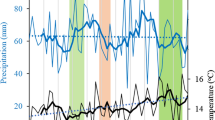
Abstract
Total phosphorus budget and studies on dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations have been made for a small, hypertrophic, shallow lake, Little Mere, for a year prior to effluent diversion and three years following effluent diversion. Considerable resilience in phosphate concentrations was expected from experiences elsewhere with shallow lakes. Pre-diversion clear water was associated with a high dominance of large-bodied Daphnia magna due to an absence of fish in the relatively low-oxygen conditions. Unexpectedly, the phosphorus and nitrogen concentrations declined rapidly after effluent diversion (92% and 91%, respectively) and the lake has maintained the pre-diversion state of clear water. Little Mere provides evidence for importance of biological structure in determining the extent of chemical resilience. The laboratory sediment release rates of N and P were considerably higher than the net release rates, calculated from mass balance of the lake chemistry, as found elsewhere. Probably, lack of phytoplankton sedimentation, phytoplankton and plants uptake were the reasons for several fold high release rates that were observed in laboratory experiment. Therefore, it appeared to approach the gross release rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beklioglu, M. & B. Moss, 1996a. Existence of a macrophytedominated clear water state over a wide range of nutrient concentrations in a small shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 337: 93-106.
Beklioglu, M. & B. Moss, 1996b. Mesocosm experiments on the interaction of sediment influence, fish predation and aquatic plants with the structure of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities. Freshwat. Biol. 36: 315-325.
Boers, P. C. M., 1986. Studying the phosphorus release from the Loosdrecht lakes sediment using continuous flow system. Hydrobiol. Bull. 20: 5-7.
Boström, B., M. Jansson & C. Forsberg, 1982. Phosphorus release from lake sediments. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 18: 5-59.
Carpenter, S. R., J. F. Kitchell & J. R. Hodgson, 1985. Cascading trophic interactions and lake productivity. BioScience 35: 634-639.
Carvalho, L., 1994. Top-down control of phytoplankton in a shallow hypertrophic lake: Little Mere, England. Hydrobiologia 275/276 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 94): 53-63.
Carvalho, L., M. Beklioglu & B. Moss, 1995. Changes in a deep lake following sewage diversion - a challenge to the orthodoxy of external phosphorus control as a restoration strategy. Freshwat. Biol. 34: 399-410.
Chaney, A. L & E. P. Morbach, 1962. Modified reagents for the determination of urea and ammonia. Clin. Chem. 8: 130-132.
Christensen, P. B., L. P. Nielsen, J. J. Sørensen & N. P. Recsbech, 1990. Denitrification in nitrate-rich streams: diurnal and seasonal variation related to benthic oxygen metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 640-651.
Cullen, P. & C. Forsberg, 1988. Experience with reducing point sources of phosphorus to lakes. Hydrobiologia 170 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 48): 321-336.
Edmonson, W. T., 1985. Recovery of Lake Washington from eutrophication. Proceedings from lakes pollution and recovery, Rome 15-18 April, 228-234.
Eriksson, P. G. & S. E. B. Weisner, 1996. Functional differences in epiphytic microbial communities. Freshwat. Biol. 36: 555-562.
Hamilton, D. P. & S. F. Mitchell, 1996. An empirical model for sediment resuspension in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 317: 209-220.
Holden, A. V. & L. A. Caines, 1974. Nutrient chemistry of Loch Leven, Kinross. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. B 74: 101-121.
James, W. F. & J. W. Barko, 1990. Macrophyte influences on the zonation of sediment accretion and composition. Arch. Hydrobiol. 120: 120-129.
Jensen, J. P., E. Jeppesen, P. Kristensen, P. B. Christensen & M. Søndergaard, 1992. Nitrogen loss and denitrification as studied in relation to reductions in nitrogen loading in a shallow, hypertrophic lake (Lake Søbygaard, Denmark). Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 77: 29-42.
Jeppesen, E., P. Kristensen, J. P. Jensen, M. Soøndergaard, E. Mortensen & T. Lauridsen, 1991. Recovery resilience following a reduction in external phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: duration, regulating factors and methods for overcoming resilience. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 48: 127-148.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søondergaard, T. L. Lauridsen, L. J. Pedersen & L. Jensen, 1997. Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia 342/343 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 119): 151-161.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, Ole Sortkjær, E. Mortensen & P. Kristensen, 1990. Interactions between phytoplankton, zooplankton and fish in a shallow hypertrophic lake: a study of phytoplankton collapses in Lake Søbygaard, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 191 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 53): 149-164.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, E. Mortensen, A.M. Hansen & T. Jørgensen, 1998a. Major perturbation in biological structure and dynamics of a shallow hypertrophic lake following a reduction in sewage loading: an 18-year study in Lake Soøbygaard, Denmark. Ecosystem 1: 250-267.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, T. Lauridsen, P. H. Møller & K. Sandby, 1998b. Changes in nitrogen retention in shallow eutrophic lakes following a decline in density of cyprinids. Arch. Hydrobiol. 142: 129-151.
Johnes, P. J. & T. P. Burt, 1991. Water quality trends in the Windrush catchment: nitrogen speciation and sedimeent interactions. In Sediment and Stream Water Quality in a Changing Environment: Trends and Explanation. International Association of Hydrological Science Publ. no. 203.
