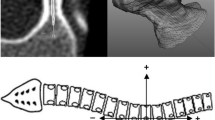
Abstract
In posterior pedicle screw instrumentation of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis, screw malposition might cause significant morbidity in tems of possible pleural, spinal cord, and aorta injury. Preoperative axial magnetic resonace images (MRI) in 12 consecutive patients with right thoracic adolescent scoliosis, all with King type 3 curves, were analyzed in order to evaluate the relationship between the inserted pedicle screw position to pleura, spinal cord, aorta. Axial vertebral images for each thoracic level were scanned and the simulation of pedicle screw insertion was performed using a digital measurement programme. The angular contact value for each parameter regarding the pleura and spinal cord was measured on both sides of the curve. The aorta-vertebral distance was also measured. Aorta-vertebral distance was found to be decreasing gradually from the cephalad to the caudad with the shortest distance being measured at T12 with a mean of 1.2 mm. Concave-sided screws on T5–T9 and convex-sided screws on T2–T3 had the greatest risk to spinal cord injury. Pleural injury is most likely on T4–T9 segments by the convex side screws. T4–T8 screws on the concave side and T11–T12 screws on the convex side may pose risk to the aorta. This MRI-based study demonstrated that in pedicle instrumentation of thoracic levels, every segment deserves special consideration, where computer scanning might be mandatory in immature spine and in patients with severe deformity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaro S, Dahhlborn M (1981) Estimation of vertebral rotation and the spinal rib cage deformity in scoliosis by computer tomography. Spine 6:460–467
Assaker R, Reyns N, Vinchon M, Demondion X, Louis E (2001) Transpedicular screw placement: image-guided versus lateral-view fluoroscopy: in vitro simulation. Spine 26:2160–2164
Belmont PJ Jr, Klemme WR, Dhawan A, Polly DW Jr (2001) In vivo accuracy of thoracic pedicle screws. Spine 26:2340–2346
Bess RS, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Cheh G, Mandel S, Sides B (2007) Comparison of thoracic pedicle screw to hook instrumentation for the treatment of adult spinal deformity. Spine 32:555–561
Brown CA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Geideman WM, Hasan SA, Blanke K (1998) Complications of pedicle thoracolumbar and lumbar pedicle screws. Spine 23:1566–1571
Bullmann V, Fallenberg EM, Meier N, Fischbach R, Lerner T, Schulte TL, Osada N, Liljenqvist UR (2006) The position of the aorta relative to the spine before and after anterior instrumentation in right thoracic scoliosis. Spine 31:1706–1713
Cinotti G, Gumina S, Ripani M, Postacchini F (1999) Pedicle instrumentation in the thoracic spine: a morphometric and cadaveric study for placement of screws. Spine 24:114–119
Dvorak M, MacDonald S, Gurr KR, Bailey SI, Haddad RG (1993) An anatomic, radiographic, and biomechanical assessment of extrapedicular screw fixation in the thoracic spine. Spine 18:1689–1694
Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Ahmad M, Yeasting RA (1997) Projection of the thoracic pedicle and its morphometric analysis. Spine 22:233–238
Frank EH (1998) The use of small malleable endoscopes to assess pedicle screw placement: technical note. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 41:10–21
Gertzbein SD, Bobbins SE (1990) Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo. Spine 15:11–14
Kothe R, O’Holleran JD, Liu W, Panjabi MM (1996) Internal architecture of the thoracic pedicle: an anatomic study. Spine 21:264–270
Liljenqvist U, Lepsien U, Hackenberg L, Niemeyer T, Halm H (2002) Comparative analysis of pedicle screw and hook instrumentation in posterior correction and fusion of idiopathic thoracic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 11:336–343
Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM (1997) Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 22:2239–2245
Milbrandt TA, Sucato DJ (2007) The position of the aorta relative to the spine in patients with left thoracic scoliosis. A comparison with normal patients. Spine 32:E348–E353
Panjabi MM, O’Holleran JD, Crisco JJ III, Kothe R (1997) Complexity of the thoracic spine pedicle anatomy. Eur Spine J 6:19–24
Rampersaud YR, Simon DA, Foley KT (2001) Accuracy requirements for image-guided spinal pedicle screw placement. Spine 26:352–359
Schwarzenbach O, Berlemann U, Jost B, Visarius H, Arm E, Langlotz F, Nolte LP, Ozdoba C (1997) Accuracy of computer-assisted pedicle screw placement. An in vivo computed tomography analysis. Spine 22:452–458
Smorgick Y, Millgram MA, Anekstein Y, Floman Y, Mirovsky Y (2005) Accuracy and safety of thoracic pedicle screw placement in spinal deformities. J Spinal Disord Tech 18:522–526
Sucato DJ, Duchene C (2003) The position of the aorta relative to the spine: a comparison of patients with and without idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85:1461–1469
Suk SI, Lee SM, Chung ER, Kim JH, Kim SS (2005) Selective thoracic fusion with segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis: more than 5-year follow-up. Spine 30:1602–1609
Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Kim JH, Chung ER (2001) Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities. Are they really safe? Spine 26:2049–2057
Suk SI, Lee CK, Min HJ, Kim JH, Chung ER (1994) Comparison of Cotrel–Dubousset pedicle screws and hooks in the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Int Orthop 18:341–346
Togawa D, Kayanja MM, Reinhardt MK, Shoham M, Balter A, Friedlander A, Knoller N, Benzel EC, Lieberman IH (2007) Bone-mounted miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw and translaminar facet screw placement: part 2––evaluation of system accuracy. Neurosurgery 60(ONS Suppl):129–139
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Balderston RA, Allardyce TJ, Garfin SR, Dolinkas C, An HS (1995) Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part II: an anatomical and radiographic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:1200–1206
Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Shepherd ME, Yeasting RA (1999) Thoracic pedicle screw placement guided by computed tomographic measurements. J Spinal Disord 12:222–226
Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Ou Y (1998) Anatomical considerations of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine. Roy-Camille technique versus open-lamina technique. Spine 23:1065–1068
Yahiro MA (1994) Comprehensive literature review: pedicle screw fixation devices. Spine 20(Suppl):2274–2278
Yingsakmonkol W, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW (2002) The accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine using the “Funnel Technique”: part 1. A cadaveric study. J Spinal Disord Tech 15:445–449
Zindrick MR, Knight GW, Sartori MJ, Carnevale TJ, Patwardhan AG, Lorenz MA (2000) Pedicle morphology of the immature thoracolumbar spine. Spine 25:2726–2735
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şarlak, A.Y., Buluç, L., Sarısoy, H.T. et al. Placement of pedicle screws in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis of screw placement relative to structures at risk. Eur Spine J 17, 657–662 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0639-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0639-4