Abstract
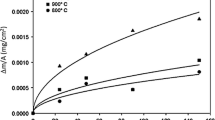
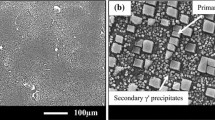
This study assessed the oxidation behavior of three commercial alloys in airand low partial pressures of oxygen roman (PO 2. The kinetics ofoxidation in air were compared with values obtained in an atmosphere of lowroman PO 2. The low partial pressure of oxygen was of the order of10−16 atm at 930°C and was generated using an H2/4% H2Omixture. The nature of the corrosion products, structure, morphology, andcomposition were assessed and characterized using scanning electronmicroscopy (SEM), X-ray mapping, and scanning Auger microscopy (SAM). Theresults were compared with those obtained for 99.99% pure chromium. Parabolickinetics were exhibited by all of the alloys, with the overall kp valuesbeing of the order constant for chromia-forming alloys. Large variations inthe morphologies of the oxide scales were observed as a result of oxidationin the high and low roman PO 2 environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Stringer, High Temperature Materials Corrosion in Coal Gasification Atmospheres, F. Norton, ed., pp. 83-102.
W. R. Johnson, L. D. Thompson, and T. A. Lechtenberg, Nuclear Technol. 66 (1984).
X. G. Zheng and D. J. Young, Oxid. Met. 42, (1994).
P. Kofstad, High Temperature Corrosion, Chap. 12 (Elsevier, London, 1988).
P. L. Surman, Corros. Sci. 13, 113-124 (1973).
F. Armanet, A. Vejux, and G. Beranger, Behavior of High Temperature Alloys in Aggressive Environments, Proc. Intern. Conf., Petten (N.H.), The Netherlands, October 15-18, 1979 (The Metals Society for the Commission of the European Communities), p. 423.
K. N. Strafford and J. M. Harrison, Oxid. Met. 10, 347-359 (1976).
C. Wagner, J. Electrochem. Soc. 103, 571 (1956).
C. T. Sims and W. C. Hagel, The Superalloys [Wiley (Interscience), New York, 1972].
J. K. Tien and T. Caulfield, Superalloys, Supercomposites and Superceramics (Academic Press, New York).
Book of Data, Revised Nuffield Advanced Science (Longman Group, London, 1993).
P. Lacombe, Behavior of High Temperature Alloys in Aggressive Environments. Proc. Intern. Conf., Petten (N.H.), The Netherlands, October 15-18, 1979. (The Metals Society for the Commission of the European Communities), p. 180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabbani, F., Ward, L.P. & Strafford, K.N. A Comparison of the Growth Kinetics and Scale Morphology for Three Superalloys at 930°C in Air and Low PO2 Environments. Oxidation of Metals 54, 139–153 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004658814608
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004658814608