Abstract
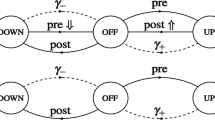
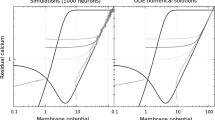
Stochastic and reduced biophysical models of synaptictransmission are formulated and evaluated. Thesynaptic transmission involves presynapticfacilitation of neurotransmitter release, depletionand recovery of the presynaptic pool of readilyreleasable vesicles containing neurotransmittermolecules and saturation of postsynaptic receptors ofboth fast non-NMDA and slow NMDA types. The models areshown to display the principal dynamicalcharacteristics experimentally observed of synaptictransmission. The two main types of neural coding,i.e. rate and temporal coding, can be distinguished bymeans of different dynamical properties of synaptictransmission determined by initial neurotransmitterrelease probability and presynaptic firing rate. Fromthe temporal evolution of the postsynaptic membranepotential response to a train of presynaptic actionpotentials at a sustained firing rate, in particularthe steady-state amplitude and steady-state averagelevel of postsynaptic membrane potentials aredetermined as functions of both initial releaseprobability and presynaptic firing rate. The modelsare applicable to studies of the primary stages oflearning processes and can be extended to incorporateshort-term and long-term potentiation in memoryconsolidation processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Magleby, K.L.: Short-term changes in synaptic efficacy, In: G.M. Edelman, V.E. Gall and K.M. Cowan (eds.), Synaptic Function, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1987, pp. 21-56.
Zucker, R.S.: Short-term synaptic plasticity, Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 12 (1989), 13-31.
Betz, W.J.: Depression of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog, J. Physiol. 206 (1970), 629-644.
Kusano, K. and Landau, E.M.: Depression and recovery of transmission at the squid giant synapse, J. Physiol. 245 (1975), 13-32.
Larkman, A., Stratford, K. and Jack, J.: Quantal analysis of excitatory synaptic action and depression in hippocampal slices, Nature, 350 (1991), 344-347.
Clements, J.D.: Transmitter timecourse in the synaptic cleft: its role in central synaptic function, Trends Neurosci. 19 (1996), 163-171.
Malenka, R.C.: Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: LTP and LTD, Cell 78 (1994), 535-538.
Huang, Y.-Y., Nguyen, P.V., Abel, T. and Kandel, E.R.: Long-lasting forms of synaptic potentiation in the hippocampus, Learning Mem. 3 (1996), 74-85.
Katz, B. and Miledi, R.: The effect of calcium on acetylcholine release from motor nerve terminals, Proc. R. Soc. B 161 (1965), 496-503.
Dodge Jr., F.A. and Rahamimoff, R.: Co-operative action of calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction, J. Physiol., 193 (1967), 419-432.
Katz, B. and Miledi, R.: The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation, J. Physiol. 195 (1968), 481-492.
Swandulla, D., Hans, M., Zipser, K. and Augustine, G.J.: Role of residual calcium in synaptic depression and posttetanic potentiation: fast and slow calcium signaling in nerve terminals, Neuron 7 (1991), 915-926.
Regehr, W.G., Delaney, K.R. and Tank, D.W.: The role of presynaptic calcium in short-term enhancement at the hippocampal mossy fiber synapse, J. Neurosci. 14 (1994), 523-537.
Linial, M. and Parnas, D.: Deciphering neuronal secretion: tools of the trade, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1286 (1996), 117-152.
Stevens, C.F. and Wang, Y.: Facilitation and depression at single synapses, Neuron 14 (1995), 795-802.
Murthy, V.N., Sejnowski, T.J. and Stevens, C.F.: Heterogeneous release properties of visualized individual hippocampal synapses, Neuron 18 (1997), 599-612.
Dobrunz, L.E. and Stevens, C.F.: Heterogeneity of release probability, facilitation, and depletion at central synpases, Neuron 18 (1997), 995-1008.
Debanne, D., Guérineau, N.C., Gähwiler, B.H. and Thompson, S.M.: Paired-pulse facilitation and depression at unitary synapses in rat hippocampus: quantal fluctuation affects subsequent release J. Physiol. 491 (1996), 163-176.
Markram, H. and Tsodyks, M.: Redistribution of synaptic efficacy between neocortical pyramidal neurons, Nature 382 (1996), 807-810.
Tsodyks, M.V. and Markram, H.: The neural code between neocortical pyramidal neurons depends on neurotransmitter release probability, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (1997), 719-723.
Markram, H., Wang, Y. and Tsodyks, M.: Differential signaling via the same axon of neocortical pyramidal neurons, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (1998), 5323-5328.
