Abstract
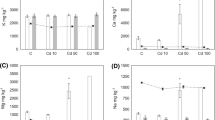
Tilapia larvae were exposed to 0 (control), 50 (50-Cd) or 100 (100-Cd) µg l-1 cadmium for 4 days and then transferred to cadmium-free fresh water for 3 days of detoxification. Total length and weight, calcium influx and total body calcium and cadmium content were examined at various times during detoxification. All the groups grew normally with regards to total length and body weight. Within the first 12h of detoxification the 50- and 100-Cd exposed groups released cadmium at the similar rate of about 24 ng mg-1 h-1 (or 140 ng larva-1 h-1). Later, however, this rate declined to only 4–16% of the initial level. Calcium influx in the control group showed a 10–26% increase during the detoxification period. Calcium influx in the 50-Cd group increased by about 280% and reached it peak at 12h. Calcium influx in the 100-Cd group increased by 440% and did not peak until 24h after transfer. After peaking, the influxes in both 50- and 100-Cd groups declined to the level of control at the end of the experiment. Calcium contents in 50- and 100-Cd groups increased more rapidly than that in control group within first 24h of the detoxification period. However the rate of increase in calcium content in three groups was the same after 24h. The changes in calcium influx appeared to be correlated with those in calcium content, and these suggested that tilapia larvae regulate the mechanism of calcium balance to compensate for the reduced calcium level in the body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Alderdice, D.F. 1988. Osmotic and ionic regulation in teleost eggs and larvae. In Fish Physiology. Vol. XI, part A, pp. 163–251. Edited by W.S. Hoar and D.J. Randall. Academic Press, San Diego.
Borrowitz, J.L. and McLaughlin, J.L. 1992. Evidence for calcium channels in brine shrimp: diltiazem protects shrimp against cadmium. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 48: 435–440.
Flik, G., Fenwick, J.C., Kolar, Z., Mayer-Gostan, N. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1985. Whole-body calcium flux in cichlid teleost fish Oreochromis mossambicus adapted to freshwater. Am. J. Physiol. 249: R432–437.
Flik, G., Fenwick, J.C., Kolar, Z., Mayer-Gostan, N. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1986. Effects of low ambient calcium levels on whole-body Ca2+ flux rates and internal calcium pools in the freshwater cichlid teleost, Oreochromis mossam-bicus. J. Exp. Biol. 120: 249–264.
Flik, G., Klaren, P.H., Schoenmakers, T.J.M., Verbost, P.M. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1996. Cellular calcium transport in fish: unique and universal mechanisms. Physiol. Zool. 69: 403–417.
Flik, G., Van Der Velden, J.A., Dechering, K.J., Verbost, P.M., Schoenmakers, T.J.M., Kolar, Z.I. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1993. Ca2+ and Mg2+ transport in gills and gut of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus: a review. J. Exp. Zool. 265: 356–365.
Fu, H. and Lock, R.A.C. 1990. Pituitary response to cadmium during the early development of tilapia (Oreochromis mos-sambicus). Aquat. Toxicol. 16: 9–18.
Giles, M.A. 1984. Electrolyte and water balance in plasma and urine of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) during chronic exposure to cadmium. Can. J. Aquat. Soc. 41: 1678–1685.
Harrison, S.E. and Klaverkamp, J.F. 1989. Uptake, elimination and tissue distribution of dietary and aqueous cadmium by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson) and lake white-fish (Coregonus clupeaformis Mitchill). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 8: 87–97.
Heath, A.G. 1987. Osmotic and ionic regulation. In Water Pollu-tion and Fish Physiology. pp. 107–130. Edited by A.G. Heath. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Hogstrand, C., Reid, S.D. and Wood, C.M. 1995. Ca2+ versus Zn2+ transport in the gills of freshwater rainbow trout and the cost of adaptation to waterborne Zn2+. J. Exp. Biol. 198: 337–438.
Hwang, P.P. 1989. Distribution of chloride cells in teleost larvae. J. Morphol. 200: 1–8.
Hwang, P.P. 1990. Salinity effects on development of chloride cells in the larvae of ayu Plecoglossus altivelis. Mar. Biol. 107: 1–7.
Hwang, P.P. and Hirano, R. 1985. Effects of environmental salinity on intercellular organization and junctional structure of chloride cells in early stages of teleost development. J. Exp. Zool. 236: 115–126.
