Abstract
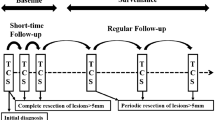
The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical characteristics of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) undergoing surgical treatment over a 10-year period and specifically to evaluate the incidence and clinical outcome of patients treated for duodenal adenomas. Patients with FAP who underwent surgical treatment for colonic polyposis at the University of Louisville from January 1992 to July 2002 were investigated. Surgical treatment included colectomy and ileal J-pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) or completion proctectomy with or without IPAA in those who had previously undergone subtotal colectomy elsewhere. All patients underwent screening gastroduodenoscopy at 3-year intervals beginning at the time of diagnosis or referral. Postoperative morbidity, mortality, and functional outcome were evaluated, as well as the occurrence of extracolonic manifestations and results of treatment for duodenal adenomas when required. Fifty-four patients were included in the study (mean age 28 ± 2 years). Twentyseven of them (50%) underwent colectomy and IPAA as the initial operation. Twenty-seven patients had previously undergone subtotal colectomy. Eight of these 27 patients had cancer in the rectum, of which three were T4 and one was T2N1 cancer. Twenty-two patients underwent a completion proctectomy and three required abdominoperineal resection. Twenty of the 54 patients developed duodenal adenomas. The mean age of diagnosis of duodenal disease was not significantly different from that of patients who were still free of duodenal polyps (40 ± 11 vs. 34 ± 12 years). Seven of these 20 patients underwent local excision of duodenal polyps (either endocopically or transduodenally); four of these patients developed recurrent disease. Six patients underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy for duodenal adenomas with severe dyplasia. These patients experienced an increased number of bowel movements, from five per day (range 4 to 8) to 10 per day (range 6 to 15). One patient required pouch excision and end ileostomy to control diarrhea. Our data demonstrate the following: (1) patients with FAP who have undergone prior subtotal colectomy and ileorectal anastomosis have a high risk of developing advanced cancer in the rectal stump; (2) duodenal adenomas are common in patients with FAP and may occur at an early age; (3) screening duodenoscopy should be initiated at the time of diagnosis of FAP; (4) local excision of duodenal adenomas is associated with a high risk of local recurrence; and (5) even though pancreaticoduodenectomy is the treatment of choice for advanced duodenal adenomas, this procedure may adversely affect pouch function in some patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belchetz LA, Berk T, Bapat BV, Cohen Z, Gallinger S. Changing causes of mortality in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum 1996;39:384–387.
Arvanitis ML, Jagelman DG, Fazio VW, Lavery IC, McGannon E. Mortality in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum 1990;33:639–642.
Ranzi T, Campanini MC, Velio P, Bianchi PA. Long-term follow-up of upper gastrointestinal tract polyps in 15 patients with familial adenomatous polyposis and Gardner’s syndrome. Gastroenterology 1989;96(Suppl):A407.
Church JM, McGannon E, Hull-Boiner S, Sivak MV, Van Stolk R, Jagelman DG, Fazio VW, Oakley JR, Lavery IC, Milsom JW. Gastroduodenal polyps in patients with familial adenomatous polypsis. Dis Colon Rectum 1992;35:1170–1173.
Heiskanen I, Kellokumpu I, Jarvinen H. Management of duodenal adenomas in 98 patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;53:265–266.
Bleau BL, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic treatment of ampullary adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1996;22:237–241.
Tonelli F, Nardi F, Bechi P, Taddei G, Gozzo P, Romagnoli P. Extracolonic polyps in familial polyposis coli and Gardner’s syndrome. Dis Colon Rectum 1985;28:664–668.
Spigelman AD, Williams CB, Talbot IC, Domizio P, Phillips RK. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet 1989;2:783–785.
Vitale GC, Zavaleta CM. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for surgeons. Semin Laparosc Surg 2003;10:19–27.
ReedDNJr, Vitale GC. Interventional endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic surgery. Surg Clin North Am 2000;80:1171–1201.
Vitale GC, Rangneker NJ, Hewlett SC. Advanced interventional endoscopy. Curr Probl Surg 2002;39:968–1053.
Kashiwagi H, Spigelman AD, Debinski HS, Talbot IC, Phillips RK. Surveillance of ampullary adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet 1994;334:1582.
