Abstract
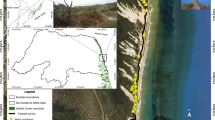
Predator-prey systems are regulated by a behavioral response race, in which the predator develops adaptations that enhance its hunting success and its prey adopt anti-predator strategies. In the present study, we analyzed the activity patterns, the influence of moonlight, and the habitat use of Leopardus pardalis and Puma concolor in comparison with their potential prey, Dasypus novemcinctus, Mazama gouazoubira, Pecari tajacu, Sapajus libidinosus, Kerodon rupestris, Cuniculus paca and Dasyprocta prymnolopha, in the Serra das Almas Nature Reserve in northeastern Brazil. Leopardus pardalis was predominantly nocturnal, while P. concolor presented a cathemeral pattern, however, the overlap coefficient between these species was high. The activity of L. pardalis overlapped strongly with three typical nocturnal prey (D. novemcinctus, K. rupestris and C. paca). While P. concolor had considerable temporal overlap with all prey. Both predators were habitat generalists, in contrast, most prey species exhibited a significant association with a specific type of habitat. The phases of the moon did not influence the activity patterns of the different species, except for K. rupestris, which was more active on moonlit nights. Our findings indicate that the predators maximize the efficiency of their foraging behavior by using habitats and the circadian cycle in a more generalist manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo, F.S., Martins, F.R., 1999. Fisionomiae organização da vegetação do carrasco no planalto da Ibiapaba, estado do Ceará. Acta Bot. Bras. 13 (1), 1–13, https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-33061999000100002.
Araújo, F.S., Martins, F.R., Shepherd, G.J., 1999. Variações estruturais e florísticas do carrasco no planalto da Ibiapaba, estado do Ceará. Rev. Bras. Biol. 59 (4), 663–678, https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-71081999000400015.
Caatinga, Associação, 2012. Plano de Manejo da Reserva Natural Serra das Almas, 3- iteração. Crateús.
Berger, J., 2010. Fear-mediated food webs. In: Terborgh, J., Estes, J.A. (Eds.), Trophic Cascades: Predators, Prey and the Changing Dynamics of Nature. Island Press, Washington, pp. 241–254.
Bianchi, R.C., Mendes, S.L., 2007. Ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) predation on primates in caratinga biological station, Southeast Brazil. Am. J. Primatol. 69, 1173–1178, https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.20415.
Bianchi, R.C., Mendes, S.L., Marco Junior, P., 2010. Food habits of the ocelot, Leopardus pardalis, in two areas in southeast Brazil. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 45 (3), 111–119, https://doi.org/10.1080/01650521.2010.514791.
Brown, J.S., 1999. Patch use under predation risk: I. Models and predictions. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 29, 301–309.
Crawley, M.J., 2013. The R Book, 2nd. edn. Wiley, Chichester.
Daan, S., 1981. Adaptive daily strategies in behaviour. In: Aschoff, J. (Ed.), Biological Rhythms. Plenum Press, New York, pp. 275–298.
Daly, M., Behrends, P.R., Wilson, M.I., Jacobs, L.F., 1992. Behavioural modulation of predation risk: monnlight avoidance and crepuscular compensation in a nocturnal desert rodent, Dipodomys merriami. Anim. Behav. 44, 1–9, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-3472(05)80748-1.
Di Bitetti, M.S., De Angelo, C., Di Blanco, Y.E., Paviolo, A., 2010. Niche partitioning and species coexistence in a neotropical felid assemblage. Acta Oecol. 36, 403–412, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actao.2010.04.001.
Dias, D.M., Bocchiglieri, A., 2015. Dieta de carnívoros (Mammalia, Carnivora) em um remanescente de Caatinga, Nordeste do Brasil. Bioikos 29 (1), 13–19.
