Abstract
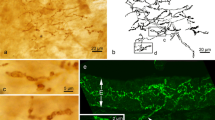
We have studied the postnatal development of the intrinsic nervous system in the circumvallate papilla–vonEbner gland complex using NADPH-diaphorase cytochemistry, immunocytochemistry (for nitric oxide synthase-1 and α-internexin) and electron microscopy. In rats sacrificed in their first day post partum (1 p.p.), only isolated NADPH-diaphorase positive neurons were visible in the organ. At 2 p.p., a small group of neurons was visible at the base of the papillae and positive neurons formed short chains close to the developing glandular tubules. In the following days, the NADPH-diapharase positive cells increased in number and nerve fibres were associated to small ganglia located at the base of the papilla or in the gland. After the first week of extrauterine life, the intrinsic nervous system was similar to the intrinsic system of adult animals. An immunocytochemical positivity for nitric oxide synthase-1 appeared at 4 p.p. in neurons located in the gland and at 7 p.p. in cells located at the base of the papilla. Immunocytochemical staining for α-internexin showed that at 1 p.p. developing nerve fibres were present in the connective tissue of the tongue's muscle layer. At 2–3 p.p., developing nerve fibres were also present at the bases and in the core of the papilla. In the following days, the positivity for α-internexin was reduced and one week after birth was virtually absent. Ultrastructural examination revealed that since 1 p.p. isolated neurons can be found at the base of the papilla. In conclusion, the intrinsic nervous system originates from neurons present in the organ at the birth which, in the first days, undergo a biochemical and morphological maturation while the nerve fibres rapidly grow. These findings support the hypothesis that the intrinsic nervous system of the circumvallate papilla has a role in the maturation of the vonEbner gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Bradley RM, Mistretta CM, Bates CA, Killackey HP (1985) Transganglionic transport of HRP from the circumvallate papilla of the rat. Brain Res 361: 154-161.
Field RB, Hand AR (1987) Secretion of lingual lipase and amylase from rat lingual serous glands. Am J Physiol 253: G217-225.
Fitzgerald MJT, Alexander RW (1969) The intramuscular ganglia of the cat's tongue. J Anat 105: 27-46.
Gairns FW, Garven HSD (1952) Ganglion cells in the mammalian tongue. J Physiol Lond 118: 53-54.
Goyal RK, Hirano I (1996) The enteric nervous system. N Eng J Med 334: 1106-1115.
Graziadei PPC, Monti Graziadei GA (1978) Observations on the ultrastructure of ganglion cells in the circumvallate papilla of rat and mouse. Acta Anat 100: 289-305.
Hamosh M, Burns WA (1977) Lypolitic activity of human lingual glands (Ebner). Lab Invest 37: 603-608.
Kaplan MP, Chin SSM, Fliegner KH, Liem RKH (1990) Internexin, a novel neuronal intermediate filament protein, precedes the low molecular weight neurofilament protein (nf-l) in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci 10: 2735-2748.
Kirchgessner AL, Gershon MD (1990) Projections of sub mucosal neurons to the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig intestine: in vitro tracing of microcircuits by retrograde and anterograde transport. J Comp Neurol 227: 487-498.
Kock K, Blaker M, Schmale H (1992) Postnatal development of von Ebner's glands: accumulation of a protein of the lipocalin superfamily in taste papillae of rat tongue. Cell Tiss Res 267: 313-320.
Lindemann B, Gilbertson TA, Kinnamon SC (1999) Amiloride sensitive sodium channels in taste. In: Benos DJ, ed. Amiloride Sensitive Sodium Channels: Physiology and Functional Diversity. San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 315-336.
Matini P, Mayer B, Faussone-Pellegrini MS (1997) Neurochemical differentiation of rat enteric neurons during pre-and postnatal life. Cell Tiss Res 288: 11-23.
Pham T, Gershon MD, Rothman TP (1991) Time of origin of neurons in the murine enteric nervous system: sequence in relation to phenotype. J Comp Neurol 314: 789-798.
Remak R. (1852) Uber peripherische ganglien an den nerven des nahrungsrohrs. Arch Anat Physiol Wissensch 17: 56-62.
Rothman TP, Gershon MD (1982) Phenotypic expression in the developing murine enteric nervous tissue. J Neurosci 2: 381-393.
Sbarbati A, Crescimanno C, Benati D, Osculati F (1998) Solitary chemosensory cells in the developing chemoreceptorial epithelium of the vallate papilla. J Neurocytol 27: 631-635.
Sbarbati A, Crescimanno C, Osculati F (1999a) The anatomy and the functional role of the circumvallata papilla/von Ebner gland complex. Med Hyp 53: 40-44.
Sbarbati A, Crescimanno C, De Rossi V, Bernardi P, Osculati F (1999b) NADPH-diaphorase and nos-1 positive ganglion cells are found in the vallate papilla/von Ebner gland complex. Histochem J 31: 417-424.
Sbarbati A, Crescimanno C, Bernardi P, Osculati F (1999c) ?-Gustducin-immunoreactive solitary chemosensory cells in the developing chemoreceptorial epithelium of the rat vallate papilla. Chem Senses 24: 469-472.
Sbarbati A, Crescimanno C, Benati D, Bernardi P, Romagnoli S, Osculati F (1999d) Intra-epithelial lipids in the dorsoposterior area of the tongue in new-born rats. Arch Oral Biol 44: 129-134.
Schmale H, Holtgreve-Grez H, Cristiansen H (1990) Possible role for salivary gland protein in taste reception indicated by homology to lipophilic-ligand carrier proteins. Nature 343: 366-369.
Schmale H, Ahlers C, Blaker M, Kock K, Spielman AI (1993) Perireceptor events in taste. Ciba Found Symp 179: 167-180.
Toto PD, Nadimi H, Martinez R (1993) von Ebner gland. An immunohistochemical study. Ann NY Acad Sci 694: 322-324.
Van Ginneken C, Van Meir F, Sommereyns G (1998) Nitric oxide synthase expression in enteric neurons during development in the pig duodenum. Anat Embryol 198: 399-408.
Witt M, Reutter K (1998) Innervation of developing human taste buds. An immunohistochemical study. Histochem Cell Biol 109: 281-291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sbarbati, A., Crescimanno, C., Bernardi, P. et al. Postnatal Development of the Intrinsic Nervous System in the Circumvallate Papilla–vonEbner Gland Complex. Histochem J 32, 483–488 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004144317336
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004144317336