Abstract
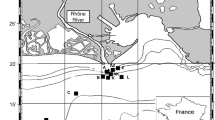
We investigated P-input by the Rhone river into the Mediterranean Sea taking into account P trapped in the surface sediment of the Gulf of Lions. Total phosphate concentration was determined every cm in the upper 10 cm-layer of sediments sampled at 11 stations in the Gulf of Lions during two cruises (March 1998 and January 1999). Two low downward gradients, one East–West and another North–South, with distance to the Rhone river mouth were found. Except at one station, total phosphate concentration in surface sediments was found to be constant with depth down to 10 cm. Values for individual stations ranged between 400 and 700 μg g−1 with an average value of 547 μg g−1 (st. dev. = 63 μg g−1) for the whole gulf. The low variability in total-P concentration in sediments is in contrast to the large variability in suspended matter load of the river Rhone and suggests the dominance of authigenic P removal mechanisms in P burial. The total P-pool in the upper 10 cm-layer of the sediments in the gulf was estimated at 562 kt, with about 80% trapped into the shelf and 20% into the slope. Annual P-deposition was estimated as 7.2–12.4 kt y−1, from the P-pool in the sediment and the sedimentation rates. This is equivalent to a previous estimation of the river Rhone input, estimated to be about 6.5–12.2 kt y−1. As the Rhone is the major river flowing into the Mediterranean Sea, total P in surface sediments of the Gulf of Lions should be taken into account in P-budgets at the scale of the Mediterranean Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrieux, F. & A. Aminot, 1997. A two-year survey of phosphorus speciation in the sediments of the Bay of Seine (France). Cont. Shelf Res. 17(10): 1229–1245.
Balzer, W., 1986. Forms of phosphorus and its accumulation in coastal sediments of Kieler Bucht. Ophelia 26: 19–35.
Bethoux, J. P., 1989. Oxygen consumption, new production, vertical advection and environmental evolution in theMediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. 36: 769–781.
Bethoux, J. P., P. Morin, C. Madec & B. Gentili, 1992. Phosphorus and nitrogen behaviour in the Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. 39(9): 1641–1654.
Bethoux, J. P., P. Morin, C. Chaumery, O. Connan, B. Gentili & D. Ruiz-Pino, 1998. Nutrients in the Mediterranean Sea, mass balance and statistical analysis of concentrations with respect to environmental change. Mar. chem. 63: 155–169.
Blomqvist, S., K. Hjellstrom & A. Sjosten, 1993. Interference from arsenate, fluoride and silicate when determining phosphate in water by the phosphoantimonylmolybdenum blue method. Int. J. Env. Anal. Chem. 54: 31–43.
Carpenter, R., T. M. Beasley, D. Zahnle & B. L. K. Somayajulu, 1987. Cycling of fallout Pu, 241Am, 137Cs and natural U, Th, 210Pb radionuclides in Washington continental slope sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 45: 1155–1172.
Charmasson, S., O. Radakovitch, M. Arnaud, P. Bouisset & A. S. Pruchon, 1998. Long-core profiles of 137Cs, 134Cs, 60Co and 210Pb in sediment near the Rhone river mouth (Northwestern Mediterranean). Estuaries 21: 367–378.
Coste, B., P. Le Corre & H. J. Minas, 1988. Re-evaluation of the nutrient exchanges in the Strait of Gibraltar. Deep Sea Res. 35(5): 767–775.
De Jong, A. L., N. T. De Oude, A. H. Smits & J. Volz, 1989. The phosphate load of the River Rhine 1975–1986. Aqua 38: 176–188.
Denis, L., 1999. Dynamique des flux d'oxygène et de sels nutritifs à l'interface eau-sédiment sur la marge continentale du Golfe du Lion (Méditerranée Nord Occidentale). PhD thesis, University of Aix-Marseille II: 129 pp.
Denis, L., C. Grenz, E. Alliot & M. Rodier, 2001. Temporal variability in dissolved inorganic nitrogen fluxes at the sediment–water interface and related annual budget on a continental shelf (NW Mediterranean). Oceanol. Acta 24(1): 85–97.
Diaz, F., P. Raimbault, B. Boudjellal, N. Garcia & T. Moutin, 2001. Early spring phosphorus limitation of primary productivity in a NW Mediterranean coastal zone (Gulf of Lions). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 211: 51–62.
Durrieu de Madron, X., A. Abassi, S. Heussner, A. Monaco, J. C. Aloisi, O. Radakovitch, P. Giresse, R. Buscail & P. Kerhervé, 2000. Particulate matter and organic carbon budgets for the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean). Oceanol. Acta 23(6): 717–730.
El Habr, H. & H. L. Golterman, 1987. Input of nutrients and suspended matter into the Golfe du Lion and the Camargue by the river Rhône. Sciences de l'eau 6: 393–402.
Eppley, R. W., E. H. Renger, E. L. Venrick & M. M. Mullin, 1973. A study of plankton dynamics and nutrient cycling in the central gyre of the North Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18: 534–551.
Fang, T. H., 2000. Partitioning and Behaviour of Different Forms of Phosphorus in the Tanshui Estuary and One of its Tributaries, Northern Taiwan. Estuar. coast. shelf Sci. 50(5): 689–701.
Fernex, F. E., C. Migon & J. R. M. Chisholm, 2001. Entrapment of pollutants in Mediterranean sediments and biogeochemical indicators of their impact. Hydrobiologia 450: 31–46.
