Abstract
Study Design
Computed tomographic (CT) study of thoracic spine pedicles.
Objective
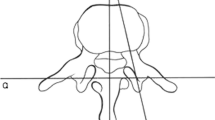
To analyze the usefulness of the superior articular process (SAP) as an external landmark for determining the transverse plane angulation of thoracic pedicles.
Summary of Background Data
The use of thoracic pedicle screws has become commonplace. Although most authors report them to be safe, their use poses a risk to neurovascular structures. Previous studies have provided useful information regarding thoracic pedicle anatomy, but this information is difficult to apply intra-operatively. To avoid neurovascular injury, it is important to determine the correct transverse plane angulation of screw insertion.
Methods
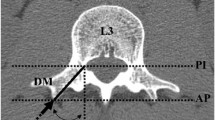
Two separate investigators reviewed thoracic spine CT scans of 53 patients, 26 years of age or younger. Measurements were taken of the angular relationship of the pedicle and the SAP of T4—T11. A 90° angle was subtended from a line parallel to the SAP with a starting point at the midpoint of the lateral half of the SAP. Measurements were then adjusted laterally for medial breeches and medially for lateral breeches, to align the trajectory down the middle of the pedicle. The degree of correction was recorded. Each investigator made 3 sets of measurements. We calculated kappa values to assess intra-observer/interobserver agreement.
Results
Of the 4,008 measurements, 95.2% were contained within bone, leaving 4.8% pedicle violations. The average correction made for medial and lateral breeches was 6.3% and 6.7%, respectively. The first rater had 92.6% agreement, and an intra-observer kappa value of 0.57. The second rater had a 95.3% agreement and an intra-observer kappa value of 0.40.
Conclusions
The results support the hypothesis that the SAP can be a useful external landmark for determining the transverse plane angulation of thoracic pedicle screw insertion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM. Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:2239–45.
Faraj AA, Webb JK. Early complications of spinal pedicle screw. Eur Spine J 1997;6:324–6.
Brown CA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Complications of pediatric thoracolumbar and lumbar pedicle screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998;15:1566–71.
Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, et al. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities: are they really safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:2049–57.
Kakkos SK, Shepard AD. Delayed presentation of aortic injury by pedicle screws: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg 2008;47:1074–82.
Sarlak AY, Buluc L, Sarisoy HT, et al. Placement of pedicle screws in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis of screw placement relative to structures at risk. Eur Spine J 2008;17:657–62.
Sarlak AY, Tosun B, Atmaca H, et al. Evaluation of thoracic pedicle screw placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 2009;18:1892–7.
Watanabe K, Yamazaki A, Hirano T, et al. Descending aortic injury by a thoracic pedicle screw during posterior reconstructive surgery: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:E1064–8.
Hicks JM, Singla A, Shen FH, et al. Complications of pedicle screw fixation in scoliosis surgery: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:E465–70.
Cardoso MJ, Helgeson MD, Paik H, et al. Structures at risk from pedicle screws in the proximal thoracic spine: computed tomography evaluation. Spine J 2010;10:905–9.
Foxx KC, Kwak RC, Latzman JM, et al. A retrospective analysis of pedicle screws in contact with great vessels. J Neurosurg Spine 2010;13:403–6.
Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, et al. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of throracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:1399–405.
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:333–42.
Polly Jr DW, Potter BK, Kuklo T, et al. Volumetric spinal canal intrusion: a comparison between thoracic pedicle screws and thoracic hooks. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:63–9.
Li G, Lv G, Passias P, et al. Complications associated with thoracic pedicle screws in spinal deformity. Eur Spine J 2010;19:1576–84.
Samdani AF, Ranade A, Sciubba DM, et al. Accuracy of free-hand placement of thoracic pedicle screws in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: how much of a difference does surgeon experience make? Eur Spine J 2010;19:91–5.
Kim YJ, Lenke LG. Thoracic pedicle screw placement: free-hand technique. Neurol India 2005;53:512–9.
Cinotti G, Gumina S, Ripani M, et al. Pedicle instrumentation in the thoracic spine: a morphometric and cadaveric study for placement of screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1999;24:114–9.
Yingsakmonkol W, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW. The accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine using the “Funnel Technique”: part 1. A cadaveric study. J Spinal Tech 2002;15:445–9.
Dhawan A, Klemme WR, Polly Jr DW. Thoracic pedicle screws: comparison of start points and trajectories. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:2675–81.
Yang JY, Lenke LG. Usefulness of the nutrient foramen of lamina for insertion of thoracic pedicle screws. J Spinal Disord Tech 2008;21:205–8.
Krag MH, Weaver DL, Beynnon BD, et al. Morphometry of the thoracic and lumbar spine related to transpedicular screw placement for surgical spinal fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1988;13:27–32.
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Allardyce TJ, et al. Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part I: morphometric analysis of the thoracic vertebrae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77:1193–9.
Liljenqvist UR, Link TM, Halm HF. Morphometric analysis of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:1247–53.
Datir SP, Mitra SR. Morphometric study of the thoracic vertebral pedicle in an Indian population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:1174–81.
Catan H, Anik Y, Ayyildiz E, et al. Pedicle morphology of the thoracic spine in preadolescent idiopathic scoliosis: magnetic resonance supported analysis. Eur Spine J 2007;16:1203–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author disclosures: KHP (none); AML (none); JTA (none); DGH (consultancy for Orthopedatrics; grant(s) from Stryker Spine to author and institution; patents from Orthopediatrics, royalties from Orthopediatrics, stock/stock options from Orthopediatrics); DSH (member of expert group for AO Spine; payment for lectures from Synthes Spine; royalties from Synthes Spine).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pade, K., Long, A., Anderson, J.T. et al. The Superior Articular Process as an External Landmark for Determining the Transverse Plane Angulation of Thoracic Pedicles. Spine Deform 1, 185–188 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2013.03.001
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2013.03.001