Abstract
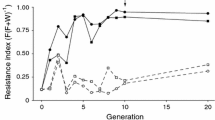
The developmental success of Leptopilina boulardi parasitoids within host species of the melanogaster subgroup is determined mainly by their ability to suppress the host immune reaction (virulence). Host resistance and parasitoid virulence are genetically variable in both partners. A gene for specific resistance against L. boulardi (Rlb) has been identified in Drosophila melanogaster, and a gene for the immune suppression (IS) of D. melanogaster has been identified in L. boulardi. To understand the evolution of the IS gene, we determined its specificity regarding potential hosts of the melanogaster subgroup. It did not affect the virulence against any other species of the melanogaster subgroup and was called ISm for immune suppression of D. melanogaster. Another gene (ISy), non-linked to the gene ISm, was characterized for the specific immune suppression of D. yakuba. These results suggesting that natural selection for virulence against one host species does not influence the evolution of virulence against another will allow us to develop pertinent hypotheses concerning the evolution of this character which is expected to drive the evolution of the parasitoid toward narrow host specialization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askew, R.R. and Shaw, M.R. (1986) Parasitoid Communities: Their Size, Structure and Development. Academic Press Inc., Orlando, Florida.
Benassi, V., Frey, F. and Carton, Y. (1998) A new specific gene for wasp cellular immune resistance in Drosophila. Heredity 80(3), 347–352.
Boulétreau, M. (1986) Genetic and Coevolutionary interactions between parasitoids and their hosts. In J.A.G. Waage and D. Greathead (eds) Insect Parasitoids. Academic Press Inc., Orlando, pp. 169–200.
Bulmer, M.G. (1980) The Mathematical Theory of Quantitative Genetics. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Carton, Y. and Dupas, S. (1998) Genetic of resistance and virulence in host-parasitoid system. In A. Wiesner, A.G. Dunphy, V.J. Marmaras, I. Morishima, M. Sugumaran and M. Yamakawa (eds) Techniques in Insect Immunology. S.O.S. publications, Fair Haven, NJ, pp. 279–288.
Carton, Y. and Kitano, H. (1981) Evolutionary relationships to parasitism by seven species of the Drosophila melanogaster subgroup. Biol. J. Linnean Soc. 16, 350–362.
Carton, Y. and Nappi, A.J. (1997) Drosophila cellular immunity against parasitoids. Parasitology Today 13, 218–226.
Carton, Y. and Nappi, A.J. (1991) The Drosophila immune reaction and the parasitoïd capacity to evade it: genetic and coevolutionnary aspects. Acta Oecol. 12, 89–104.
Carton, Y., Capy, P. and Nappi, A.J. (1989) Genetic variability of host parasite relationship traits: utilization of isofemale lines in a Drosophila parasitic wasp. Genetics, Selection, Evolution 21, 437–447.
de Belle, S. and Sokolowski, M.B. (1987) Heredity of rover/sitter: alternative foraging strategies of Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Heredity 59, 73–83.
Dupas, S., Brehelin, M., Frey, F. and Carton, Y. (1996) Immune suppressive virus-like particles in a Drosophila parasitoid: significance of their intraspecific morphological variations. Parasitology 113, 207–212.
Dupas, S., Frey, F. and Carton, Y. (1998) A single parasitoid segregating factor controls immune suppression in Drosophila. J. Hered. 89(4), 306–311.
Dupas, S. and Boscaro, M. (1999) Geographic variation and evolution of immune suppressive genes in a Drosophila parasitoid. Ecography 22, 284–291.
Eslin, P., Giordanengo, P., Fourdrain, Y. and Prevost, G. (1996) Avoidance of encapsulation in the absence of VLP by a braconid parasitoid of Drosophila larvae: an ultrastructural study. Can. J. Zool. 74, 2193–2198.
Fellowes, M.D.E., Kraaijeved, A.R. and Godfray, H.C.J. (1999) Cross-resistance following artificial selection for increased defense against parasitoids in Drosophila melanogaster. Evolution.
Fisher, R.A. (1930) The genetical theory of natural selection. Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford.
Hoffman, A.A. and Parsons, P.A. (1998) Consistent heritability changes under poor growth conditions. T.R.E.E. 12(12), 460.
Kawecki, T.J. (1998) Red queen meets Santa Rosalia: arms races and the evolution of host specialization in organisms with parasitic lifestyles. Am. Nat. 152, 635–651.
Kraaijeveld, A.R. and Godfray, H.C.J. (1999) Geographic patterns in the evolution of resistance and virulence in Drosophila and its parasitoids. Am Nat. 153, S61-S74.
Kraaijeveld, A.R., van Alphen, J.J.M. and Godfray, H.C.J. (1998) The coevolution of host resistance and parasitoid virulence. Parasitology 116, S29-S45.
Kraaijeveld, A.R. and van Alphen, J.J.M. (1994) Geographical variation in resistance of the parasitoid Asobara tabida against encapsulation by Drosophila melanogaster larvae: the mechanism explored. Physiological Entomology 19, 9–14.
Kraaijeveld, A.R. and van der Wel, N.N. (1994) Geographical variation in reproductive success of the parasitoid Azobara tabida in larvae of several Drosophila species. Ecol. Entomol. 19, 221–229.
Orr, H.A. and Irving, S. (1997) The genetic basis of resistance to wasp parasitism in Drosophila melanogaster. Evolution 51, 1877–1885.
Rizki, R.M. and Rizki, T.M. (1990) Parasitoid virus-like particles destroy Drosophila cellular immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 8388–8392.
Sokal, R.R. and Rolf, F.J. (1995) Biometry, the Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, W.H. Freeman and co., New York.
Walker I. (1959) Die Abwehrreacktion des Wirtes Drosophila melanogaster gegen die zoophage Cinipide Pseudeucoila bochei Weld. Revue Suisse de Zoologie 66(27), 569–631.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dupas, S., Carton, Y. Two non-linked genes for specific virulence of Leptopilina boulardi against Drosophila melanogaster and D. yakuba. Evolutionary Ecology 13, 211–220 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006691431658
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006691431658