Abstract
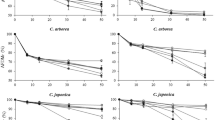
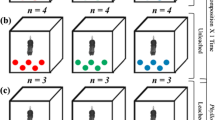
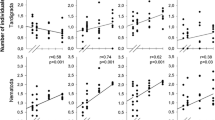
The effect of macroinvertebrate detritivore density on the mass loss rates of leaf litter of Alnus glutinosa (alder) was assessed. Experimental freshwater macrocosms, with increasing densities of four species of macroinvertebrate detritivores belonging to two functional groups (shredders and scrapers), were set up outdoors. The litter bag technique was used to assess decomposition rates of alder leaves. Indirect effects of increasing density of macroinvertebrates on phytoplankton standing crop in the water column were investigated by analysing Chlorophyll a concentration. Decomposition rate increased as animal density increased, although a continuous increase in detritivores density resulted in a discrete, step-wise increase of the decomposition rates. Animal colonisation followed an exponential pattern in low-medium density treatments versus a typical `bell-shape' curve in high density treatments; animals started to leave the consumed patches when about 60% of the initial leaf mass was lost (35th day in high-density treatments). Diversity (Hs) of the simplified detritivore community decreased as decomposition proceeded, with a dominance of shredders during the last phase of decomposition. Faster decomposition rate of detritus in the benthic compartment lead to a higher microalgae standing crop in the water column emphasising the role of allochthonous detritus as a source of nutrients for algae primary production in coastal freshwater ecotones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bärlocher, F., 1980. Leaf-eating invertebrates as competitors of aquatic hyphomicetes. Oecologia 47: 303–306.
Bärlocher, F., 1991. Fungal colonization of fresh and dried leaves in the River Teign (Devon, England). Nova Hedwigia 52: 349–357.
Berrie, A. D., 1976. Deritus, micro-organisms and animals in fresh water. In Anderson, J. M. & A. Macfadyen (eds), The Role of Terrestrial and Aquatic Organisms in Decomposition Processes. Blackwell, Oxford: 323–338.
Briggs, K. B., K. R. Tenore & R. B. Hanson, 1979. The role of microfauna in detrital utilization by the polychaete Nereis succinea (Frey and Leuckart). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 36: 225–234.
Buth, G. J. C. & L. de Wolf, 1985. Decomposition of Spartina anglica, Elytrigia pungens and Halimione portulacoides in a Dutch salt marsh in association with faunal and habitat influences. Vegetatio 62: 337–355.
Cerfolli, F. & L. Rossi, 1995. Numerical variation in three coexisting macrodetritivore species (Proasellus coxalis, Planorbarius corneus and Bithynia tentaculata) under different levels of vertical forces in aquatic microcosms. Hydrobiologia 302: 103–112.
Canhoto, C. & M. A. S. Graça, 1996. Decomposition of Eucalyptus globulus leaves and three native leaf species (Alnus glutinosa, Castanea sativa and Quercus faginea) in a Portuguese low order stream. Hydrobiologia 333: 79–85.
Cummins, K. W., 1973. Trophic relations of aquatic insects. Ann. Rev. Ent. 18: 183–206.
Cummins, K. W., M. A. Wilzbach, D. M. Gates, J. B. Perry & W. B. Taliaferro, 1989. Shredders and riparian vegetation. BioScience 39: 24–30.
Fazi, S., 1994. Trophic Availability for the Detritivorous and Structural Relationships in the Community. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rome, Italy.
Gallardo, A. & J. Merino, 1993. Leaf decomposition in two Mediterranean ecosystems of southwest Spain: influence of substrate quality. Ecology 74: 152–161.
Graça, M. A. S., 1993. Patterns and processes in detritus-based stream systems. Limnologica 23(2): 107–114.
Hassage R. L. and R. C. Harrel, 1986. Allochthonous leaves as a substrate for macrobenthos. J. Freshwat. Ecol. 3: 453–465.
Jordan T. E., D. F. Whigham & D. L. Correll, 1989. The role of litter nutrient cycling in a brackish tidal marsh. Ecology 70: 1960–1971.
