Abstract
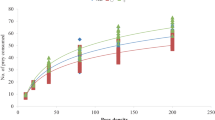
The functional response of fourth instars, adult males and females of the sevenspotted lady beetle, Coccinella septempunctata Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), was studied at different densities of aphid, Lipaphis erysimi (Kaltenbach) (Homoptera: Aphididae). The maximum prey consumption was recorded for fourth instars at the highest prey density (800) and the minimum for the male lady beetle at the lowest prey density (25). The prey consumption by the predatory stages of the lady beetle was directly and the percent prey consumption inversely proportional to prey density. Prey handling time decreased with increasing prey density. Regression analysis showed a linear relationship between the log number of prey exposed for prédation and prey consumed. The predatory efficiency of the predator stages was directly proportional to prey density, indicating a Holling Type II functional response.
Résumé
La réponse fonctionnelle du 4ème stade larvaire et des adultes mâles et femelles de la coccinelle à 7 points, Coccinella septempunctata Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), a été étudiée à différentes densités du puceron, Lipaphis erysimi (Kaltenbach) (Homoptera: Aphididae). La consommation maximale de proies a été enregistrée pour le 4ème stade larvaire à la densité la plus élevée de proies (800) et la minimale pour les mâles de coccinelle à la plus faible densité de proies (25). La consommation de proies par les différents stades est proportionnelle à la densité de proies alors que le pourcentage de proies consommées est inversement proportionnel. Le temps de manipulation des proies diminue avec l’augmentation de la densité des proies. Un analyse de régression montre une relation linéaire entre le logarithme du nombre de proies présentes et celui du nombre de proies consommées. L’efficacité prédatrice des différents stades est directement proportionnelle à la densité de proies, ce qui indique une réponse fontionnelle d’Holling de type II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwala B. K. and Bardhanroy P. (1997) Oviposition behaviour and reproduction efficiency in ladybird beetles (Coccinellidae: Coleoptera): A case study of Menochilns sexmaculatus (Fabr.). J. Aphidol. 11, 49–59.
Bind R. B. (1998) Bioecology and behaviour of a ladybird beetle, Cheilomenes (=Menochilus) sexmaculata (Fabricius) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). PhD Thesis. University of Lucknow, Lucknow. 164 pp.
Ghosh L. K. and Singh R. (2000) Biodiversity of Indian insects with special reference to aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Aphidol. 14, 113–123.
Hasseil M. P. (1978) The Dynamics of Arthropod Predator-Prey System. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. 237 pp.
Hodek I. and Honek A. (1996) Ecology of Coccinellidae. Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht Boston London. 464 pp.
Holling C. S. (1959) Some characteristics of simple types of prédation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 91, 385–398.
Nault L. R. and Bowers W. S. (1974) Multiple alarm pheromones in aphids. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 17, 455–457.
Ofuya T. I. and Akingbohungbe A. E. (1988) Functional and numerical responses of Chielomenes. lunata (Fabricius) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae)Teedirig on cowpea aphid, Aphis craccivora Koch (Homoptera: Aphididae). Insect Sci. Applic. 9, 543–546.
Omkar and Bind R. B. (1993) Records of aphids-natural enemies complex of Uttar Pradesh. II. The coccinellids. J. Adv. Zool 14, 96–99.
Omkar and James B. E. (2001) Prédation efficacy of a lady beetle, Coccinella transversalis Fabricius in relation to certain aphids. Biol. Mem. 27, 20–26.
Omkar and Srivastava S. (2000) Integrated strategies of ai]insect pest management: An overview. Indian Farmer’s Digest 33, 29–34.
Omkar and Srivastava S. (2001a) Comparative predatory potential of a ladybird beetle, Coccinella septempunctata Linn, on six prey species. Biol. Mem. 27, 59–63.
Omkar and Srivastava S. (2001b) Ovipositional preference of Coccinella septempunctata Linnaeus (Coccinellidae: Coleoptera). J. Aphidol. 15, 5–8.
Rhamhalinghan M. (1987) Feeding behaviour of Coccinella septempunctata L. var. confusa Weidemann (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in relation to temperature—I. Pre-oviposition period. J. Entomol. Res. 11, 178–183.
Sengonca C. and Liu B. (1994) Responses of the different instar predator, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), to the kairomones produced by the prey and non-prey insects as well as the predator itself. Z. Pflanzenkr. Pflanzenschutz 101, 173–177.
Stubbs M. (1980) Another look at prey detection by coccinellids. Ecol. Entomol. 5, 179–182.
Suri S. M., Singh D. and Brar K. S. (1988) Estimation of losses in yield of brown Sarson due to aphids in Kangra valley. I, effect of crop growth stage and aphid feeding exposure. Insect Sci. Applic. 1, 162–167.
Waage J. (1979) Foraging for patchily-distributed hosts by the parasitoid Nemaritis canescens. J. Anim. Ecol. 48, 353–371.
Wagiman F. X. (1996) Functional response ofMenochilus sexmaculatus (Fabricius) against Aphis gossypii. J. Perlindungan Tanaman, Indonesia 2, 38–43.
Wang J. J. and Tsai J. H. (2001) Development and functional response of Coelophora inaequalis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) feeding on brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida (Homoptera: Aphididae). Agric. Forest Entomol. 3, 65.
Wells M. L. and McPherson J. H. (1999) Population dynamics of three coccinellids in fluecured tobacco and functional response of Hippodamia convergens (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) feeding on tobacco aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 28, 768–773.
Zebitz C. P. W. (1988) Efficiency of coccinellid larvae in dependence from prey distribution. Mitt. Deutsc. Gesellschaft Allgem. Angew. Entomol. 6, 454–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omkar, Srivastava, S. Functional Response of the Sevenspotted Lady Beetle, Coccinella septempunctata Linnaeus on the Mustard Aphid, Lipaphis erysimi (Kaltenbach). Int J Trop Insect Sci 23, 149–152 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400020373
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400020373