Abstract
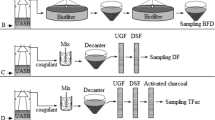
Deep bed filtration is becoming increasing important in wastewater treatment particularly in tertiary treatment as stringent water quality standards are emphasized. A detailed pilot-scale filtration study conducted with secondary effluent in a sewage treatment plant indicated that tertiary filtration with prior alum flocculation is capable of producing high quality effluent, particularly an effluent with phosphorus content of less than 0.3 mg/L (Vigneswaran and Ngo, 1994). Main problem of dual media filter has been rapid headloss development thus frequent backwash requirement. To overcome this problem two independent experimental studies were conducted: one with mobile bed filtration (MBF) and the other with combined downflow floating medium flocculator/prefilter (DFF) and coarse sand filter (CSF) system. A semi-pilot scale mobile bed filtration study conducted using oxidation pond effluent indicated that MBF with contact-flocculation arrangement was good in removing COD, T-P and turbidity with practically no headloss development. Sand of 0.6-0.84 nm dia and 50 cm depth was sufficient to reduce the COD and P from 55 mg/L and 4.5 mg/L to 15 mg/L and 0.5 mg/L respectively at a filtration rate of 7.5 m3/m2.h. Another experimental study with combined DFF-CSF system indicated that the DFF with in-line flocculation addition is a good pretreatment unit to reduce the phosphate upto 80-90%. The fact that DFF resulted in uniform filterable-flocs, it can also successfully be used as a static flocculator/prefilter unit. The introduction of DFF on top of a coarse sand filter increased the filter run time and removal efficiency (more 90-95% of NH3-N and T-P removal respectively). Most importantly, the backwashing of this system was achieved with small quantity of water at low backwash indicated that the removal efficiency was also superior with this system apart from the major advantage of low operating cost.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ngo, H. H. and Vigneswaran, S. (1995). Floating medium filter for water and wastewater treatment. Jour. Water Research-IAWQ (In print).
Ngo, H. H. and Vigneswaran, S. (1995). Application of downflow floating medium flocculator/prefilter (DFF)-coarse sand filter in nutrient removal. 3rd Conference on Appropriate Waste Management Technologies for Developing Countries, Nagpur, India, 699–708.
Vigneswaran, S and Ngo, H. H. (1994). Improved phosphorus removal in sewage treatment plants, International Conference on Asian Water Technology, Singapore 1994, 112–123.
Vigneswaran, S. and Bandulahewa, R. (1990). Applicability of mobile bed filtration in Reuse of domestic wastewater, Project Report, CIDA-AIT Partnership Project, June 1990.
Vigneswaran, S. (1991) Appication of deep bed filtration in tertiary wastewater treatment, J. Water, Aust.WWA, 19,3, 32–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vigneswaran, S., Ngo, H.H. & Jeyaseelan, J. Application of Non-Conventional Filtration Technologies in Pollution Control. Environ Monit Assess 44, 231–240 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005736607572
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005736607572