze, E. & Kirschner, M. (1988) New features of microtubule behavior observed in vivo. Nature 334,356–9.
Simon, J. R., Parsons, S. F. & Salmon, E. D. (1992) Buffer conditions and non-tubulin factors critically affect the microtubule dynamic instability of sea urchin egg tubulin. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 21,1–14.
Sorge, L. K., Levy, B. T. & Maness, P. F. (1984) pp60c-src is developmentally expressed in the neural retina. Cell 36,249–57.
Tanaka, E., Ho, T. & Kirschner, M.W. (1995) The role of microtubule dynamics in growth cone motility and axonal growth. Journal of Cell Biology 128,139–55.
Tanaka, E. M. & Kirschner, M. W. (1991) Microtubule behaviour in the growth cones of living neurons during axon elongation. Journal of Cell Biology 115,345–63.
Voter, W. A. & Erickson, H. P. (1984) The kinetics of microtubule assembly. Journal of Biological Chemistry 259,10430–8.
Walker, R. A., O′Brien, E. T., Pryer, N. K., Soboiro, M. F., Voter, W. A., Erickson, H. P. & Salmon, E. D. (1988) Dynamic instability of individual microtubules analyzed by video light microscopy: Rate constants and transition frequencies. Journal of Cell Biology 107,1437–48.
Waxman, P. G., del Campo, A. A., Lowe, M. C. & Hamel, W. (1981) Induction of polymerization of purified tubulin by sulfonate buffers. European Journal of Biochemistry 120,129–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, J.R., Graff, R.D. & Maness, P.F. Microtubule dynamics in a cytosolic extract of fetal rat brain. J Neurocytol 27, 119–126 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006999306413
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006999306413