Abstract
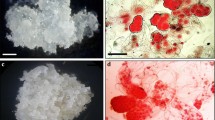
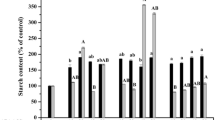
To promote SE maturation, the influence of different media components on different developmental stages was quantitatively evaluated. Advanced maturation was achieved with a sequence of culture media (prematuration medium and maturation medium) that contained various carbohydrates, organic nitrogen compounds and plant growth regulators. Application of lactose, BA, L-glutamine and casein hydrolysate in the prematuration medium enhanced the total number of SEs and promoted advanced differentiation. The highest number of late torpedo stage SEs was observed on maturation medium supplemented with 200 mM lactose and 29 mM sucrose. Lactose and sorbitol favoured SE maturation up to the early cotyledonary stage. With application of PEG and high ABA concentrations (20–40 μM), only early torpedo stages were formed. The number of late torpedo stage SEs was significantly higher on hormone free media or with lower ABA concentrations (0–5 μM). Formation of early and late cotyledonary SEs was significantly enhanced by adding BA in the maturation medium: neither Zeatin nor 2iP were effective. In addition, low sucrose concentrations in the proliferation medium (29 mM compared to 58 mM) also favoured the formation of cotyledonary SE in the maturation medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attree SM, Moore D, Sawhney VK& Fowke LC (1991) Enhanced maturation and desiccation tolerance of white spruce (Picea glauca [Moench.] Voss) somatic embryos: Effects of a non-plasmolysing water stress and abscisic acid. Ann. Bot. 68: 519–525
Attree SM, Pomeroy MK& Fowke LC (1992) Manipulation of conditions for the culture of somatic embryos of white spruce for improved triacylglycerol biosynthesis and desiccation tolerance. Planta 187: 395–404
Attree SM& Fowke LC (1993) Embryogeny of gymnosperms: advance in synthetic seed technology of conifers. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 35: 1–35
Bozhkov PV, Lebedenko LA& Shiryaeva GA (1992) A pronounced synergistic effect of abscisic acid and 6-benzyladenine on Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst) somatic embryo maturation. Plant Cell Rep. 11: 386–389
Button J (1978) The effects of some carbohydrates on the growth and organization of Citrus ovular callus. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 88: 61–68
Durzan DJ& Gupta PK (1987) Somatic embryogenesis and polyembryogenesis in Douglas-Fir cell suspension cultures. Plant Sci. 52: 229–235
Finer JJ, Kriebel HB& Becwar MR (1989) Initiation of embryogenic callus and suspension cultures of eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.). Plant Cell Rep. 8: 203–206
Guevin TG& Kirby EG (1997) Induction of embryogenesis in cultured mature zygotic embryos of Abies fraseri (Pursh) Poir. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 49: 219–222
Handa AK, Bressan AR, Handa S& Hasegawa PM (1982) Characteristics of cultured tomato cells after prolonged exposure to medium containing polyethylene glycol. Plant Physiol. 69: 514–521
Harry IS& Thorpe TA (1991) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from mature zygotic embryos of red spruce. Bot. Gaz. 152 (4): 446–452
Hrib J, Vookova B& Kormutak A (1997) Biochemical differences between normal callus and embryogenic suspensor mass of silver fir. Biologia Plantarum 39(4): 507–513
Klimaszewska K (1989) Plantlet development from immature zygotic embryos of hybrid larch through somatic embryogenesis. Plant Sci. 63: 95–103
Kochba J, Spiegel-Roy P, Neumann H& Saad S (1982) Effect of carbohydrates on somatic embryogenesis in subcultured nucellar callus of Citrus cultivars. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 105: 359–368
Krogstrup P, Eriksen EN, Moller JD& Roulund H (1988) Somatic embryogenesis in Sitka Spruce (Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr.). Plant Cell Rep. 7: 594–597
Norgaard JV& Krogstrup P (1991) Cytokinin induced somatic embryogenesis from immature embryos of Abies nordmanniana Lk. Plant Cell Rep. 9: 509–513
Reuther G, Schuller A& Gajdosova A (1995) The role of carbohydrates in somatic embryogenesis of Abies ESM-cultures. In: Recent Advances in Plant Biotechnology. Book of abstracts (pp. 1–11). Institute of plant genetics SAS, Nitra, Slovak Republic, October 2–6, 1995
Roberts DR (1991) Abscisic acid and mannitol promote early development, maturation and storage protein accumulation in somatic embryos of interior spruce. Physiol. Plant. 83: 247–254
Roberts DR, Flinn BS, Webb DT, Webster FB& Sutton BCS (1990) Abscisic acid and indole-3-butyric acid regulation of maturation and accumulation of storage proteins in somatic embryos of interior spruce. Physiol. Plant. 78: 355–360
Schenk RU& Hildebrandt AC (1972) Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 50: 199–204
Schuller A, Reuther G& Geier T (1989) Somatic embryogenesis from seed explants of Abies alba. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 17: 53–58
Schuller A& Reuther G (1993) Response of Abies alba embryonal-suspensor mass to various carbohydrate treatments. Plant Cell Rep. 12: 199–202
Simola LK& Santanen A (1990) Improvement of nutrient medium for growth and embryogenesis of megagametophyte and embryo callus lines of Picea abies. Physiol. Plant. 80: 27–35
Tremblay L& Temblay FM (1991) Carbohydrate requirements for the development of black spruce (Picea mariana (Mill.) B.S.P.) and red spruce (P. rubens Sarg.) somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 27: 95–103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuller, A., Kirchner-Neß, R. & Reuther, G. Interaction of plant growth regulators and organic C and N components in the formation and maturation of Abies alba somatic embryos. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 60, 23–31 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006429428170
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006429428170