Abstract
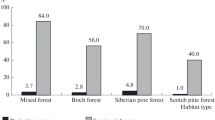
The wild boar (Sus scrofa) is an exotic agent of disturbance that arrived in the Ñacuñán Reserve of Argentina in the 1980s. When foraging, the wild boar overturns extensive areas of soil leaving them bare of vegetation. Knowledge is scarce about the boar's impact on vegetation composition and soil properties in the Monte Desert, Argentina. The objective of our study was to determine the short terms effects of wild boar rooting on vegetation and on soil physical, chemical and microbiological properties. Our results indicate that rooting activities significantly reduced the plant cover of herbs, perennial grasses and shrubs, and decreased plant richness and diversity. Disturbed soils showed less compaction, more moisture, a low C/N ratio, and high content of mineral nitrogen. These new soil characteristics could be responsible for a reduced plant cover and less soil bulk density, which could increase soil degradation by wind erosion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaigar, T., del Barro, G., Vericad, J.R., 1994. Habitat preference of wild boar (Sus scrofa L., 1758) in a Mediterranean environment. Indirect evaluation by signs. Mammalia 58, 201–210.
Abraham, E.M., del Valle, H.F., Roig, F., Torres, L., Ares, J.O., Coronato, F., Godagnone, R., 2009. Overview of the geography of the Monte Desert biome (Argentina). J. Arid Environ. 73, 144–153.
Abril, A., 2002. La microbiología del suelo: su relación con la agricultura sustentable. In: Sarandón, S.J. (Ed.), Agroecología. El camino hacia una agricultura sustentable. Ediciones Científicas Americanas, La Plata, Argentina, pp. 129–150.
Alef, K., 1995. Soil respiration. In: Alef, K., Nannipieri, P. (Eds.), Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry. Academic Press, London, United Kingdom, pp. 214–219.
Anderson, C.B., Griffith, C.R., Rosemond, A.D., Rozzi, R., Dollenz, O., 2006. The effect of invasive North American beavers on riparian plant communities in Cape Horn Chile. Do exotic beavers engineer differently in sub-Antarctic ecosystems? Biol. Conserv. 128, 467–474.
Arrington, D.A., Toth, L.A., Koebel Jr., J.W., 1999. Effects of rooting by feral hogs Sus scrofa L. on the structure of a floodplain vegetation assemblage. Wetlands 9, 535–544.
Austin, A.T., Yahdjian, L., Stark, J.M., Belnap, J., Porporato, A., Norton, U., 2004. Water pulses and biogeochemical cycles in arid and semiarid ecosystems. Oecologia 141, 221–235.
Bragg, C.J., Donaldson, J.D., Ryan, P.G., 2005. Density ofCape porcupines in a semi-arid environment and their impact on soil turnover and related ecosystem processes. J. Arid Environ. 61, 261–275.
Bratton, S.P., 1974. The effect of the European wild boar (Sus scrofa) on the highelevation vernal florain Great Smoky Mountains National Park. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 101, 198–206.
Bratton, S.P., 1975. The effect of the European wild boar Sus scrofa, on gray beech forest in the Great Smoky Mountains. Ecology 56, 1356–1366.
Campbell, D.J., Rudge, M.R., 1984. Vegetation changes induced over ten years by goats and pigs at Port Ross Auckland Islands (SubAntarctic). N.Z. J. Ecol. 7, 103–118.
Carrera, A., Mazzarino, M., Bertiller, M., del Valle, H., Carretero, E., 2009. Plant impacts on nitrogen and carbon cycling in the Monte Phytogeographical Province, Argentina. J. Arid Environ. 73, 192–201.
Claver, S., Roig-Juñent, S., 2001. El desierto del Monte: La Reserva de Biosfera de Ñacuñán. IADIZA, MAB, UNESCO, Triunfar, Argentina.
Collins, S.L., Barber, S.C., 1985. Effects of disturbance on diversity in mixed-grass prairie. Vegetatio 64, 87–94.
Connell, J.H., 1978. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 199, 1302–1310.
