Abstract
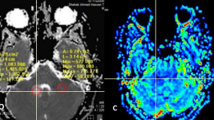
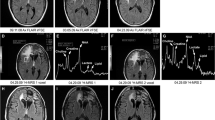
We wished to determine the utility of single voxel proton (1H) magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) when used as an alternative or adjunct to brain biopsy in patients harboring lesions suggestive of brain tumors identified by MRI scan. Fifteen patients (age 7–58 years) with MRI scans and clinical histories suggestive of primary brain tumors underwent single voxel 1H-MRS. MRS (16 regions of interest in 15 patients) was used to aid in differentiation between tumor and other pathologies such as stroke or demyelinating plaque (n=6), radiation necrosis (n=5), or edema (n=5). Spectra were quantified to determine absolute molar values of N-acetyl aspartate (NAA), choline (Cho), creatine (Cr), lactate (LAC), and myo-inositol (mI), metabolite ratios relative to Cr were calculated, and spectra were interpreted based on metabolite ratios. Subsequent clinical management was based on MRS interpretation, and patients were then followed to determine if MRS interpretation accurately predicted clinical outcome or surgical findings. Mean follow-up was 12.5 months (range 3–28 months). MRS suggested the presence of recurrent tumor in 7 cases, all of which were subsequently ‘confirmed’ by tumor resection (n=4) or disease progression (n=3). MRS suggested the presence of new tumor in 1 case, subsequently confirmed by surgical resection. MRS suggested the presence of necrosis in 3 patients; all 3 remained radiographically stable during the follow-up period, and one was confirmed by stereotactic biopsy. MRS suggested non-neoplastic lesions in 4 cases, 3 of whom were followed until radiographic resolution of lesions and one of which was confirmed as a pyogenic abscess via stereotactic aspiration. Overall, MRS accurately predicted the pathological nature and clinical outcome of lesions in 15/16 (96%) situations, influenced clinical decision making in 12 cases, and altered surgery planning in 7 patients. In appropriate circumstances MRS can reduce the need for biopsy and provide an important guide for clinical decision-making in difficult cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein M, Parrent AG: Complications of CT-guided stereotactic biopsy of intra-axial brain lesions. J Neurosurg 81(2): 165–168, 1994
Soo TM, Bernstein M, Provias J, Tasker R, Lozano A, Guha A: Failed stereotactic biopsy in a series of 518 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 64(4): 183–196, 1995
Alesch F, Armbruster C, Budka H: Diagnostic value of stereotactic biopsy of cerebral lesions in patients with AIDS. Acta Neurochir 134(3–4): 214–219, 1995
Negendank W: Studies of human tumors by MRS: a review. NMR Biomed 5(5): 303–324, 1992
Negendank WG, Sauter R, Brown TR, Evelhoch JL, Falini A, Gotsis ED, Heerschap A, Kamada K, Lee BC, Mengeot MM, Moser E, Padavic-Shaller KA, Sanders JA, Spraggins TA, Stillman AE, Terwey B, Vogl TJ, WicklowK, Zimmerman RA: Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with glial tumors: a multicenter study. J Neurosurg 84(3): 449–458, 1996
Poptani H, Gupta RK, Roy R, Pandey R, Jain VK, Chhabra DK: Characterization of intracranial mass lesions with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Am J Neuroradiol 16(8): 1593–1603, 1995
Preul MC, Caramanos Z, Collins DL, Villemure JG, Leblanc R, Olivier A, Pokrupa R, Arnold DL: Accurate, noninvasive diagnosis of human brain tumors by using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Nat Med 2(3): 323–325, 1996
Ross B, Michaelis T: Clinical applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Q 10(4): 191–247, 1994
Sijens PE, Knopp MV, Brunetti A, Wicklow K, Alfano B, Bachert P, Sanders JA, Stillman AE, Kett H, Sauter R et al.: 1H MR spectroscopy in patients with metastatic brain tumors: a multicenter study. Magn Reson Med 33(6): 818–826, 1995
Heesters MA, Kamman RL, Mooyaart EL, Go KG: Localized proton spectroscopy of inoperable brain gliomas. Response to radiation therapy. J Neuro-Oncol 17(1): 27–35, 1993
Kamada K, Houkin K, Abe H, Sawamura Y, Kashiwaba T: Differentiation of cerebral radiation necrosis from tumor recurrence by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 37(3): 250–256, 1997
Nelson SJ, Huhn S, Vigneron DB, Day MR, Wald LL, Prados M, Chang S, Gutin PH, Sneed PK, Verhey L, Hawkins RA, Dillon WP: Volume MRI and MRSI techniques for the quantitation of treatment response in brain tumors: presentation of a detailed case study. J Magn Reson Imaging 7(6): 1146–1152, 1997
Taylor JS, Langston JW, Reddick WE, Kingsley PB, Ogg RJ, Pui MH, Kun LE, Jenkins JJ, 3rd, Chen G, Ochs JJ, Sanford RA, Heideman RL: Clinical value of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy for differentiating recurrent or residual brain tumor from delayed cerebral necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36(5): 1251–1261, 1996
Tedeschi G, Lundbom N, Raman R, Bonavita S, Duyn JH, Alger JR, Di Chiro G: Increased choline signal coinciding with malignant degeneration of cerebral gliomas: a serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging study. J Neurosurg 87(4): 516–524, 1997
Tien RD, Lai PH, Smith JS, Lazeyras F: Single-voxel proton brain spectroscopy exam (PROBE/SV) in patients with primary brain tumors. Am J Roentgenol 167(1): 201–209, 1996