Hwang, P.P., Lin, S.W. and Lin, H.C. 1995. Different sensitivities to cadmium in tilapia larvae (Oreochromis mossambicus; Teleostei). Arch. Envir. Contam. Tox. 29: 1–7.
Hwang, P.P. and Tsai, Y.N. 1993. Arsenic affects the osmoregu-lation in seawater-adapted tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Mar. Biol. 117: 551–558.
Hwang, P.P., Tsai, Y.N. and Tung, Y.C. 1994. Calcium balance in embryos and larvae of the freshwater-adapted teleost, Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 13: 325–333.
Hwang, P.P., Tung, Y.C. and Chang, M.H. 1996. Effect of environmental calcium levels on calcium uptake in tilapia larvae (Oreochromis mossambicus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 15: 363–370.
Hwang, P.P. and Wu, S.M. 1993. Role of cortisol in hypoosmo-regulation in larvae of the tilapia (Oreochromis mossambi-cus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 92: 318–324.
Lauren, D.J. and McDonald, D.G. 1987. Acclimation to copper by rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Physiology. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 44: 99–104.
Laurent, P. and Perry, S.F. 1991. Environmental effects on fish gill morphology. Physiol. Zool. 64: 4–25.
Lee, T.H., Hwang, P.P. and Lin, H.C. 1996. Morphological changes of integumental chloride cells to ambient cadmium during the early development of the teleost, Oreochromis mossambicus. Environ. Biol. Fish. 45: 95–102.
McCormick, S.D., Hasegawa, S. and Hirano, T. 1992. Calcium uptake in the skin of a freshwater teleost. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 3635–3638.
Payan, P., Mayer-Gostan, N. and Pang, P.K.T. 1981. Site of calcium uptake in the freshwater trout gill. J. Exp. Zool. 216: 345–347.
Perry, S.F. and Flik, G. 1988. Characterization of branchial transepithelial calcium fluxes in freshwater trout, Salmo gairdneri. Am. J. Physiol. 254: R491–498.
Perry, S.F., Goss, G.G. and Fenwick, J.C. 1992. Interrelationships between gill chloride cell morphology and calcium uptake in freshwater teleosts. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 10: 327–337.
Perry, S.F. and Wood, C.M. 1985. Kinetics of branchial calcium uptake in the rainbow trout: effects of acclimation to various external calcium levels. J. Exp. Biol. 116: 411–433.
Pratap, H.B., Fu, H., Lock, R.C.A. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1989. Effect of waterborne and dietary cadmium on plasma ions of the teleosts Oreochromis mossambicus in relation to water calcium levels. Arch. Envir. Contam. Toxicol. 18: 568–575.
Pratap, H.B. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1993. Effect of ambient and dietary cadmium on pavement cells, chloride cells, and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the gills of freshwater teleost, Oreochromis mossambicus at normal and high calcium levels in the ambient water. Aquat. Toxicol. 26: 133–150.
Roesijadi, G. and Robinson, W.E. 1994. Metal regulation in aquatic animals: mechanisms of uptake, accumulation, and release. In Aquatic Toxicology: Molecular, Biochemical, and Cellular Perspectives. pp. 387–420. Edited by D.C. Malins and G.K. Ostrander. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton.
Schoenmakers, T.J.M., Klaren, P.H.M., Flik, G., Lock, R.C.A., Pang, P.K.T. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1992. Actions of cadmium on basolateral plasma membrane proteins involved in calcium uptake by fish intestine. J. Membrane Biol. 127: 161–172.
Thevenod, F. and Jones, S.W. 1992. Cadmium block of calcium current in frog sympathetic neurons. Biophys. J. 63: 162–168.
Verbost, P.M., Flik, G., Lock, R.C.A. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1988. Cadmium inhibits plasma membrane calcium transport. J. Membrane Biol. 102: 97–104.
Verbost, P.M., Rooij, J.V., Flik, G., Lock, R.C.A. and Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. 1989. The movement of cadmium through fresh-water trout branchial epithelium and its interference with calcium transport. J. Exp. Biol. 145: 185–197.
Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. and Flik, G. 1982. Prolactin and calcium metabolism in a teleost fish, Sarotherodon mossambicus. In Comparative Endocrinology of Calcium Regulation. pp. 21–26. Edited by C. Oguro and P.K.T. Pang. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, P., Yang, C. Modulation of calcium uptake in cadmium-pretreated tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) larvae. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 16, 403–410 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007707009855
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007707009855