Abstract
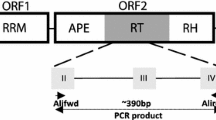
To better understand the genetic diversity of the wild relatives of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the O. officinalis species complex repetitive DNA markers were obtained from the diploid species of this complex. One cloned sequence from O. eichingeri gave intense hybridization signals with all species of the O. officinalis complex. This 242 bp clone, named pOe.49, has a copy number from 0.9 to 4.0 × 104 in diploid species of this complex. Analysis of the primary structure and database searches revealed homology of pOe.49 to a number of sequences representing part of the integrase coding domain of retroviruses and gypsy-like retrotransposons. Sequencing of specific PCR products confirmed that pOe.49 is part of a gypsy-like retrotransposon. RFLP analysis was used to study the genomic organisation of pOe.49 among 30 accessions of the O. officinalis complex using 10 restriction enzymes. Diversity analysis based on 120 polymorphic fragments obtained from the RFLP assay grouped the O. officinalis complex accessions by genome, species and eco-geographic groups. The results suggest that, with further characterization, this retrotransposon-like DNA sequence may be useful for phylogenetic analysis of species in the O. officinalis complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal R.K., D.S. Brar, S. Nandi, N. Huang & G.S. Khush, 1999. Phylogenetic relationships among Oryza species revealed by AFLP markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98: 1320–1328.
Bennetzen, J.L., 2000. Transposable element contributions to plant gene and genome evolution. Plant Mol. Biol. 42: 251–269.
Boeke J.D. & V.G. Corces, 1989. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 43: 403–434.
Brar D.S. & G.S. Khush, 1997. Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 35: 35–47.
Capy, P., D. Anxolabehere & T. Langin, 1994. The strange phylogenies of transposible elements: are horizontal transfers the only explanation. Trends Genet. 10: 7–12.
Cordesse, F., F. Grellet, A.S. Reddy & M. Delseny, 1992. Genome specificity of rDNA spacer fragments from O. sativa L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 864–870.
Ellis, T.H.N., S.J. Poyser, M.R. Knox, A.V. Vershinin & M.J. Ambrose, 1998. Ty1-copia class retrotransposon insertion site polymorphism for linkage and diversity analysis in pea. Mol. Gen. Genet. 260: 9–19.
Felsenstein, J., 1990. PHYLIP Manual Version 3.3. University Herbarium, University of California, Berkeley, California.
Flavell, A.J., E. Dunbar, R. Anderson, S.R. Pearce, R. Hartley & A. Kumar, 1992. Ty1-copia group retrotransposons are ubiquitous and heterogeneous in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 20: 3639–3644.
Flavell, A.J., M.R. Knox, S.R. Pearce & T.H.N. Ellis, 1998. Retrotransposon-based insertion polymorphisms (RBIP) for high throughput marker analysis. Plant J. 16: 643–650.
Grunstein, M. & D. Hogness, 1975. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72: 3961–3965.
Hirochika, H., A. Fukuchi & F. Kikuchi, 1992. Retrotransposon families in rice. Mol. Gen. Genet. 233: 209–216.
Iwamoto, M., H. Nagashima, T. Nagamine, H. Higo & K. Higo, 1999. A Tourist element in the 50-flanking region of the catalase gene CatA reveals evolutionary relationships among Oryza species with various genome types. Mol. Gen. Genet. 262: 493–500.
Kalendar, R., T. Grob, M. Regina, A. Suoniemi & A. Schulman, 1999. IRAP and REMAP: two new retrotransposon based DNA fingerprinting techniques. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98: 704–711.
Kumekawa, N., H. Ohtsubo & E. Ohtsubo, 1999. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of gypsy-type retrotransposons in the plant kingdom. Genes Genet. Syst. 74: 299–307.
Kumekawa, N., H. Ohtsubo, T. Horiuchi & E. Ohtsubo, 1999. Identification and characterization of novel retrotransposons of the gypsy type in rice. Mol. Gen. Genet. 260: 593–602.
Motohashi, R., E. Ohtsubo & H. Ohtsubo, 1997. Structures and distribution of p-SINE1 members in rice genomes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95: 359–368.
Nakajima, R., K. Noma, H. Ohtsubo & E. Ohtsubo, 1996. Identification and characterization of two tandem repeat sequences (TrsB and TrsC) and a retrotransposon (RIRE-1) as genome-general sequences in rice. Genes Genet. Syst. 71: 373–382.
Nei, M. & W.H. Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 5269–5273.
Noma, K., R. Nakajima, H. Ohtsubo & E. Ohtsubo, 1997. RIRE-1, a retrotransposon from wild rice Oryza australiensis. Genes Genet. Syst. 72: 131–140.
Ohtsubo, H., M. Umeda & E. Ohtsubo, 1991. Organization of DNA sequences highly repeated in tandem in rice genomes. Jpn. J. Genet. 66: 241–254.
Pearce, S.R., C. Stuart-Rogers, M.R. Knox, A. Kumar, T.H.N. Ellis & A.J. Flavell, 1999. Rapid isolation of plant Ty1-copia group retrotransposon LTR sequences for molecular marker studies. Plant J. 19: 711–717.
Smyth, D.R., 1991. Dispersed repeats in plant genomes. Chromosoma 100: 355–359.
Sokal, R.R. & C.D. Michener, 1958. A statistic method for evaluating systematic relationships. Univ. Kans. Sci. Bull. 28: 1409–1438.
Suoniemi, A., J. Tanskanen & A.H. Schulman, 1998. Gypsy-like retrotransposons are widespread in the plant kingdom. Plant J. 13: 699–705.
Tateoka, T., 1962. Taxonomic studies of Oryza. II. Several species complexes. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 76: 165–173.
Tenzen, T., Y. Matsuda, H. Ohtsubo & E. Ohtsubo, 1994. Transpositions of Trn1 in rice genomes to 5-PuTAPy-3, duplicating the TA sequence. Mol. Gen. Genet. 245: 441–448.
Vaughan, D.A., 1989. The genus Oryza L.: Current Status of Taxonomy. IRRI Res. Paper Series 138.
Vaughan, D.A., 1994. The Wild Relatives of Rice. A Genetic Resources Handbook. IRRI, P.O. Box 933, 1099 Manila, Philippines.
Vershinin, A.V. & T.H.N. Ellis, 1999. Heterogeneity of the internal structure of PDR1, a family of Ty1/copia-like retrotransposons in pea. Mol. Gen. Genet. 262: 703–713.
Uozu, S., H. Ikehashi, N. Ohmido, H. Ohtsubo, E. Ohtsubo & K. Fukui, 1997. Repetitive sequences: cause for variation in genome size and chromosome morphology in the genus Oryza. Plant Mol. Biol. 35: 791–799.
Xiong, Y. & T. H. Eickbush, 1990. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 9: 3353–3362.
Zhang, H.B. & R.A. Wing, 1997. Physical mapping of the rice genome with BACs. Plant Mol. Biol. 35: 115–127.
Zhao X., T. Wu, Y. Xie & R. Wu, 1989. Genome specific repetitive sequences in the genus Oryza. Theor. Appl. Genet. 78: 201–209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shcherban, A.B., Vaughan, D.A. & Tomooka, N. Isolation of a new retrotransposon-like DNA sequence and its use in analysis of diversity within the Oryza officinalis. Genetica 108, 145–154 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004165903202
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004165903202