Abstract
Study Design
Retrospective review of prospectively accrued patient cohort.
Objective
To report minimum 2 years’ follow-up after a single-surgeon series of 47 consecutive patients in whom fixed sagittal imbalance or segmental kyphosis was treated with a novel unilateral transforaminal annular release.
Summary of Background Data
Fixed sagittal imbalance has been treated most recently with pedicle subtraction osteotomy with great success but is associated with significant blood loss and neurologic risk.
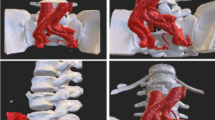
Method
Forty-seven consecutive patients with fixed sagittal imbalance (n = 29) or segmental kyphosis (n = 18) were treated by a single surgeon with a single-level transforaminal anterior release (TFAR) to effect an opening wedge correction. Sagittal and coronal correction was performed with in situ rod contouring. An interbody cage was captured in the disc space with rod compression. Radiographic and clinical outcome analysis was performed with a minimum 2-year follow-up (range 2-7. 8 years).
Results
The average increase in lordosis was 36° (range 24°-56°) in the fixed sagittal deformity group. Coronal corrections averaged 34° (range 18°- 48°). The average improvement in plumb line was 13. 6 cm. There were four pseudarthroses, one at the TFAR. Average blood loss was 578 mL (range 200-1,200). One patient had a transient grade 4/5 anterior tibialis weakness. There were no vascular injuries or permanent neurologic deficits. There were significant improvements in the Oswestry Disability Index (p <. 001) and Scoliosis Research Society Questionnaire scores (p =. 003). Eighty-four percent of patients reported improvement in pain, self-image, and satisfaction with the procedure.
Conclusion
TFAR is a useful procedure for correcting segmental kyphosis and fixed sagittal imbalance with relatively low blood loss and was found to be neurologically safe in this single-surgeon series.
Level of Evidence
Therapeutic study, Level IV (case series, no control group).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Lenke LG, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;2:54–63.
Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities. Spine 2002;2:2374–82.
Potter BK, Lenke LG, Kuklo TR. Prevention and management of iatrogenic flat back deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;2:1793–808.
Gill JB, Levine A, Bird T, et al. Corrective osteotomies in the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;2:2509–20.
Lenke LG, O’Leary PT, Bridwell KH, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe pediatric deformity; minimum 2 year follow-up of 35 consecutive patients. Spine 2009;2:2213–21.
Suk SI, Chung ER, Kim JH, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe rigid scoliosis. Spine 2005;2:1682–7.
Smith JS, Bess S, Shaffrey CI, et al. Dynamic changes of the pelvis and spine are key to predicting postoperative sagittal alignment after pedicle subtraction osteotomy: critical analysis of preoperative planning techniques. Spine 2012;2:845–53.
Smith JS, Sansur CA, Donaldson III WF, et al. Short term morbidity and mortality associated with correction of thoracolumbar fixed sagittal plane deformity: report from the Scoliosis Research Society, Morbidity and Mortality Committee. Spine 2011;2:958–64.
Lenke LG, Newton PO, Sucato DJ, et al. Complications after 147 consecutive vertebral column resections for severe pediatric spinal deformity: multicenter analysis. Spine 2013;2:119–32.
Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Results of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance: minimum 5-year follow-up study. Spine 2007;2:2189–97.
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Edwards C, et al. Complications and outcomes of pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine 2003;2:2093–101.
Buchowski JM, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Neurologic complications of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy; a 10 year assessment. Spine 2007;2:2245–52.
Cho SK, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Major complications and revision adult deformity surgery: risk factors and clinical outcomes with 2-7 year follow-up. Spine 2012;2:489–500.
Auerbach JD, Lenke LJ, Bridwell KH, et al. Major complications and comparison between 3-column osteotomy techniques in 105 consecutive spinal deformity procedures. Spine 2012;2:1198–210.
Carreon LY, Puno RM, Dimar JR, et al. Perioperative complications of posterior lumbar decompression and arthrodesis in older adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;2:2089–92.
Daubs MD, Lenke LG, Cheh G, et al. Adult spinal deformity surgery: complications and outcomes in patients over 60. Spine 2007;2:2238–44.
Cho SK, Suk SI, Park SR, et al. Complications in posterior fusion and instrumentation for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine 2007;2:2232–7.
Hassanzadeh H, Jain A, El Dafrawy MH, et al. Three column osteotomies in the treatment of spinal deformity in adult patients 60 years old and older: outcomes and complications. Spine 2013;2:726–31.
Rose PS, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Role of pelvic incidence, thoracic kyphosis, and patient factors on sagittal plane correction following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine 2009;2:785–91.
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Rinella A, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance: surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;86(A suppl 1):44–50.
O’Brien MF, Kuklo TR, Blanke KM, et al. Spinal Deformity Study Group Radiographic Measurement Manual. Memphis, TN: Medtronic Sofamor Danek; 2004.
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine. Is it safe? Spine 2004;2:333–42.
Murrey DB, Brigham CD, Kiebzak GM, et al. Transpedicular decompression and pedicle subtraction osteotomy (eggshell procedure): retrospective review of 59 patients. Spine 2002;2:2338–45.
Kim KT, Lee SH, Suk KS, et al. Outcome of pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance of multiple etiologies: retrospective review of 140 patients. Spine 2012;2:1667–75.
Bradford DS, Tribus CB. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of rigid coronal decompensation. Spine 1997;2:1590–9.
Lehmer SM, Keppler L, Biscup RS, et al. Posterior transvertebral osteotomy for adult thoracolumbar kyphosis. Spine 1994;2:2060–7.
O’Shaughnessy BA, Kuklo TR, Hsieh PC, et al. Thoracic pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal spinal deformity. Spine 2009;2:2893–9.
Qian BP, Wang XH, Qiu Y, et al. The influence of closing-opening wedge osteotomy on sagittal balance and thoracolumbar kyphosis secondary to ankylosing spondylitis: comparison with closing wedge osteotomy. Spine 2012;2:1415–23.
Suk SI, Chung ER, Lee SM, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection in fixed lumbosacral deformity. Spine 2005;30:E703–10.
Weatherley C, Jaffray D, Terry A, et al. Vascular complications associated with osteotomy and ankylosing spondylitis: report of 2 cases. Spine 1988;2:43–6.
Van Royen BJ, Degast A. Lumbar osteotomy for correction of thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity in ankylosing spondylitis. A structured review of three methods of treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 1999;2:399–406.
Lichtblau PO, Wilson P. Possible mechanism of aortic rupture in orthopaedic correction of rheumatoid spondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg 1956;38A:123–7.
Chang KW, Cheng CW, Chen HC, et al. Closing-opening wedge osteotomy for the treatment of sagittal imbalance. Spine 2008;2:1470–7.
Chang KW, Chen YY, Lin CC, et al. Closing wedge osteotomy versus opening wedge osteotomy for ankylosing spondylitis with thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity. Spine 2005;2:1584–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Informed consent: Signed informed consent was obtained from all patients in the study.
IRB approval: Our institutional review board reviewed and approved of our study.
Funding sources: none.
Author disclosures: FAS (none); AS (none).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sweet, F.A., Sweet, A. Transforaminal Anterior Release for the Treatment of Fixed Sagittal Imbalance and Segmental Kyphosis, Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up Study. Spine Deform 3, 502–511 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2015.02.006
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2015.02.006