Dias, D.M., Bocchiglieri, A., 2016. Trophic and spatio-temporal niche of the crab-eating fox, Cerdocyon thous (Linnaeus, 1766) (Carnivora: Canidae), in a remnant of the Caatinga in Northeastern Brazil. Mammalia 80 (3), 281–291, https://doi.org/10.1515/mammalia-2014-0108.
Duarte, J.M.B., Vogliotti, A., Zanetti, E.S., Oliveira, M.L., Tiepolo, L.M., Rodrigues, L.F., Almeida, L.B., 2012. Avaliação do risco de extinção do veado-catingueiro Mazama gouazoubira G. Fischer [von Waldheim], 1814,3. Biodiversidade Brasileira, Brasil, pp. 50–58.
Elbroch, L.M., Wittmer, H.U., 2012. Puma spatial ecology in open habitats with aggregate prey. Mamm. Biol. 77, 377–384, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2012.02.010.
Eriksen, A., Wabakken, P., Zimmermann, B., Andreassen, H.P., Arnemo, J.M., Gundersen, H., Liberg, O., Linnell,J., Milner, J.M., Pedersen, H.C., Sand, H., Solberg, E.J., Storaas, T., 2011. Activity patterns of predator and prey: a simultaneous study of GPS-collared wolves and moose. Anim. Behav. 81, 423–431, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2010.11.011.
Fernández-Duque, E., 2003. Influences of moonlight, ambient temperature, and food availability on the diurnal and nocturnal activity of owl monkeys (Aotus azarai). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54, 431–440, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-003-0637-9.
Foster, V.C., Sarmento, P., Sollmann, R., Tôrres, N., Jácomo, A.T.A., Negrões, N., Fonseca, C., Silveira, L., 2013. Jaguar and Puma activity patterns and predator-prey interactions in four Brazilian biomes. Biotropica, 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1111/btp.12021.
Gorini, L., Linnell, J.D.C., May, R., Panzacchi, M., Boitani, L., Odden, M., Nilsen, E.B., 2012. Habitat heterogeneity and mammalian predator-prey interactions. Mammal Rev. 42 (1), 55–77, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2907.2011.00189.x.
Griffin, P.C., Griffin, S.C., Waroquiers, C., Mills, LS., 2005. Mortality by moonlight: predation risk and the snowshoe hare. Behav. Ecol. 16, 938–944, https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/ari074.
Gursky, S., 2003. Lunar philia in a nocturnal primate. Int. J. Primatol. 24, 351–367, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023053301059.
Harmsen, B.J., Foster, R.J., Silver, S.C., Ostro, L.E.T., Doncaster, C.P., 2011. Jaguar and puma activity patterns in relation to their main prey. Mamm. Biol. 76, 320–324, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2010.08.007.
Hernández-Saintmartín, A.D., Rosas-Rosas, O.C., Palacio-Núñez, J., Tarango-Arámbula, L.A., Clemente-Sánchez, F., Hoogesteijn, A.L., 2013. Activity patterns of jaguars, puma and their potential prey in San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Acta Zool. Mex. 29 (3), 520–533.
Huck, M., Juárez, C.P., Fernández-Duque, E., 2017. Relationship between moonlight and nightly activity patterns of the ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) and some of its prey species in Formosa, Northern Argentina. Mamm. Biol. 82, 57–64, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2016.10.005.
Iriarte, J.A., Franklin, W.L., Johnson, W.E., Redford, K.H., 1990. Biogeographic variation of food habits size ofthe America puma. Oecologia 85, 185, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319400.190.
Jenny, D., Zuberbuhler, K., 2005. Hunting behaviour in West African forest leopards. Afr.J. Ecol. 43, 197–200, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2028.2005.00565.x.
Kotler, B.P., Brown, J.S., Bouskila, A., Mukherjee, S., Goldberg, T., 2004. Foraging games between gerbils and their predators: seasonal changes in schedules of activity and apprehension. Isr.J. Zool. 50, 255–271, https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2009.2036.
Laundré, J.W., Hernández, L., Ripple, W.J., 2010. The landscape of fear: ecological implications of being afraid. Open Ecol. J. 3, 1–7.
