Abstract
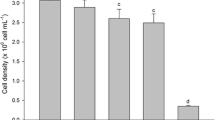
Defence mechanisms against Cu toxicity were examined in two dominant Enteromorpha species from two coastal water types. The macroalgae were collected at three locations in the eulittoral of the Scheldt Estuary (Netherlands, Belgium) and the Thermaikos Gulf (Greece). For 10 days E. prolifera (Scheldt) and E. linza (Thermaikos) were incubated in seawater media of different salinities: 6, 9, 23 psu and 25, 30, 35 psu, respectively. In one series, media were enriched with 100 μg Cu l-1; responses were compared with those in controls with no extra Cu added. Enteromorpha, which is frequently used as a monitor species for heavy metal contamination, had relatively high Cu tissue levels (0.5–3.8 μmol Cu gdwt-1). Cu levels in E. prolifera controls (Scheldt) decreased with salinity; this was not the case with Cu levels in E. linza controls (Thermaikos). During the 10-d incubation algal protein contents and tissue Cu were rather stable. In E. linza (Thermaikos) algal protein contents were significantly lower than those of E. prolifera (Scheldt), although there was no indication for nitrogen limitation in E. linza. E. linza also had much lower glutathione pools than E. prolifera. Only under acute Cu stress (metal addition) did E. prolifera synthesise metal-binding thiols (phytochelatins). Phytochelatin pools are not suitable as an indicator of the Cu levels in these algae. The glutathione redox ratio GSH:(GSH + 0.5GSSG) was used as an indicator of (Cu-induced) oxidative stress. In E. prolifera (Scheldt) this ratio decreased with algal Cu content (P <0.05), from ~0.5 to ~0.2. The average glutathione ratios in Enteromorpha from the Scheldt and Thermaikos showed some oxidative stress induction with increasing algal Cu contents, however more clearly if Cu was added. As this redox ratio can also be influenced by environmental factors such as irradiance and desiccation, it may not be useful as an indicator for Cu-induced oxidative stress in situ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, S. B., 1992. Effects of supplemental U.V.-B radiation on photosynthetic pigment, protein and glutathione contents in green algae. Envir. Exp. Bot. 32: 137–143.
Anderson, M. E., 1985. Tissue glutathione. In Greenwald, R. A. (ed.), Handbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research. CRC Press, Boca Raton: 317–323.
Brown, L. N., M. G. Robinson & B. D. Hall, 1988. Mechanisms for copper tolerance in Amphora coffaeformis - internal and external binding. Mar. Biol. 97: 581–586.
Clayton, J. R., Q. Dortch, S. S. Thoresen & S. I. Ahmed, 1988. Evaluation of methods for the separation and analysis of proteins and free amino acids in phytoplankton samples. J. Plankton Res. 10: 341–359.
Corzo, A. & F. X. Niell, 1991. C/N ratio in response to nitrogen supply and light quality in Ulva rigida C. Agardh (Chlorophyta: Ulvophyceaea). Sci. Mar. 55: 405–411.
De Knecht, J. A., P. L. M. Koevoets, J. A. C. Verkleij & W.H.O. Ernst, 1992. Evidence against a role for phytochelatins in naturally selected increased cadmium tolerance in Silene vulgaris (Moench) Garcke. New Phytol. 122: 681–688.
De Knecht, J. A., N. Van Baren, W. M. Ten Bookum, H. W. N. F. Sang, P. L. M. Koevoets, H. Schat & J.A.C. Verkleij, 1995. Synthesis and degradation of phytochelatins in cadmium-sensitive and cadmium-tolerant Silene vulgaris. Plant Sci. 106: 9–18.
De Vos, C. H. R., M. J. Vonk, R. Vooijs & H. Schat, 1992. Glutathione depletion due to copper induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalis. Plant Physiol. 98: 853–858.
Gekeler, W., E. Grill, E. Winnacker & M. H. Zenk, 1988. Algae sequester heavy metals via synthesis of phytochelatin complexes. Arch. Mikrobiol. 150: 197–202.
Gledhill, M., M. Nimmo, S. J. Hill & M. Brown, 1997. The toxicity of copper (II) species to marine algae, with particular reference to macroalgae. J. Phycol. 33: 2–11.
Haritonidis, S., 1978. A survey of the marine algae of Thermaikos Gulf, Thessaloniki, Greece. I. Distribution and seasonal periodicity. Bot. mar. XXI: 527–535.
Haritonidis, S. & P. Malea, 1995. Seasonal and local variation of Cr, Ni and Co concentrations in Ulva rigida C. Agardh and Enteromorpha linza (Linneaus) from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Envir. Pollut. 89: 319–327.
Haritonidis, S., 1996. Chapter 17: Greece. In Schramm, W. & P.H. Nienhuis (eds), Marine Benthic Vegetation: Recent Changes and the Effects of Eutrophication, Ecological Studies 123. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg: 403–419.
Ho, Y. B., 1990. Ulva lactuca as bioindicator of metal contamination in intertidal waters in Hong Kong. Hydrobiologia 203: 73–81.
Koeman, R. P. T., 1985. The taxonomy of Ulva Linnaeus, 1753, and Enteromorpha, Link, 1820 (Chlorophyceae) in the Netherlands. PhD Thesis, University Groningen, Netherlands, Van Tienderen Press: 1–201.
Miersch, J., F. Bärlocher, I. Bruns & G. J. Kraus, 1997. Effects of cadmium, copper, and zinc on growth and thiol content of aquatic hyphomycetes. Hydrobiologia 346: 77–84.
