Abstract
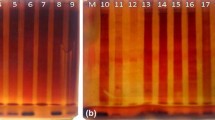
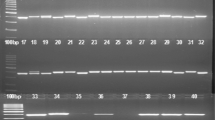
Forty five Pisum sativum cultivars were analysed by isozyme electrophoresis with the objective to find protein markers for exact and reproducible discrimination of individual genotypes. The combination of six enzyme systems (acid phosphatase, amylase, esterase, leucine aminopeptidase, shikimate dehydrogenase and phosphoglucomutase) with two electrophoretic techniques (NATIVE-PAGE, isoelectric focusing) and use of seed and leaf tissue enabled to identify all 45 studied cultivars. Critical factors which may affect utilization of isozyme electrophoresis for commercial applications in pea breeding and seed production and testing are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almgard, G., 1970. Cultivar distinction by means of isozyme technique in Pisum. Pisum Newslet 2: 9.
Almgard, G. & K. Ohlund, 1970. Inheritance and location of a biochemical character in Pisum. Pisum Newslet 2: 9.
Bell, J.A. & D.W. Simpson, 1994. The use of isoenzyme polymorphism as an aid for cultivar identification in strawberry. Euphytica 77: 113–117.
Chase, C.D., Ortega, V.M. & C.E. Vallejos, 1991. DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism correlate with isozyme diversity in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Theor Appl Genet 81: 806–811.
Cisneros, P.L. & C.F. Quiros, 1995. Variation and phylogeny of the triploid cultivated potato Solanum chaucha Juz. et Buk. based on RAPD and isozyme markers. Genet Resources and Crop Evolution 42: 373–386.
Gepts, P., 1993. The use of molecular and biochemical markers in crop evolution studies. Evolutionary Biology 27: 51–94.
Gepts, P., 1995. Genetic markers and core collections. In: T., Hodgkin, A.H.D. Brown, T.J.L. van Hintum & E.A.V. Morales (Eds.), Core Collections of Plant Genetic Resources, pp. 127–146. J. Wiley and Sons, Chichester.
Griga, M., A. Březinová, V. Motyka, J. Holík, E. Zažímalová, M. Kamínek & J. Stejskal, 1996. Endogenous phytohormone and protein changes connected with early somatic embryogenesis of soybean. Biologia 51 (Suppl. 4): 7.
Griga, M. & J. Stejskal, 1994. Micropropagation of pea (Pisum sativum L.)-in vitro system and its practical applications. In: P.J. Lumsden, J.R. Nicholas & W.J. Davies (Eds.), Physiology, Growth and Development of Plants in Culture, pp. 278–283. Kluwer Acad Publ, Dordrecht-Boston-London, 1994.
Griga, M., J. Stejskal & K. Beber, 1995. Analysis of tissue culture-derived variation in pea (Pisum sativum L.)-preliminary results. Euphytica 85: 335–339.
Havey, M.J. & F.J. Muehlbauer, 1989. Linkages between restriction fragment length, isozyme, and morphological markers in lentil. Theor Appl Genet77: 395–401.
Hoey, B.K., K.R. Crowe, V.M. Jones & N.O. Polans, 1996. A phylogenetic analysis of Pisum based on morphological characters, and allozyme and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 92: 92–100.
Parzysz, H., L. Gruchala & J. Przybylska, 1985. Isoenzyme variation in the genus Pisum. III. Electrophoretic patterns of esterases from cotyledons of ungerminated seeds. Genetica Polonica 26: 297–301.
Parzysz, H. & J. Przybylska, 1984. Isoenzyme variation in the genus Pisum. II. Electrophoretic patterns of alcohol dehydrogenase and isocitrate dehydrogenase from cotyledons of ungerminated seeds. Genetica Polonica 25: 255–260.
Pošvec, Z., L. Švábová & M. Griga, 1999. Characterization of pea differential standards with declared reaction to Fusarium oxysporum races by selected isozyme spectra. In: Second Intern. Fusarium Biocontrol Workshop, p. 18. I.N.R.A.-C.M.S.E., Dijon, France.