Björk J, Åkerbrant H, Iselius L, Bergman A, Engwall Y, WahlströmJ, Martinsson T, Nordling M, Hultcrantz R. Periampullary adenomas and adenocarcinoma in familial adenomatous polyposis: Cumulative risks and APC gene mutations. Gastroenterology 2001;121:1127–1135.
Moozar KL, Madlensky L, Berk T, Gallinger S. Slow progression of periampullary neoplasia in familial adenomatous polyposis. J GASTROINTEST SURG 2002;6:831–837.
Offerhaus GJA, Giardiello FM, Krush AJ, Booker SV, Tersmette AC, Kelley C, Hamilton SR. The risk of upper gastrointestinal cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastroenterology 1992;102:1980–1982.
Jagelman DG, DeCosse JJ, Bussey HJR. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet 1988;1:1149–1150.
Groves CJ, Saunders BP, Spigelman AD, Phillips RKS. Duodenal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): Results of a 10 year prospective study. Gut 2002;50:636–641.
Penna C, Bataille N, Balladur P, Tiret E, Parc R. Surgical treatment of severe duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 1998;85:665–668.
Penna C, Phillips RKS, Tiret E, Spigelman AD. Surgical polypectomy of duodenal adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis: Experience of two European centers. Br J Surg 1993;80:1027–1029.
Burke CA, Beck GJ, Church JM, van Stolk RU. The natural history of untreated duodenal and ampullary adenomas in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis followed in an endoscopic surveillance program. Gastrointest Endosc 1999; 49:358–364.
Iida M, Yao T, Itoh H, Watanabe H, Matsui T, Iwashita A, Fujishima M. Natural history of duodenal lesions in Japanese patients with familial adenomatosis coli (Gardner’s syndrome). Gastroenterology 1989;96:1301–1306.
Norton ID, Geller A, Petersen BT, Sorbi D, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic surveillance and ablative therapy for periampullary adenomas. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:101–106.
Soravia C, Berk T, Haber G, Cohen Z, Gallinger S. Management of advanced duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. J GASTROINTEST SURG 1997;1:474–478.
Wright BE, Kozarek RA, Traverso LW, Wechter D, Thirlby R, Raltz SL. Recurrent pancreatitis in Gardner variant familial polyposis: Etiology, diagnostic approach, and interventional results. Arch Surg 1999;134:311–315.
Shively EH, Heine MJ, Schell R, Sharpe JN, Garrison RN, Vallance SR, DeSimone K, Polk HC Jr. Practicing surgeons lead in quality care, safety, and cost control. Ann Surg (in press).
Phillips RKS, Wallace MH, Lynch PM, Hawk E, Gordon GB, Saunders BP, Wakabayashi N, Shen Y, Zimmermann S, Godio L, Rodrigues-Bigas M, Su LK, Sherman J, Kelloff G, Levin B, Steinbach G. A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study of celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, on duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 2002;50:857–860.
Conio M, Gostout CJ. Comment on [management of duodenal adenomas in 98 patients with familial adenomatous polyposis]. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;53:265–266.
Sarmiento JM, Thompson GB, Nagorney DM, Donohue JH, Farnell MB. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy for duodenal polyposis. Arch Surg 2002;137:557–563.
Kalady MF, Clary BM, Tyler DS, Pappas TN. Pancreaspreserving duodenectomy in the management of duodenal familial adenomatous polyposis. JGASTROINTEST SURG 2002; 6:82–87.
Ruo L, Coit DG, Brennan MF, Guillem JG. Long-term follow-up of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis undergoing pancreaticoduodenal surgery. J GASTROINTEST SURG 2002;6:671–675.
Huang JJ, Yeo CJ, Sohn TA, Lillemoe KD, Sauter PK, Coleman JA, Hruban RH, Cameron JL. Quality of life and outcomes after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg 2000;231:890–898.
McLeod RS, Taylor BR, O’Connor BI, Greenberg GR, Jeejeebhoy KN, Royall D, Langer B. Quality of life, nutritional status, and gastrointestinal hormone profile following the Whipple procedure. Am J Surg 1995;169:179–185.
Saurin JC, Chayavialle JA, Ponchon T. Management of duodenal adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis. Endoscopy 1999;31:472–478.
Clark SK, Phillips RKS. Desmoids in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 1996;83:1494–1504.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morpurgo, E., Vitale, G.C., Galandiuk, S. et al. Clinical characteristics of familial adenomatous polyposis and management of duodenal adenomas. J Gastrointest Surg 8, 559–564 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2004.03.001
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2004.03.001