Müller M., M. Schirmer & J. Kettler, 1993. Use of Enteromorpha intestinalis (Chlorophyceae) for active biomonitoring of heavy metals in the Weser Estuary. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 27: 189–195.
Nassiri, Y., J. L. Mansot, J. Wery, T. Ginsburger-Vogel & J. C. Amiard, 1997. Ultrastructural and electron energy loss spectroscopy studies of sequestration mechanisms of Cd and Cu in the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Arch. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 33: 147–155.
Nieuwenhuize, J., Y. Maas & J. J. Middelburg, 1994. Rapid analysis of organic carbon and nitrogen in particulate materials. Mar. Chem. 45: 217–224.
Rajendran, K., P. Sampathkumar, C. Govindasamy, M. Ganesan, R. Kannan & L. Kannan, 1993. Levels of trace metals (Mn, Fe, Cu and Zn) in some Indian seaweeds. Mar. Poll. Bull. 26: 283–285.
Reed R. H. & L. Moffat, 1983. Copper toxicity and copper tolerance in Enteromorpha compressa (L.) Grev. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 69: 85–103.
Rijstenbil, J. W. & T. C. W. Poortvliet, 1992. Copper and zinc in estuarine water: chemical speciation and bioavailability to the marine planktonic diatom Ditylum brightwellii. Envir. Toxicol. Chem. 11: 1615–1625.
Rijstenbil, J. W, S. Haritonidis, P. Malea, J. van Drie & J. A. Wijnholds, 1993. Interactions of copper with trace metals and thiols in the macro-algae Enteromorpha prolifera (O.F. Müll) J. Ag., grown in water of the Scheldt Estuary (Belgium and S.W. Netherlands). Sci. Tot. Envir. Suppl. 1993: 539–549.
Rijstenbil, J. W., J. W. M. Derksen, L. J. A. Gerringa, T. C. W. Poortvliet, A. Sandee, M. van den Berg, J. van Drie & J. A. Wijnholds, 1994. Oxidative stress induced by copper: defense and damage in the marine planktonic diatom Ditylum brightwellii (Grunow) West, grown in continuous cultures with high and low zinc levels. Mar. Biol. 119: 583–590.
Rijstenbil, J. W. & J. A. Wijnholds, 1996. HPLC analysis of nonprotein thiols in planktonic diatoms: pool size, redox state and response to copper and cadmium exposure. Mar. Biol. 127: 45- 54.
Rijstenbil, J. W., F. Dehairs, R. Ehrlich & J. A. Wijnholds, 1998. Effect of the nitrogen status on copper accumulation and pools of metal-binding peptides in the planktonic diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. Aquat. Toxicol. 42: 187–209.
Robinson, N. J., 1989. Algal metallothioneins: secondary metabolites and proteins. J. appl. Phycol. 1: 5–18.
Say, P. J., I. G. Burrows & B. A. Whitton, 1990. Enteromorpha as a monitor of heavy metals in estuaries. Hydrobiologia 195: 119–126.
Seeliger, U. & C. Cordazzo, 1982. Field and experimental evaluation of Enteromorpha sp. as a quali-quantitative monitoring organism for copper and mercury in estuaries. Envir. Pollut. A 29: 197–206.
Siller-Cepeda, J. H., T. H. H. Chen & L. H. Fuchigami, 1991. High performance liquid chromatography analysis of reduced and oxidized glutathione in woody plant tissues. Plant Cell Physiol. 32: 1179–1185.
Smith, I. K., A. C. Kendall, A. J. Keys, J. C. Turner & P. J. Lea, 1985. The regulation of the biosynthesis of glutathione in leaves of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Sci. 41: 11–17.
Stauber, J. L. & T. M. Florence, 1987. Mechanisms of toxicity of ionic copper and copper complexes to algae. Mar. Biol. 94: 511- 519.
Stegenga, H. & I. Mol, 1983. Flora van de Nederlandse Zeewieren. KNNV Series 33. Erla Amsterdam Print: 1–263.
Steffens, J. C., D. F. Hunt & B. G. Williams, 1986. Accumulation of non-protein metal-binding polypeptides (gamma-glutamylcysteinyl) n-glycine in selected cadmium-resistent tomato cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 13879–13982.
Steffens, J. C., 1990. Heavy metal stress and the phytochelatin response. In Alscher, R.G. & J.R. Cumming (eds), Stress Responses in Plants: Adaptation and Acclimation Mechanisms, Vol. 12. Wiley & Liss Inc., New York, 17: 377–394.
Strickland, J. D. H. & T. R. Parsons, 1972. A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Fish. Res. Bd Can. Bull. 167: 1–311.
Sueur, S., C. M. G. van den Berg & J. P. Riley, 1982. Measurement of the metal complexing ability of exudates of marine macroalgae. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27: 536–543.
Vögeli-Lange, R. & G. J. Wagner, 1990. Subcellular localization of cadmium and cadmium-binding peptides in tobacco leaves. Implication of a transport function for cadmium-binding peptides. Plant Physiol. 92: 1086–1093.
Zolotukhina, E. Y. & E. E. Gavrilenko, 1990. Binding of copper, cadmium, zinc and manganese in proteins of aquatic macrophytes. Fyziologiya Rastenii 37: 651–658.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rijstenbil, J., Haritonidis, S., Malea, P. et al. Thiol pools and glutathione redox ratios as possible indicators of copper toxicity in the green macroalgae Enteromorpha spp. from the Scheldt Estuary (SW Netherlands, Belgium) and Thermaikos Gulf (Greece, N Aegean Sea). Hydrobiologia 385, 171–181 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003502428466
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003502428466