Abbott, L.F., Varela, J.A., Sen, K. and Nelson S.B.: Synaptic depression and cortical gain control, Science 275 (1997), 220-224.
Nelson, S.B., Varela, J.A., Sen, K. and Abbott, L.F.: Functional significance of synaptic depression between cortical neurons, In: J.M. Bower (ed.), Computational Neuroscience, Plenum Press, New York, 1997, pp. 429-434.
Varela, J.A., Sen, K., Fost, J., Abbott, L.F. and Nelson, S.B.: A quantitative description of shortterm plasticity at excitatory synapses in layer 2/3 of rat primary visual cortex, J. Neurosci. 17 (1997), 7926-7940.
Ravin, R., Spira, M.E., Parnas, H. and Parnas, I.: Simultaneous measurement of intracellular Ca2+ and asynchronous transmitter release from the same crayfish bouton, J. Physiol. 501 (1997), 251-262.
Hille, B.: Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, Sinauer, Sunderland, 1992.
Cartling, B.: A generalized neuronal activation function derived from ion-channel characteristics, Network 6 (1995), 389-401.
Cartling, B.: Response characteristics of a low-dimensional model neuron, Neural Comput. 8 (1996), 1643-1652.
Cartling, B.: A low-dimensional, time-resolved and adapting model neuron, Int. J. Neural Syst. 7 (1996), 237-246.
Cartling, B.: Control of computational dynamics of coupled integrate-and-fire neurons, Biol. Cybern. 76 (1997), 383-395.
Rosenmund, C. and Stevens, C.F.: Definition of the readily releasable pool of vesicles at hippocampal synapses, Neuron 16 (1996), 1197-1207.
McCormick, D.A., Connors, B.W., Lighthall, J.W. and Prince, D.A.: Comparative electrophysiology of pyramidal and sparsely spiny stellate neurons of the neocortex, J. Neurophysiol. 54 (1985), 780-806.
Connors, B.W. and Gutnick, M.J.: Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons, Trends Neurosci. 13 (1990), 99-104.
Ekeberg, Ö., Wallén, P., Lansner, A., Tråvén, H., Brodin, L. and Grillner, S.: A computer based model for realistic simulations of neural networks I: the single neuron and synaptic interaction, Biol. Cybern. 65 (1991), 81-90.
Fransén, E. and Lansner, A.: A model of cortical associative memory based on a horizontal network of connected columns, Network 9 (1998), 235-264.
Yamada, W., Koch, C. and Adams, P.R.: Multiple channels and calcium dynamics, In: C. Koch and I. Segev (eds.), Methods in Neuronal Modeling. From Synapses to Networks, MIT Press, Cambridge, 1989, pp. 97-133.
Markram, H., Lübke, J., Frotscher, M., Roth, A. and Sakmann, B.: Physiology and anatomy of synaptic connections between thick tufted pyramidal neurones in the developing rat neocortex, J. Physiol. 500 (1997), 409-440.
Parnas, H. and Segel, L.A.: A theoretical study of calcium entry in nerve terminals, with application to neurotransmitter release, J. Theoret. Biol. 91 (1981), 125-169.
Mallart, A. and Martin, A.R.: An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog, J. Physiol. 193 (1967), 679-694.
Zengel, J.E. and Magleby, K.L.: Augmentation and facilitation of transmitter release. A quantitative description at the frog neuromuscular junction, J. Gen. Physiol. 80 (1982), 583-611.
Thomson, A.M. and Radpour, S.: Excitatory connections between CA1 pyramidal cells revealed by spike triggered averaging in slices of rat hippocampus are partially NMDA receptor mediated, Eur. J. Neurosci. 3 (1991), 587-601.
Asztely, F., Wigström, H. and Gustafsson, B.: The relative contribution of NMDA receptor channels in the expression of long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region, Eur. J. Neurosci. 4 (1992), 681-690.
Fischer, T.M., Blazis, D.E.J., Priver, N.A. and Carew, T.J.: Metaplasticity at identified inhibitory synapses in Aplysia, Nature 389 (1997), 860-865.
Fossier, P., Tauc, L. and Baux, G.: Calcium transients and neurotransmitter release at an identified synapse, Trends Neurosci., 22 (1999), 161-166.
Cartling, B.: Control of the complexity of associative memory dynamics by neuronal adaptation, Int. J. Neural Syst. 4 (1993), 129-141.
Cartling, B.: Autonomous neuromodulatory control of associative processes, Network 6 (1995), 247-260.
Cartling, B.: Control of resolution and perception in working memory, Behav. Brain Res. 100 (1999), 255-271.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cartling, B. Stochastic and Reduced Biophysical Models of Synaptic Transmission. Journal of Biological Physics 26, 113–131 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005223902152
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005223902152