Abstract
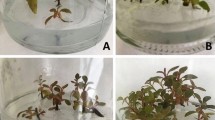
The individual effects of sucrose, plant growth regulators and basal salt media formulations were investigated on microtuber induction and development in shoot cultures of the steroid yam Dioscorea composita. Sucrose at 8% (w/v) was the single most significant medium constituent for microtuber induction. Of the four cytokinins tested, 6-benzyladenine at 1.25 and 2.5 μM showed strong inhibitory effects on microtuber induction. By contrast, the auxins α-naphthaleneacetic acid and indole-3-butyric acid at 5.0 μM showed striking promotive effects on microtuber induction and growth. In the presence of either one of these auxins at 5.0 μM shoot cultures produced microtubers weighing 300–400 mg fresh weight whilst kinetin, 6-(γ,γ-dimethylallylamino)-purine, 6-benzyladenine and abscisic acid failed to promote microtuber growth (microtubers weighed generally <200 mg). Media formulations Lloyd and MacCown and White supported the lowest frequencies of microtuber induction when kinetin was present at 2.5 μM. Anderson Rhododendron was as effective as Murashige and Skoog overall in promoting both microtuber induction and growth. When removed from cultures and planted in sterilized moist sand, microtubers sprouted readily (60–87% within 2 weeks) and produced vigorous shoot growth and after 5–7 months minitubers of sizes (30–80 g) suitable for direct field planting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammirato PV (1982) Growth and morphogenesis in cultures of the monocot yam, Dioscorea. In: Fujiwara A (ed) Plant Tissue Culture (pp 169–170). Maruzen, Tokyo
Ammirato PV (1984) Yams. In: Ammirato PV, Evans DA, Sharp WR & Yamada Y (eds) Handbook of Plant Cell Culture, Vol 3, Crop Species, (pp 327–354). Macmillan, New York
Anderson WC (1978) Tissue culture propagation of Rhododendrons. In Vitro 14: 334
Coursey DG (1967) Yams. Longmans, London
Chaturvedi HC (1979) Tissue culture of economic plants. In: Khoshoo TN, Nair PKK (eds) Progress in Plant Research, Vol 1, Applied Morphology and Allied Subjects (pp 265–288). Today and Tomorrow's Printers and Publishers, Karolbagh, New Delhi
Forsyth C & Van Staden J (1982) An improved method of in vitro propagation of Dioscorea bulbifera. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 1: 275–281
Forsyth C & Van Staden J (1984) Tuberization of Dioscorea bulbifera stem nodes in culture. J. Plant Physiol. 115: 79–83
Gamborg OL, Eveleigh DE (1968) Culture methods and detection of glucanases in suspension cultures of wheat and barley. Can. J. Biochem. 46: 417–421
Kao KN & Michayluk MR (1975) Nutritional requirements for growth of Vicia hajastana cells and protoplasts at a very low population density in liquid media. Planta 126: 105–110
Lloyd G & McCown B (1981) Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot tip culture. Int. Plant Prop. Soc. Proc. 30: 421–427
Mantell SH, Haque SQ & Whitehall AP (1978) Clonal multiplication of Dioscorea alata L and Dioscorea rotundata Poir yams by tissue culture. J. Hort. Sci. 53: 95–98
Mantell SH & Hugo SA (1989) Effects of photoperiod, mineral strength, inorganic ammonium, sucrose and cytokinin on root, shoot and microtuber development in shoot cultures of Dioscorea alata L and D. bulbifera L yams. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 16: 23–37
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Ng SYC (1988) In vitro tuberization in white yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 14: 121–128
Preston WH Jr & Haun JR (1962) Factors involved in the vegetative propagation of Dioscorea spiculiflora Hemsl. from vines. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 80: 417–429
Schenk RU & Hildebrandt AC (1972) Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 50: 199–204
Sengupta J, Mitra GC & Sharma AK (1984) Organogenesis and tuberization in cultures of Dioscorea floribunda. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 3: 325–331
Sita L, Bammi RK & Randhawa GS (1976) Clonal propagation of Dioscorea floribunda by tissue culture. J. Hort. Sci. 51: 551–554
Viana AM & Felippe GM (1988) Root formation in cuttings of Dioscorea composita. J. Agric. Sci. 110: 451–454
Viana AM & Mantell SH (1989) Callus induction and plant regeneration from excised zygotic embryos of the seed-propagated yams Dioscorea composita Hemsl. and D. cayenensis Lam. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 16: 113–122
White PR (1963) The Cultivation of Animal and Plant Cells, 2nd edition. Ronald Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alizadeh, S., Mantell, S.H. & MariaViana, A. In vitro shoot culture and microtuber induction in the steroid yam Dioscorea composita Hemsl. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 53, 107–112 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006036324474
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006036324474