Kristensen, P. & H. O. Hansen, 1994. European rivers and lakes. Assessment of their environmental state. European Environmental Agency: 122 pp.
Lauridsen, T. L., E. Jeppesen & F. Ø. Andersen, 1993. Colonisation of submerged macrophytes in shallow fish manipulated Lake Veaæng: Impact of sediment composition and waterfowl grazing. Aquat. Bot. 46: 1-15.
Lijklema, L., 1985. Nutrient cycling in lakes. Proceedings of the Dutch-Hungarian Symposium on Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes, Siofok.
Mackereth, F. J. H., J. Heron & J. F. Talling, 1978. Water Analysis: some methods for limnologists. Freshwater Biological Association Scientific Publication, 36.
Malthus, T. J., E. F. H. Best & A. G. Dekker, 1990. An assessment of the importance of emergent and floating-leaved macrophytes to trophic status in the Loosdrecht lakes (The Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 191 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 53): 257-263.
Marsden, S., 1989. Lake restoration by reducing external phosphorus loading: the influence of sediment phosphorus release. Freshwat. Biol. 21: 139-162.
Monthly Weather Report, 1990-1994. The Meteorological Office, Manchester Ringway Airport.
Moss, B., 1990. Engineering and biological approaches to the restoration from eutrophication of shallow lakes in which aquatic plant communities are important components. Hydrobiologia 200/201 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 61): 367-378.
Moss, B., M. Beklioglu, L. Carvalho, S. Kilinç, S. McGowan & D. Stephen, 1997. Vertically-challenged limnology; contrasts between deep and shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 342/343 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 119): 257-267.
Moss, B., J. Stansfield & K. Irvine, 1990. Problems in the restoration of a hypertrophic lake by diversion of a nutrient-rich inflow. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 24: 568-572.
North West Water Authority (NWWA), 1983. The effects of Mere STW on Rostherne Mere. NWWA Report River Management Group (South) Scientists Department Ref. No. TSS 83/7.
Ozimek, T., E. Van Donk & R. D. Gulati, 1990. Can macrophytes be useful in biomanipulation of lakes? Lake Zwemlust example. Hydrobiologia 200/201 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 61): 399-407.
Reinertsen, H. & Y. Olsen, 1984. Effects of fish elimination on the phytoplankton community of a eutrophic lake. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 649-657.
Sas, H., 1989. Lake restoration by reduction of nutrient loading. Expectation, experience, extrapolation. Acad. Ver. Richarz Gmbh: 497 pp.
Scheffer, M., S. H. Hosper, M.-L. Meijer, B. Moss & E. Jeppesen, 1993. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. TREE 8: 275-279.
Shapiro, J. & D. I. Wright, 1984. Lake restoration by biomanipulation: Round lake, Minnesota, the first two years. Freshwat. Biol. 14: 371-383.
Sinke, A. J. C., 1992. Phosphorus dynamics in the sediment of a eutrophic lake. Roefschrift Wageningen: 120 pp.
Søndergaard, M., 1989. Phosphorus release from the hypertrophic lake sediment: experiments with intact sediment cores in a continuous flow system. Arch. Hydrobiol. 116: 45-59.
Søndergaard, M., E. Jeppesen, P. Kristensen & O. Sortkjær, 1990. Interactions between sediment and water in a shallow and hypertrophic lake: a study on phytoplankton collapses in Lake Søbygaard, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 53: 139-148.
Søndergaard, M., P. Kristensen & E. Jeppesen, 1993. Eight years of internal phosphorus loading and changes in the sediment phosphorus profile of Lake Søbygaard, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 253: 345-356.
Soderlund, R., L. Granat & H. Rodhe, 1985. Nitrate in precipitationa presentation of data from the European air chemistry network. Dept. of Meteorology, University of Stockholm Report cm-69.
Stephen, D., B. Moss & G. Phillips, 1997. Do rooted macrophytes increase sediment phosphorus release? Hydrobiologia 342/343 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 119): 27-34.
Sutcliffe, D. W., T. R. Carrick, J. Heron, E. Rigg, J. F. Talling, C. Woof & J. W. G. Lund, 1982. Long-term and seasonal changes in chemical composition of precipitation and surface waters of lakes and tarns in the English Lake District. Freshwat. Biol. 12: 451-506.
Vollenweider, R. A, 1975. Input-output models; special reference to the phosphate loading concept in limnology. Schweiz Z. Hydrol. 37: 53-84.
Weisner, S., G. Eriksson, W. Graneli & L. Leonardson, 1994. Influence of macrophyte on nitrate removal in wetlands. Ambio 23: 363-366.
Williams, R. J. B., 1976. Chemical composition of rain, land drainage and borehole water from Rothamstead, Broom's Barn, Saxmundham and Woburn experimental stations. Tech. Bull. Minist. Agr. Fish. Fd. 32: 174-200. Her Majesty's Stationary Office, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beklioglu, M., Carvalho, L. & Moss, B. Rapid recovery of a shallow hypertrophic lake following sewage effluent diversion: lack of chemical resilience. Hydrobiologia 412, 5–15 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003705518774
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003705518774