Abstract
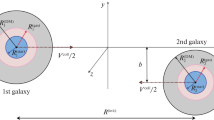
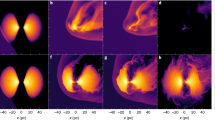
We study the tidal effects of a deeply penetrating collision between two spherical galaxies, one twice massive but less dense than the other, by numerical simulations. We consider the relative motion of the galaxies to be initially in a hyperbolic orbit. The collision parameters are so chosen that the primary (bigger) galaxy is just below the limit of disruption and the relative velocity of the pair is slightly in excess of the escape limit and the primary suffer greater tidal damage than the secondary. The primary develops a core halo structure and shows over all expansion while the secondary while the secondary shows contraction in the inner region and less significant expansion in the outer parts. The initially hyperbolic orbit is transformed into a parabolic orbit as a result of the collision. The result also indicate that the tidal interaction does not induce appreciable rotation in hyperbolic collision. We calculate the angle of deflection of the orbit and compare it with that computed using analytical work. The numerical work shows larger angle of deflection which is attributed to the large tidal effects of the bigger galaxy in the interpenetrating collision.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar, L.A. and White, S.D.M.: 1985, Astrophys.J. 295, 374.
Barnes, J.E. and Hut, P.: 1986, Nature 324, 446.
Barnes, J.E.: 1988, Astrophys.J. 331, 669.
Chatterjee, T.K.: 1984, Astrophys.Space Sci. 106, 309.
Dekel, A., Lecar, M. and Shaham, J.: 1980, Astrophys.J. 241, 946.
Devdas Rao, P., Ramamani, N. and Alladin, S.M.: 1987, J.Astrophys.Astron. 8, 17.
Farouki, R.T. and Shapiro, S.L.: 1982, Astrophys.J. 259, 103.
McGlynn, T.A.: 1990, Astrophys.J. 384, 515.
Miller, R.H. and Smith, B.F.: 1980, Astrophys.J. 235, 421.
Miller, R.H.: 1986, Astron.Astrophys. 167, 41.
Namboodiri, P.M.S. and Kochhar, R.K.: 1990, Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc. 243, 276.
Narasimha Rao, N., Alladin, S.M. and Narasimhan, K.S.V.S.: 1994, Celest.Mech.Dyn.Astron. 58, 65.
Narasimhan, K.S.V.S. and Alladin, S.M.: 1982, Bull.Astron.Soc.India 10, 244.
Navarro, J.F.: 1989, Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc. 239, 257.
Negroponte, J. and White, S.D.M.: 1983, Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc. 205, 1009.
van Albada, T.S. and van Gorkom, J.H.: 1977, Astron.Astrophys. 54, 121.
Villumsen, J.V.: 1982, Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc. 199, 493.
White, S.D.M.: 1978, Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc. 184, 185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namboodiri, P., Sastry, K. & Narasimhan, K. N-Body Simulation of a Deeply Penetrating Collision Between Unequal Galaxies. Astrophysics and Space Science 259, 433–444 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001769410754
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001769410754