Lima, J.R., Sampaio, E.V.S.B., Rodal, M.J.N., Araújo, F.S., 2007. Estrutura da floresta estacional decidual montana (mata seca) da RPPN Serra das Almas. Ceará. Rev. Bras. Biocienc. 5 (2), 438–440.
Lima, J.R., Sampaio, E.V.S.B., Rodal, M.J.N., Araújo, F.S., 2009. Composição florística da floresta estacional decídua montana de Serra das Almas, CE, Brasil. Acta Bot. Bras 23 (3), 756–763, https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-33062009000300015.
Lima, S.L., Dill, L.M., 1990. Behavioral decisions made underthe risk of predation: a review and prospectus. Can. J. Zool. 68, 619–640, https://doi.org/10.1139/z90-092.
Lucherini, M., Reppucci, J.I., Walker, R.S., Villalba, M.L., Wurstten, A., Gallardo, G., Iriarte, A., Villalobos, R., Perovic, P., 2009. Activity pattern segregation of carnivores in the high Andes. J. Mammal. 90 (6), 1404–1409, https://doi.org/10.1644/09-MAMM-A-002R.1.
Luttbeg, B., Rowe, L., Mangel, M., 2003. Prey state and experimental design affect relative size oftrait- and density-mediated indirect effects. Ecology 84, 1140–1150, https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2003)084[1140:PSAEDA]2.0.CO;2.
Maffei, L., Cuellar, E., Noss, J., 2002. Uso de trampas-cámara para la evaluación de mamíferos en el ecotono Chaco-Chiquitanía. Rev. Bol. Ecol. 11, 55–65.
Maffei, L., Noss, A.J., Cuéllar, E., Rumiz, D.L., 2005. Ocelot (Felis pardalis) population densities, activity, and ranging behaviour in the dry forests of eastern Bolivia: data from camera trapping. J. Trop. Ecol. 21, 349–353, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266467405002397.
Marinho, P.H., Bezerra, D., Antongiovanni, M., Fonseca, C.R., Venticinque, E.M., 2018. Activity patterns ofthe threatened northern tiger cat Leopardus tigrinus and its potential prey in a Brazilian dry tropical forest. Mamm. Biol. 89, 30–36, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2017.12.004.
Meredith, M., Ridout, M., 2014. Overlap: estimates of coefficient of overlapping for animal activity patterns. R package version 0.2.4. Available at https://doi.org/CRAN.Rproject.org/package=overlap.
Monterroso, P., Alves, P.C., Ferreras, P., 2014. Plasticity in circadian activity patterns of mesocarnivores in southwestern Europe: implications forspecies coexistence. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 68, 1403–1417, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-014-1748-1.
Moreno, R.S., Kays, R.W., Samudio Jr., R., 2006. Competitive release in diets of ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) and puma (Puma concolor) after jaguar (Panthera onca) decline. J. Mammal. 87 (4), 808–816, https://doi.org/10.1644/05-MAMM-A-360R2.1.
Murray, J.L., Gardner, G.L., 1997. Leopardus pardalis. Mamm. Species 548, 1–10.
Núñez, R., Miller, B., Lindzey, F., 2000. Food habits of jaguars and pumas inJalisco. Mexico. J. Zool. 252, 373–379, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.2000.tb00632.x.
Oliveira, L.O., Bonvicino, C.R., 2011. Ordem Rodentia. In: Reis, N.R., Peracchi, A.L., Pedro, W.A., Lima, I.P. (Eds.), Mamíferos do Brasil. Edição do Autor, Londrina, pp. 358–414.
Oliveira, M.F., Carter, A.M., Bonatelli, M., Ambrosio, C.E., Miglino, M.A., 2006. Placentation in the rock cavy, Kerodon rupestris (Wied). Placenta 27, 87–97, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2004.11.012.
