Abstract
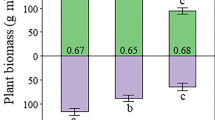
In a long-term study (1980 to 1993), the survival, growth performance and biomass production of two grass species viz. Chrysopogon fulvus (Spreng.) Chiov. and Eulaliopsis binata (Retz.) C.E. Hubb. were assessed when intercropped with four tree species viz. Albizia lebbek (L.) Benth., Grewia optiva Drumm., Bauhinia purpurea L. and Leucaena leucocephala (Lamk.) de Wit. on the bouldery riverbed lands of Doon Valley of north-west India. The survival of grass clumps was higher under the canopy of B. purpurea (48.3% in 1993 of the initial planting density of 20,000 clumps ha−1 in 1980) and G. optiva (47.4%) than of L. leucocephala (31.1%) and A. lebbek (29.4%), and at 75% intensity of tree lopping (40.9%) than at 50% (37.1%). The effect of tree species on different growth parameters of grasses was not uniform, with G. optiva and B. purpurea causing comparatively more synergistic effect on clump height and clump diameter respectively. Although the performance of grasses was good under A. lebbek and L. leucocephala in the early years (1980--1987), these tree species resulted in the lowest grass dry weight in the later years up to 1993. The beneficial effect of higher lopping intensity of 75% was observed on the growth and biomass production of grasses over 50% lopping, presumably due to increased light penetration into the under-storey. The biomass production of grasses reached a maximum at four years of growth in 1983, after which, it decreased gradually to less than half in 1993. Eulaliopsis binata showed higher survival, growth and biomass production than C. fulvus throughout the period of study. The total biomass production was highest in association with B. purpurea followed by G. optiva, which appeared to be the most suitable tree species along with E. binata for sustainable silvopasture development on the marginal lands of Doon Valley of north-west India.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acciaresi H, Ansiu OE and Marlats RM (1994) Silvopastoral systems: effects of tree density on light penetration and forage production in poplar (Populus deltoides Marsh) stands. Agroforestria-en-las-Americas 1(4): 6-9
Batra L and Kumar A (1994) Biomass production and nitrogen accumulation by Rhodes grass and three tree species in an agroforestry system under alkali soil conditions. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol II, pp 713-719. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Bhatt BP and Todaria NP (1992) Studies on allelopathic exclusion of under-storey by some agroforestry tree crops of Garhwal Himalaya. In: Tauro P and Narwal SS (eds) Proceedings of the First National Symposium on Allelopathy in Agroecosystems (Agriculture and Forestry), pp 129. Haryana Agricultural University, Hissar
Bhatt RK, Misra LP and Pathak PS (1994) Forage yield and related plant processes in Cenchrus and Panicum under silvipastoral system. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol II, pp 732-738. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Bidwell RGS (1974) Physiology of plant under stress. In: Plant Physiology, pp 563-576. Macmillan Publishing Co Inc, New York
Chou CH (1987) Allelopathy in subtropical vegetation and soils in Taiwan. In: Waller GR (ed) Allelochemicals — Role in Agriculture and Forestry, pp 102-117. ACS, Washington, DC
Deb-Roy R (1994) Common agroforestry systems and their management for optimising production. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol I, pp 379-387. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Katoch DC (1994) Sustainable silvipastoral system for sub-tropical rangelands infested with Lantana camara L. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol I, pp 159-163. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Khola OPS and Saroj PL (1995) Conservation efficiencies of grasses in bouldery riverbed lands. Indian J Soil Cons 23(1): 34-38
Parihar SS, Shankar V and Kak A (1996) Toxic allelochemicals in forages and their ecological significance. Forage Res 21(4): 163-173
Qarro M and De-Montard FX (1989) A study of rangeland productivity in the air-bench region (Middle Atlas, Central Plateau). I. The effects of cutting frequency and relative tree cover on herbaceous production. Agronomie 9(5): 477-487
Shukla GP and Hazra CR (1994) Evaluation of perennial forage species and their varieties for use in silvipastoral system. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol II, pp 693-699. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Shukla NP and Lal M (1994) Production of forage grasses in relation to nitrogen nutrition on wetland ecosystem. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol II, pp 604-607. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Sood AD, Mittal SP and Mishra PR (1986) Raising bhabbar grass in eucalyptus plantation. Indian Farming 35(12): 11-33
Sood BR, Sharma VK and Kumar K (1994) Performance of some improved grass cultivars under tree canopy and open grassland of Kangra valley. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol II, pp 700-704. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Upadhyay VS and Pathak PS (1994) Silvipastoral system evaluation for secondary production in central India. In: Singh P, Pathak PS and Roy MM (eds) Agroforestry Systems for Degraded Lands, Vol II, pp 780-787. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi
Vishwanatham MK, Samra JS and Sharma AR (1999) Biomass production of trees and grasses in a silvopasture system on marginal lands of Doon Valley of north-west India. 1. Performance of tree species. Agrofor Syst 46(2): 181-196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samra, J.S., Vishwanatham, M.K. & Sharma, A.R. Biomass production of trees and grasses in a silvopasture system on marginal lands of Doon Valley of north-west India 2. Performance of grass species. Agroforestry Systems 46, 197–212 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006293424209
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006293424209