Abstract
Objective
The purpose of the current study was to determine whether maternal circulating components could regulate oxidative status of glutathione redox cycle and adhesion molecule expression in endothelial cells (ECs).
Methods
Maternal plasma was extracted from venous blood obtained from normal term pregnant women and from women with preeclampsia (PE). Normal and PE pregnancies were defined as American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists criteria. Confluent ECs were incubated with EC growth medium (EGM) containing 20% plasma from women with normal (n = 8) and PE (n =8) pregnancies for 4 hours. ECs incubated with EGM only were used as control. EC oxidative status was assessed by measuring cellular glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities. Adhesion molecule expressions for intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM), vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM), P-selectin, and E-selectin were determined by colorimetric assays detected on EC surface by UV spectrophotometer at OD 450 nm. Data are presented as mean ± Se and analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA). A P value <.05 was set as statistically significant.
Results
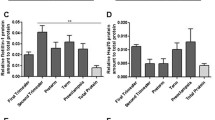
Cellular GR activity was reduced approximately 35% in ECs treated with normal plasma and 70% in ECs treated with PE plasma compared to that in untreated control cells: 0.072 ± 0.014 (P <;.05), 0.039 ± 0.006 (P <;.01), versus 0.117 ± 0.010 U/mg cellular protein, respectively. In contrast, GPx activity was slightly increased in ECs treated with normal plasma and significantly increased in ECs treated with PE plasma compared to that in untreated control cells: 0.059 ± 0.005, 0.07 ± 0.012 (P <;.05) versus 0.044 ± 0.002 U/mg cellular protein, respectively. P-selectin, E-selectin, and VCAM expressions were elevated in cells treated with normal plasma but significantly increased in cells treated with PE plasma compared to those of untreated controls: P-selectin—0.18 ± 0.03, 0.35 ± 0.04 versus 0.04 ± 0.01 OD 450 nm, P <;.01; E-selectin—0.06 ± 0.02, 0.10 ± 0.02 (P <;.05) versus 0.03 ± 0.01 OD 450 nm; VCAM—0.12 ± 0.02, 0.16 ± 0.03 (P <;.01) versus 0.08 ± 0.02 OD 450 nm, respectively. There was no difference for ICAM expression in cells treated with normal or PE plasma compared to controls.
Conclusions
These data suggest that endothelial pro- and anti-oxidative status could be directly affected by circulating components during pregnancy. Reduced cellular GR activity and increased GPx activity accompany increased inflammatory reactions in ECs responding to circulating “toxic” factors in preeclampsia
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishihara M. Studies on lipoperoxide of normal pregnant women and of patients with toxemia of pregnancy. Clin Chim Acta 1978;84:1–9.
Redman CWG, Sacks GP, Sargent IL. Preeclampsia: An excessive maternal inflammatory response to pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:499–506.
Hubel CA, Roberts JM, Taylor RN, Musci TJ, Rodgers GM, McLaughlin Mk. Lipid peroxidation in pregnancy: New perspectives on preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1989;161:1025–34.
Chen KH, Reece LM, Leary JF. Mitochondrial glutathione modulates TNF-α-induced endothelial cell dysfunction. Free Rad Biol Med 1999;27:100–9.
Cooper D, Stokes KY, Tailor A, Granger DN. Oxidative stress promotes blood cell-endothelial cell interactions in the microcirculation. Cardiovasc Toxicol 2002;2:165–80.
Wang Y, Adair CD, Coe L, Weeks JW. Lewis DF, Alexander JS. Activation of endothelial cells in preeclampsia: increased neutrophil-endothelial adhesion correlates with up-regulation of adhesion molecule P-selectin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells isolated from preeclampsia. J Soc Gynecol Investig 1998;5:237–43.
Lyall F, Greer IA, Boswell F, Macara LM, Walker JJ, Kingdom JCP. The cell adhesion molecule, VCAM-1, is selectively elevated in serum in pre-eclampsia: Does this indicate the mechanism of leucocyte activation? BJOG 1994;101:485–7.
Haller H, Ziegler E-M, Homuth V, et al. Endothelial adhesion molecules and leukocyte integrins in preeclamptic patients. Hypertension 1997;29:291–6.
Lorentzen B, Endresen MJ, Hovig T, Haug E, Henriksen T. Sera from preeclamptic women increase the content of triglycerides and reduce the release of prostacyclin in cultured endothelial cells. Thromb Res 1991;63:363–72.
Gallery EDM, Rowe J, Campbell S, Hawkins T. Effect of serum on secretionof prostacyclin and endothelin-1 by decidual endothelial cells from normal and preeclamptic pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;173:918–23.
Baker PN, Davidge ST, Roberts JM. Plasma from women with preeclampsia increases endothelial cell nitric oxide production. Hypertension 1995;26:244–8.
Scalera F, Schlembach D, Beinder E. Production of vasoactive substances by human umbilical vein endothelial cells after incubation with serum from preeclampsia patients. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2001;99:172–8.
Zhang Y, Gu Y, Li H, Lucas MJ, Wang Y. Increased endothelial monolayer permeability is induced by serum from women with preeclampsia but not by serum from women with normal pregnancy or that are not preganat. Hypertens Pregnancy 2003;22:121–31.
Harlan JM, Levine JD, Callahan KS, Schwartz BR, Harker LA. Glutathione redox cycle protects cultured endothelial cells against lysis by extracellularly generated hydrogen peroxide. J Clin Invest 1984;73:706–13.
Jaffe EA, Nachamn RL, Becker CG, Minick CR. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 1973;52:2745–56.
Wang Y, Waslsh SW, Guo J, Zhang J. The imbalance between thromboxane and prostacyclin in preeclampsia is associated with an imbalance between lipid peroxides and vitamin E in maternal blood. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1991;165:1695–700.
Dekker GA, Bast A, Louter A, Sibai BM. Oxidant-antioxidant imbalance in preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 1993;12:251.
Many A, Hubel CA, Roberts JM. Hyperuricemia and xanthine oxidase in preeclampsia, revisited. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;174:288–91.
Hubel CA, Kozlov AV, Kagan VE, et al. Decreased transferrin and incresed transferrin saturation in sera of women with preeclampsia: Implications for oxidative stress. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:692–700.
Ludwig A, Lorenz M, Grimbo N, et al. The tea flavonoid epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces cytokine-induced VCAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004;316:659–65.
Haraldsen G, Kvale D, Lien B, Farstad IN, Brandtzaeg P. Cytokineregulated expression of E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in human microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 1996;156:2558–65.
Kupferminc MJ, Peaceman AM, Aderka D, Wallach D, Socol ML. Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors adn interleukin-6 levels in patients with severe preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 1996;88:420–7.
Vince GS, Starkey PM, Austgulen R, Kwiatkowski D, Redmn CWG. Interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors in women with pre-eclampsia. BJOG 1995;102:20–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by grants from National Institute of Health, National Institute of Child Health Development (NICHD), HD36822 and National Heart Blood Lung Institute (NHBLI), HL 65997.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Gu, Y., Lewis, D.F. et al. Reduced Cellular Glutathione Reductase Activity and Increased Adhesion Molecule Expression in Endothelial Cells Cultured With Maternal Plasma From Women With Preeclampsia. Reprod. Sci. 13, 412–417 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2006.05.009
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2006.05.009