Oliveira, T.G., Pereira, J.A., 2014. Intraguild predation and interspecific killing as structuring forces of carnivoran communities in South America. J. Mammal. Evol. 21, 427–436, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10914-013-9251-4.
Olmos, F., 1993. Notes on the food habits of Brazilian Caatinga carnivores. Mammalia 57, 126–130.
Penido, G., Astete, S., Jácomo, A.T.A., Sollmann, R., Tôrres, N., Silveira, L., Marinho Filho,J., 2017. Mesocarnivore activity patterns in the semiarid Caatinga: limited by the harsh environment or affected by interspecifc interactions? J. Mammal. 98 (6), 1732–1740, https://doi.org/10.1093/jmammal/gyx119.
Pratas-Santiago, L.P., Gonçalves, A.L.S., da Maia Soares, A.M.V., Spironello, W.R., 2016. The moon cycle effect on the activity patterns of ocelots and their prey. J. Zool. 299, 275–283, https://doi.org/10.1111/jzo.12359.
Prugh, L.R., et al., 2009. The rise ofthe mesopredator. BioScience 59, 779–791, https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2009.59.9.9.
Prugh, L.R., Golden, C.D., 2014. Does moonlight increase predation risk? Meta-analysis reveals divergent responses of nocturnal mammals to lunar cycles. J. Anim. Ecol. 83, 504–514, https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12148.
RCore Team, 2017. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria https://doi.org/www.R-project.org
Ridout, M.S., Linkie, M., 2009. Estimating overlap of daily activity patterns from camera trap data. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 14, 322–327, https://doi.org/10.1198/jabes.2009.08038.
Sábato, M.A.L., Melo, L.F.B., Magni, E.M.V., Young, R.J., Coelho, C.M., 2006. A note on the effect ofthe full moon on the activity of wild maned wolves, Chrysocyon brachyurus. Behav. Process. 73, 228–230, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2006.05.012.
Schmid, F., Schmidt, A., 2006. Nonparametric estimation ofthe coefficient of overlapping — theory and empirical application. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 50, 1583–1596, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2005.01.014.
Schoener, T.W., 1974. Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science 185, 27–39.
Schwitzer, N., Kaumanns, W., Seitz, P.C., Schwitzer, C., 2007. Cathemeral activity patterns ofthe blue-eyed black lemur Eulemur macaco flavifrons in intact and degraded forest fragments. Endanger. Species Res. 3, 239–247.
Scognamillo, D., Maxit, I.E., Sunquist, M., Polisar, J., 2003. Coexistence of jaguar (Panthera onca) and puma (Puma concolor) in a mosaic landscape in the Venezuelan Ilanos. J. Zool. 259, 269–279.
Sih, A., 1984. The behavioral response race between predator and prey. Am. Nat. 123 (1), 143–150.
Theuerkauf, J., Jędrzejewski, W., Schmidt, K., Okarma, H., Ruczynski, I., Śnieżko, S., Gula, R., 2003. Patterns and duration of wolf activity in the Białowieża Forest. Pol. J. Mammal. 84 (1), 243–253.
Tiepolo, L.M., Tomas, W.M., 2011. Ordem Artiodactyla. In: Reis, N.R., Peracchi, A.L., Pedro, W.A., Lima, I.P. (Eds.), Mamíferos do Brasil. Edição do Autor, Londrina, pp. 293–313.
White, A., Kerodon rupestris(On-line), Animal Diversity Web. https://doi.org/animaldiversity.org/accounts/Kerodon_rupestris/. (Online accessed 22 July 2016).
Willig, M.R., Lacher Jr., T.E., 1991. Food selection of a tropical mammalian folivore in relation to leaf-nutrient content. J. Mammal. 72 (2), 314–321, https://doi.org/10.2307/1382101.
Zar, J.H., 2010. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data, 947p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Matos Dias, D., de Campos, C.B. & Guimarães Rodrigues, F.H. Behavioural ecology in a predator-prey system. Mamm Biol 92, 30–36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2018.04.005
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2018.04.005