Cuevas, M.F., Novillo, A., Campos, C., Dacar, M.A., Ojeda, R.A., 2010. Food habits and impact of rooting behaviour of the invasive wild boar, Sus scrofa, in a protected area of the Monte Desert, Argentina. J. Arid Environ. 74, 1582–1585.
Cushman, J.H., Tierney, T.A., Hinds, J.M., 2004. Variable effects of feral pig disturbances on native and exotic plants in a California grassland. Ecol. Appl. 14, 1746–1756.
Daciuk, J., 1978. Estado actual de las especies de mamíferos introducidos en la Subregión Araucana (Rep Argentina) y grado de coacción ejercido en algunos ecosistemas surcordilleranos. Anales de Parques Nacionales 14, 105–130.
Döbereiner, J., 1995. Isolation and identification of aerobic nitrogen fixing bacteria from soil and plants. In: Alef, K., Nannipieri, P. (Eds.), Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry. Academic Press, London, United Kingdom, pp. 134–141.
Gómez, J.M., Hódar, J.A., 2008. Wild boars (Sus scrofa) affect the recruitment rate and spatial distribution of holm oak (Quercus ilex). For. Ecol. Manag. 256, 1384–1389.
Herrick, J.E., Van Zee, J.W., Havstad, K.M., Burkett, L.M., Whitford, W.G., 2005. Monitoring Manual for Grassland, Shrubland, and Savanna Ecosystems Volume II: Design, Supplementary Methods, and Interpretation. University of Arizona Press, Tucson, Arizona.
Hobbs, R.J., Huenneke, L.F., 1992. Disturbance, diversity, and invasion: implications for conservation. Conserv. Biol. 6, 324–337.
Hone, J., 2002. Feral pigs in Namadgi National Park Australia: dynamics, impacts and management. Biol. Conserv. 105, 231–242.
Huston, M., 1979. A general hypothesis of species diversity. Am. Nat. 113, 81–101.
Jones, C.G., Lawton, J.H., Shachak, M., 1994. Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69, 373–386.
Keeney, D., Nelson, D., 1982. Nitrogen inorganic forms. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R., Keeney, D. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, vol. 2. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science, Madison, WI, pp. 643–698.
Klute, A., 1986. Methods of Soil Analysis. Physical and Mineralogical Methods, vol. 1. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science, Madison, WI, 980 pp.
Kotanen, P., 1995. Responses of vegetation to a changing regime of disturbance: effects of feral pigs in a Californian coastal prairie. Ecography 18, 190–199.
Kotanen, P., 1996. Revegetation following soil disturbance in a California meadow: the role of propagule supply. Oecologia 108, 652–662.
Labraga, J., Villalba, R., 2009. Climate in the Monte Desert: past trends, present conditions, and future projections. J. Arid Environ. 73, 154–163.
Lockwood, J.L., Hoopes, M.F., Marchetti, M.P., 2007. Invasion Ecology. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, United Kingdom.
Lorch, H.J., Benckieser, G., Ottow, J.C.G., 1995. Basic methods for counting microorganisms in soil and water. In: Alef, K., Nannipieri, P. (Eds.), Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry. Academic Press, London, United Kingdom, pp. 146–161.
Mack, M.C., D’Antonio, C.M., 1998. Impacts of biological invasions on disturbance regimes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 13, 68–75.
Mohr, D., Cohnstaedt, L.W., Topp, W., 2005. Wild boar and red deer affect soil nutrients and soil biota in steep oak stands of the Eifel. Soil Biol. Biochem. 37, 693–700.
Moody, A., Jones, J.A., 2000. Soil response to canopy position and feral pig disturbance beneath Quercus agrifolia on Santa Cruz Island California. Appl. Soil Ecol. 14, 269–281.
Navas, J.A., 1987. Los vertebrados exóticos introducidos en la Argentina. Revista del Museo Argentino de Ciencias Naturales. Serie Zoología XIV, 7–38.
Nelson, D.W., Sommers, L.E., 1982. Total carbon organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R., Keeney, D. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, vol. 2. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science, Madison, WI, pp. 539–580.