Przybylska, J., 1986. Identification and classification of the Pisum genetic resources with the use of electrophoretic protein analysis. Seeds Sci Technol 14: 529–543.
Przybylska, J., S. Blixt, H. Parzysz & Z. Zimniak-Przybylska, 1982. Isoenzyme variation in the genus Pisum. I. Electrophoretic patterns of several enzyme systems. Genetica Polonica 23: 103–121.
Przybylska, J., E. Pagowska & J. George, 1989. Isoenzyme variation in the genus Pisum. VI. Further electrophoretic analysis of different enzyme systems. Genetica Polonica 30: 129–138.
Samec, P., Z. Pošvec, J. Stejskal, V. Našinec & M. Griga, 1998. Cultivar identification and relationships in Pisum sativum L. based on RAPD and isoenzymes. Biol Plant 41: 39–48.
Stejskal, J. & M. Griga, 1995. Comparative analysis of some isozymes and proteins in somatic and zygotic embryos of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). J Plant Physiol 146: 497–502.
Stejskal, J., Z. Pošvec & M. Griga, 1996. Utilization of isoenzyme and protein spectra for identification of pea (Pisum sativum L.) cultivars. Biologia (Bratislava) 51: 99.
Šuška, M., 1993. Isoenzymes from pea (Pisum) leaves and their use in cultivar identification. Genet. a Šlecht. (Prague) 29: 27–33.
Swiecicki, W.K. & B. Wolko, 1987. Application of electrophoretic methods of isozymes separation to genetical characterization of pea (Pisum sativum L. s. lat.) cultivars. Genetica Polonica 28: 89–99.
Torres, A.M., J. Satovic, J. Canovas, A. Martín & J.I. Cubero, 1994. Faba bean mapping with trisomics. Linkage among morphological, isozyme, and RAPD markers. In: J.V. van Ooijen & J. Jansen (Eds.), Biometrics in Plant Breeding: Applications of Molecular Markers, pp. 259–260. CPRO-DLO,Wageningen, the Netherlands, 1994.
Vallejos, C.E., 1983. Enzyme activity staining. In: S.D. Tanksley & T.J. Orton (Eds.), Isozymes in plant genetics and breeding, part A, pp. 469–516. Elsevier, Amsterdam-Oxford-New York.
Weeden, N.F., 1985. An isozyme linkage map for Pisum sativum. In: P.D. Hebblethwaite, M.C. Heath & T.C.K. Dawkins (Eds.), The Pea Crop-A Basis for Improvement, pp. 55–66. Butterworths, London.
Weeden, N.F., M. Ambrose & W. Swiecicki, 1993. Pisum sativum, Pea. In: S.J. O'Brien (Ed.), Genetic maps. (Locus maps of complex genomes, book 6, pp. 6.24–6.34). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Weeden, N.F. & G.A. Marx, 1984. Chromosomal locations of twelve isozyme loci in Pisum sativum. J Heredity 75: 365–370.
Weeden, N.F. & G.A. Marx, 1987. Further genetic analysis and linkage relationships of isozyme loci in the pea. Confirmation of the diploid nature of the genome. J Heredity 78: 153–159.
Weeden, N.F. & B. Wolko, 1990. Linkage map for the garden pea (Pisum sativum) based on molecular markers. In: S.J. O'Brien (Ed.), Genetic Maps, 5th edn., pp. 6.106–6.112. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Wolko, B., M. Krzakowa & W.K. Swiecicki, 1985. Leucine aminopeptidase (LAP-2) variability in the genus Pisum. Pisum Newslet 17: 86–88.
Zimniak-Przybylska, Z. & J. Przybylska, 1989. Isoenzyme variation in the genus Pisum. V. Electrophoretic phenotypes of seed amylases in the primitive forms of P. sativum from Caucasia and the Lower Volga area. Genetica Polonica 30: 61–66.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pošvec, Z., Griga, M. Utilization of isozyme polymorphism for cultivar identification of 45 commercial peas (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 113, 249–256 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003967315213
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003967315213