Lee, C., R. Howarth & B. Howes, 1980. Sterols in decomposition of Spartina alterniflora and the use of ergosterol in estimating the contribution of fungi to detrital nitrogen. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25: 290–303.
Ligetta G., F. Vignes & A. Basset, 1999. Decomposizione della sostanza organica e rilascio di nutrienti in microcosmi a base detrito. IX National Congress of the Italian Society of Ecology. 14-17 September 1999, Lecce, Italy.
Lopez, G. R., J. S. Levinston & L. B. Slobodkin, 1977. The effect of grazing by the detritivore Orchestia on Spartina litter and its associated microbal community. Oecologia 30: 111–127.
Menendez, M., E. Fores & F. A. Comin, 1989. Ruppia cirrhosa-Decomposition in a coastal temperate lagoon as affected by macroinvertebrates. Arch. Hydrobiol. 117: 39–48.
Olson, J. S., 1963. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44: 322–331.
Picciafuoco, L. & L. Rossi, 1985. Biological interactions in detritus processing in freshwater. S. It. E. Atti, 5: 877–881.
Petersen, R. C. & K. W. Cummins, 1974. Leaf processing in a woodland stream. Freshwat. Biol. 4: 345–368.
Pozo, J., 1993. Leaf litter processing of alder and eucalyptus in the Agüera stream system (North Spain). Arch. Hydrobiol. 127: 299–317.
Rossi, L., 1985. Interaction between invertebrates and microfungi in freshwater ecosystem. Oikos 44: 175–184.
Rossi, L., A. Basset, C. Fanelli & A. A. Fabbri, 1983. An experimental study of a microfungal community on plant detritus in a mediterranean woodland stream. Mycologia 75: 887–896.
Sabetta L., L. Rossi, O. Maggi & A. M. Persiani, 1999. Interazioni tra detrito, detritivori e microfunghi durante la decomposizione (Lago di Vico-Italia centrale). IX National Congress of the Italian Society of Ecology. 14-17 September 1999, Lecce, Italy.
Saunder, G. W., 1976. The decomposition in freshwater. In Anderson, J. M. & A. Macfadygen (eds), The Role of Terrestrial and Aquatic Organisms in Decomposition Processes. Blackwell, Oxford: 341–374.
Sedell, J. R., F. J. Triska & N. S. Triska, 1975. The processing in two contrasting beech forest streams: effects of physical and biotic factors on litter breakdown. Arch. Hydrobiol. 96: 448–474.
Sneath P. H. A. & R. R. Sokal, 1973. Numerical Taxonomy. Freeman, San Francisco, CA.
Strickland, J. D. H. & T. R. Parsons, 1965. A manual of sea water analysis. Bulletin 125, 2nd edn. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 117-127.
Swift, M. J., O. W. Heal & J. M. Anderson. 1979. Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems, Studies in Ecology. University of California Press. Berkeley, California 5: 1–372.
Valiela, I., B. Howes, R. Howarth, A. Giblin, K. Foreman, J. Teal & J. E. Hobbie, 1982. The regulation primary production and decomposition in a salt marsh ecosystem. In Gopal, B., R. E. Turner, R. G. Wetzel & D. E. Whigham (eds), Wetlands: Ecology and Management. National Institute of Ecology. Jaipur, India: 151–168.
Valiela, I., J. M. Teal, S. D. Allen, R. Van Etten, D. Goehringer & S. Volkmann, 1985. Decomposition in salt marsh ecosystems: the phases and major factors affecting disappearance of aboveground organic matter. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 89: 29–54.
Wallace, J. B., W. R. Woodall & F. F. Sherberger, 1970. Breakdown of leaves by feeding of Peltoperla maria nymphs (Plecoptera: Peltoperlidae). Ann. am. ent. Soc. 63: 563–567.
Webster, J. R. & E. F. Benfield, 1986. Vascular plant breakdown in freshwater ecosystems. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 17: 567–594.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazi, S., Rossi, L. Effects of macro-detritivores density on leaf detritus processing rate: a macrocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia 435, 127–134 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004033410895
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004033410895