Novillo, A., Ojeda, R.A., 2008. The exotic mammals of Argentina. Biol. Invas. 10, 1333–1344.
Pescador, M., Sanguinetti, J., Pastore, H., Peris, S., 2009. Expansion of the introduced wild boar (Sus scrofa) in the Andean region, Argentinean Patagonia. Galemys 21, 121–132.
Risch, A.C., Wirthner, S., Busse, M.D., Page-Dumroese, D.S., Schütz, M., 2010. Grubbing by wild boar (Sus scrofa) and its impact on hardwood forest soil CO2 emissions in Switzerland. Oecologia 164, 773–784.
Roig, F., Roig-Jun¸ ent, S., Corbalán, V., 2009. Biogeography of the Monte Desert. J. Arid Environ. 73, 164–172.
Rundel, P.W., Villagra, P.E., Dillon, M.O., Roig-Juñent, S., Debandi, G., 2007. Arid and semi-arid ecosystems. In: Veblen, T.T., Young, K., Orme, A.E. (Eds.), The Physical Geography of South America. Oxford University Press, pp. 158–183.
Sanguinetti, J., Kitzberger, T., 2010. Factors controlling seed predation by rodents and non-native Sus scrofa in Araucaria araucana forests: potential effects on seedling establishment. Biol. Invas. 12, 689–706.
Singer, F.J., Swank, W.T., Clebsch, E.E.C., 1984. Effects of wild pig rooting in a deciduous forest. J. Wildl. Manage. 48, 464–473.
Settele, J., Hammen, V., Hulme, P., Karlson, U., Klotz, S., Kotarac, M., Kunin, W., Marion, G., O’Connor, M., Petanidou, T., Peterson, K., Potts, S., Pritchard, H., Pysek, P., Rounsevell, M., Spangenberg, J., Steffan-Dewenter, I., Sykes, M., Vighi, M., Zobel, M., Kühn, I., 2005. ALARM (Assessing LArge-scale Environmental Risks for biodiversity with tested Methods). Gaia 14, 69–72.
Seward, N.W., Vercauteren, K.C., Witmer, G.W., Engeman, R.M., 2004. Feral swine impacts on agriculture and the environment. Sheep Goat Res. J. 19, 34–40.
Sherrod, S.K., Seastedt, T.R., 2001. Effects of the northern pocket gopher (Thomomys talpoides) on alpine soil characteristics, Niwot Ridge, CO. Biogeochemistry 55, 195–218.
Sousa, W., 1984. The role of disturbance in natural communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 15, 353–391.
Stasi, C.R., Medero, M.N., 1983. Estudio ecológicoy bromatológico de Pitraea cuneatoovata (Cav.) Caro, una especie forrajera del “Monte” mendocino y sanjuanino. Deserta 7, 7–11.
Tierney, T.A., Cushman, J.H., 2006. Temporal changes in native and exotic vegetation and soil characteristics following disturbances by feral pigs in a California grassland. Biol. Invas. 8, 1073–1089.
Villagra, P.E., Defossé, G.E., del Valle, H.F., Tabeni, S., Rostagno, M., Cesca, E., Abraham, E., 2009. Land use and disturbance effects on the dynamics of natural ecosystems of the Monte Desert: implications for their management. J. Arid Environ. 73, 202–211.
Vitousek, P., D’Antonio, C., Loope, L., Rejmanek, M., Westbrooks, R., 1997. Introduced species: asignificant component of human-caused global change. N.Z.J.Ecol. 21, 1–16.
Williamson, M., 1996. Biological Invasions. Chapman & Hall, London, United Kingdom.
Wilson, C.J., 2004. Rooting damage to farmland in Dorset, southern England, caused by feral wild boar Sus scrofa. Mammal Rev. 34 (4), 331–335.
Zar, J.H., 1999. Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuevas, M.F., Mastrantonio, L., Ojeda, R.A. et al. Effects of wild boar disturbance on vegetation and soil properties in the Monte Desert, Argentina. Mamm Biol 77, 299–306 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2012.02.003
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mambio.2012.02.003