Preul MC, Leblanc R, Caramanos Z, Kasrai R, Narayanan S, Arnold DL: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy guided brain tumor resection: differentiation between recurrent glioma and radiation change in two diagnostically difficult cases. Can J Neurol Sci 25(1): 13–22, 1998
Carapella CM, Carpinelli G, Knijn A, Raus L, Caroli F, Podo F: Potential role of in vitro 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the definition of malignancy grading of human neuroepithelial brain tumours. Acta Neurochir Suppl 68: 127–132, 1997
Carpinelli G, Carapella CM, Palombi L, Raus L, Caroli F, Podo F: Differentiation of glioblastoma multiforme from astrocytomas by in vitro 1H MRS analysis of human brain tumors. Anticancer Res 16(3B): 1559–1563, 1996
Bernsen HJ, Heerschap A, van der Kogel AJ, van Vaals JJ, Prick MJ, Poels EF, Meyer J, Grotenhuis JA: Image-guided 1H NMR spectroscopical and histological characterization of a human brain tumor model in the nude rat: a new approach to monitor changes in tumor metabolism. J Neuro-Oncol 13(2): 119–130, 1992
Barbarella G, Ricci R, Pirini G, Tugnoli V, Tosi MR, Bertoluzza A, Calbucci F, Leonardi M, Trevisan C, Eusebi V: In vivo single voxel 1H MRS of glial brain tumors: correlation with tissue histology and in vitro MRS. Int J Oncol 12(2): 461–468, 1998
Bluml S, McComb JG, Ross BD. Differentiation between cortical atrophy and hydrocephalus using 1H MRS. Magn Reson Med 37(3): 395–403, 1997
Castillo M, Kwock L, Scatliff J, Mukherji SK: Proton MR spectroscopy in neoplastic and non-neoplastic brain disorders. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 6(1): 1–20, 1998
Kreis R, Arcinue E, Ernst T, Shonk TK, Flores R, Ross BD: Hypoxic encephalopathy after near-drowning studied by quantitative 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Clin Invest 97(5): 1142–1154, 1996
De Stefano N, Caramanos Z, Preul MC, Francis G, Antel JP, Arnold DL: In vivo differentiation of astrocytic brain tumors and isolated demyelinating lesions of the type seen in multiple sclerosis using 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Ann Neurol 44(2): 273–278, 1998
Kreis R, Farrow N, Ross BD: Localized 1H NMR spectroscopy in patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Analysis of changes in cerebral glutamine, choline and inositols. NMR Biomed 4(2): 109–116, 1991
Kreis R, Ross BD: Cerebral metabolic disturbances in patients with subacute and chronic diabetes mellitus: detection with proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 184(1): 123–130, 1992
Rand SD, Prost R, Haughton V, Mark L, Strainer J, Johansen J, Kim TA, Chetty VK, Mueller W, Meyer G, Krouwer H: Accuracy of single-voxel proton MR spectroscopy in distinguishing neoplastic from nonneoplastic brain lesions. Am J Neuroradiol 18(9): 1695–1704, 1997
Bruhn H, Michaelis T, Merboldt KD, Hanicke W, Gyngell ML, Hamburger C, Frahm J: On the interpretation of proton NMR spectra from brain tumours in vivo and in vitro. NMR Biomed 5(5): 253–258, 1992
Ernst T, Ross BD, Flores R: Cerebral MRS in infant with suspected Reye's syndrome (letter). Lancet 340(8817): 486, 1992
Danielsen ER, Michaelis T, Ross BD: Three methods of calibration in quantitative proton MR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson B 106(3): 287–291, 1995
Kreis R, Ernst T, Ross BD: Development of the human brain: in vivo quantification of metabolite and water content with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 30(4): 424–437, 1993
Conti PS: Introduction to imaging brain tumor metabolism with positron emission tomography (PET). Cancer Invest 13(2): 244–259, 1995
Duncan DB, Herholz K, Kugel H, Roth B, Ruitenbeek W, Heindel W, Wienhard K, Heiss WD: Positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance spectroscopy of cerebral glycolysis in children with congenital lactic acidosis. Ann Neurol 37(3): 351–358, 1995
Yoshino E, Ohmori Y, Imahori Y, Higuchi T, Furuya S, Naruse S, Mori T, Suzuki K, Yamaki T, Ueda S, Tsuzuki T, Takai S: Irradiation effects on the metabolism of metastatic brain tumors: analysis by positron emission tomography and 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 66(Suppl 1): 240–259, 1996
Mitsuhashi N, Hayakawa K, Hasegawa M, Furuta M, Katano S, Sakurai H, Akimoto T, Takahashi T, Nasu S, Niibe H: Clinical FDG-PET in diagnosis and evaluation of radiation response of patients with nasopharyngeal tumor. Anticancer Res 18(4B): 2827–2832, 1998
Voges J, Schroder R, Treuer H, Pastyr O, Schlegel W, Lorenz WJ, Sturm V: CT-guided and computer assisted stereotactic biopsy. Technique, results, indications. Acta Neurochir 125(1–4): 142–149, 1993
Tugnoli V, Tosi MR, Barbarella G, Ricci R, Leonardi M, Calbucci F, Bertoluzza A: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of lowgrade extra and intracerebral human neoplasms. Oncol Rep 5(5): 1199–1203, 1998
Tate AR, Griffiths JR, Martinez-Perez I, Moreno A, Barba I, Cabanas ME, Watson D, Alonso J, Bartumeus F, Isamat F, Ferrer I, Vila F, Ferrer E, Capdevila A, Arus C: Towards a method for automated classification of 1H MRS spectra from brain tumours. NMR Biomed 11(4–5): 177–191, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, A., Bluml, S. & Mamelak, A.N. Efficacy of Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Inclinical Decision Making for Patients with Suspected Malignant Brain Tumors. J Neurooncol 45, 69–81 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006387703127
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006387703127