Golterman, H. L., R. S. Clymo & M. A. M. Ohnstad, 1978. Methods for Physical & Chemical Analysis of Fresh Waters. IBP Manual no 8. Blackwell Sci. Publi., Oxford, London: 213 pp.
Golterman, H. L. & N. T. de Oude, 1991. Eutrophication of Lakes, Rivers and Coastal Seas. In Hutzinger, O. (ed.), The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry. Volume 5, Part A, Water Pollution. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg: 79–124.
Jensen, H. S., P. B. Mortensen, F. O. Andersen, E. Rasmussen & A. Jensen, 1995. Phosphorus cycling in a coastal marine sediment, Aarhus Bay, Denmark. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40(5): 908–917.
Kemp, A. L. W., R. L. Thomas, C. I. Dell & J. M. Jaquet, 1976. Cultural impact on the geochemistry of sediments in Lake Erie. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 33(3): 440–462.
Krom, M. D. & R. A. Berner, 1981. The diagenesis of phosphorus in a nearshore marine sediment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 45: 207–216.
Krom, M. D., N. Kress & S. Brenner, 1991. Phosphorus limitation of primary productivity in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 36(3): 424–432.
Lefevre, D., H. J. Minas, M. Minas, C. Robinson, P. J. Le B. Williams & E. M. S. Woodward, 1997. Review of gross community production, primary production, net community production and dark community respiration in the Gulf of Lions. Deep-Sea Res. II 44(3–4): 801–832.
Leveau, M. & B. Coste, 1987. Impact des apports rhodaniens sur le milieu pälagique du Golfe du Lion. Bulletin d'Ecologie 18: 114–122.
Lucotte, M. & B. d'Anglejan, 1988. Processes controlling phosphate adsorption by iron hydroxides in estuaries. Chem. Geol. 67: 75–83.
Mc Gill, D. A., 1969. A budget for dissolved nutrient salts in the Mediterranean Sea. Cahiers océanographiques 21: 543–554.
Millot, C., 1990. The Gulf of Lions' hydrodynamics. Cont. Shelf Res. 10(9–11): 885–894.
Monaco, A., P. Biscaye, J. Soyer, R. Pocklington & S. Heussner, 1990. Particle fluxes and ecosystem response on a continental margin: the 1985–1988 Mediterranean ECOMARGE experiment. Cont. Shelf Res. 10(9–11): 809–839.
Moutin, T., B. Picot, M. C. Ximenes & J. Bontoux, 1993. Seasonal variations of P compounds and their concentrations in two coastal lagoons (Herault, France). Hydrobiologia 252: 45–59.
Moutin, T., P. Raimbault, H. L. Golterman & B. Coste, 1998. The input of nutrients by the Rhone river into the Mediterranean Sea: recent observations and comparison with earlier Data. Hydrobiologia 373–374: 237–246.
Moutin, T.& P. Raimbault, 2002. Primary production, carbon export and nutrients availability in western and eastern Mediterranean Sea in early summer 1996 (MINOS cruise). J. Mar Syst. in press.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 27: 31–36.
Pont, D., 1997. Les débits solides du Rhône à proximité de son embouchure: Données récentes (1994–1995). Rev. Geogr. Lyon 72: 23–33.
Radakovitch, O., S. Charmasson, M. Arnaud & P. Bouisset, 1999. 210Pb and Caesium Accumulation in the Rhone Delta Sediments. Estuar. coast. shelf Sci. 48: 77–92.
Radakovitch, O. & S. Heussner, 1999. Fluxes and budget of 210Pb on the continental margin of the Bay of Biscay (Northeastern Atlantic). Deep Sea Res. II 46(10): 2175–2204.
Sempéré, R., B. Charriére, F. Van Wambeke & G. Cauwet, 2000. Carbon inputs of the Rhone river to the Mediterranean Sea: Biogeochemical implications. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 14(2): 669–681.
Smith, J. N., K. M. Ellis, K. Naes, S. Dahle & D. Matishov, 1995. Sedimentation and mixing rates of radionuclides in the Barents Sea sediments off Novaya Zemlya. Deep Sea Res. II 42: 1471–1493.
Sundareshwar, P. V. & J. T. Morris, 1999. Phosphorus sorption characteristics of intertidal marsh sediments along an estuarine salinity gradient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 44(7): 1693–1701.
Sundby, B., C. Gobeil, N. Silverberg & A. Mucci, 1992. The phosphorus cycle in coastal marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37(6): 1129–1145.
Thingstad, T. F., U. L. Zweifel & F. Rassoulzadegan, 1998. Plimitation of heterotrophic bacteria and phytoplancton in the norwest Mediterranean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 43(1): 88–94.
Thomas, W. H., 1966. Surface nitrogenous nutrients and phytoplankton in the northeastern tropical Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11(3): 393–400.
Thomas, W. H., 1969. Phytoplankton nutrient enrichment experiments off Baja California and in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 26: 1133–1145.
Vollenweider, R. A., 1976. Advance in defining critical loading level for phosphorus in lake eutrophication. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 33: 53–83.
Zuo, Z., D. Eisma & W. Berger, 1991. Determination of sediment accumulation and mixing rates in the Gulf of Lions (Mediterranean Sea). Oceanol. Acta 14(3): 253–262.
Zuo, Z., D. Eisma, R. Gieles & J. Beks, 1997. Accumulation rates and sediment deposition in the northwestern Mediterranean. Deep Sea Res. II 44(3–4): 597–609.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Den Broeck, N., Moutin, T. Phosphate in the sediments of the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean Sea), relationship with input by the river Rhone. Hydrobiologia 472, 85–94 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016308931115
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016308931115