Abstract
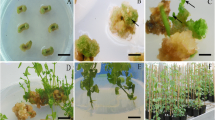
Excised embrya and subsequently divided embrya of Podophyllum peltatum were cultured on the Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with different growth regulators, because traditional methods of breaking seed dormancy failed. The growth of excised embrya was stimulated by 1 or 0.1 mg dm-3gibberellic acid (GA3), 0.1 mg dm-3 GA3 + 0.2 mg dm-3 kinetin (kin), or 0.2mg dm-3 kin. GA3 (1 mg dm-3) showed the best effect; after 5 weeks the plantlets had 1.5 - 2 cm long cotyledons, 5 - 6 cm long roots, 88 % of embrya germinated and developed further. The addition of 0.5 mg dm-3 zeatin + 0.2 mg dm-3 naphtaleneacetic acid (NAA), 0.2 mg dm-3 NAA, and 1 mg dm-3 kinetin inhibited the growth of embrya. 1 mg dm-3 kinetin + 0.1 mg dm-3 NAA, 0.1 mg dm-3 zeatin and 0.2 mg dm-3 6-benzylaminopurine resulted in a compact appearance of plantlets and a lower germination rate. Divided embryo cultures produced plantlets via somatic embryogenesis which occurred only on the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid containing media. The maturation of somatic embrya was observed on media without any auxin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumugam, N., Bhojwani Sant, S.: Somatic embryogenesis in tissue cultures of Podophyllum hexandrum.-Can. J. Bot. 68: 487–490, 1990.
Badhwar, R.L., Sharma, B.K.: A note on the germination of Podophyllum seeds.-Indian Forest Res. Inst. (Dehra Dun) Rep. 1963: 445–447. 1963.
Barykina, R.P.: [Characterization of ontogenesis phases of Podophyllum emodi and Podophyllum peltatum.]-Bot. Zh. 56: 921–931, 1971. [In Russ.]
Dos Santos, A.V.P., Outka, D.E., Cocking, E.C., Davney M.R.: Organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in tissue derived from leaf protoplasts and leaf explants of Medicago sativa.-Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 99: 261–270, 1980.
Fujii, Y.: Podophyllum spp: In vitro regeneration and the production of podophyllotoxin. In: Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry. Vol. 15. Pp. 362–375. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg 1991.
Gleddie, S.C., Keller, W., Setterfield, G.: Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf explants and cell suspesions of Solanum melongena (egg plant).-Can. J. Bot. 61: 656–666, 1991.
Lang, H., Kohlenbach, H., W.: Morphogenese in Kulturen isolierter Mesophyllzellen von Macleya cordata.-Sarita Prakaskan, Meerut 1975.
Rush, K.W., Russel, D.R.: Propagation of Podophyllum peltatum.-J. Mississippi Acad. Sci. 21(Suppl.), 1976.
Selivanova-Grodkova, E.A.: [Characterization of morphology and biology of Podophyllum hexandrum and Podophyllum peltatum L.]-Bot. Zh. 58: 273–284, 1973. [In Russ.]
Sondhal, M.R., Sharp, W.R.: High frequency induction of somatic embrya in cultured leaf explants of Coffea arabica.-Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 81: 395 408, 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadowska, A., Wiweger, M., Łata, B. et al. In vitro propagation of Podophyllum peltatum L. by the cultures of embrya and divided embrya. Biologia Plantarum 39, 331–336 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001089105961
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001089105961